力扣题目链接
class MyQueue {
public:stack<int> stIn;stack<int> stOut;/** Initialize your data structure here. */MyQueue() {}/** Push element x to the back of queue. */void push(int x) {stIn.push(x);}/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */int pop() {// 只有当stOut为空的时候,再从stIn里导入数据(导入stIn全部数据)if (stOut.empty()) {// 从stIn导入数据直到stIn为空while(!stIn.empty()) {stOut.push(stIn.top());stIn.pop();}}int result = stOut.top();stOut.pop();return result;}/** Get the front element. */int peek() {int res = this->pop(); // 直接使用已有的pop函数stOut.push(res); // 因为pop函数弹出了元素res,所以再添加回去return res;}/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */bool empty() {return stIn.empty() && stOut.empty();}
};
如果你画一下图,那应该很好理解。
c语言代码如下:
/*
1.两个type为int的数组(栈),大小为100第一个栈stackIn用来存放数据,第二个栈stackOut作为辅助用来输出数据
2.两个指针stackInTop和stackOutTop,分别指向栈顶
*/
typedef struct {int stackInTop, stackOutTop;int stackIn[100], stackOut[100];
} MyQueue;/*
1.开辟一个队列的大小空间
2.将指针stackInTop和stackOutTop初始化为0
3.返回开辟的队列
*/
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue* queue = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));queue->stackInTop = 0;queue->stackOutTop = 0;return queue;
}/*
将元素存入第一个栈中,存入后栈顶指针+1
*/
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {obj->stackIn[(obj->stackInTop)++] = x;
}/*
1.若输出栈为空且当第一个栈中有元素(stackInTop>0时),将第一个栈中元素复制到第二个栈中(stackOut[stackTop2++] = stackIn[--stackTop1])
2.将栈顶元素保存
3.当stackTop2>0时,将第二个栈中元素复制到第一个栈中(stackIn[stackTop1++] = stackOut[--stackTop2])
*/
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {//优化:复制栈顶指针,减少对内存的访问次数int stackInTop = obj->stackInTop;int stackOutTop = obj->stackOutTop;//若输出栈为空if(stackOutTop == 0) {//将第一个栈中元素复制到第二个栈中while(stackInTop > 0) {obj->stackOut[stackOutTop++] = obj->stackIn[--stackInTop];}}//将第二个栈中栈顶元素(队列的第一个元素)出栈,并保存int top = obj->stackOut[--stackOutTop];//将输出栈中元素放回输入栈中while(stackOutTop > 0) {obj->stackIn[stackInTop++] = obj->stackOut[--stackOutTop];}//更新栈顶指针obj->stackInTop = stackInTop;obj->stackOutTop = stackOutTop;//返回队列中第一个元素return top;
}//返回输入栈中的栈底元素
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {return obj->stackIn[0];
}//若栈顶指针均为0,则代表队列为空
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {return obj->stackInTop == 0 && obj->stackOutTop == 0;
}//将栈顶指针置0
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {obj->stackInTop = 0;obj->stackOutTop = 0;
}一、出错点
1.不熟悉c++的STL容器
二、理解后的思路
这题你画两个栈就很好理解了
这是一道模拟题,不涉及到具体算法,考察的就是对栈和队列的掌握程度。
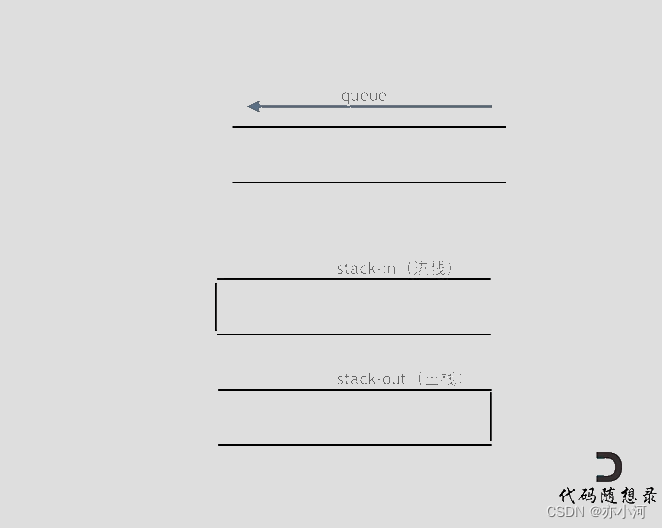
使用栈来模式队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈一个输入栈,一个输出栈,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
下面动画模拟以下队列的执行过程:
执行语句:
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.pop(); 注意此时的输出栈的操作
queue.push(3);
queue.push(4);
queue.pop();
queue.pop();注意此时的输出栈的操作
queue.pop();
queue.empty();
代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入),再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。
最后如何判断队列为空呢?如果进栈和出栈都为空的话,说明模拟的队列为空了。
在代码实现的时候,会发现pop() 和 peek()两个函数功能类似,代码实现上也是类似的,可以思考一下如何把代码抽象一下。
三、总结
要熟悉栈与队列的基本操作,多敲代码多练习!

 match_phrase的使用)


)



)


)
)




)

