1. NLP Basics Distributed Word Representation词表示
Word representation: a process that transform the symbols to the machine understandable meanings
1.1 How to represent the meaning so that the machine can understand
-
Compute word similarity
计算词相似度
• WR(Star) ≃ WR(Sun)
• WR(Motel) ≃ WR(Hotel) -
Infer word relation
推断词之间的语义关系
• WR(China) − WR(Beijing) ≃ WR(Japan) - WR(Tokyo)
• WR(Man) ≃ WR(King) − WR(Queen) + WR(Woman)
• WR(Swimming) ≃ WR(Walking) − WR(Walk) + WR(Swim
1.2 Synonym and Hypernym 同义词和上位词
过去怎么表示一个词的词义呢?
By Using set of related words, such as synonyms and hypernyms to represent a word
譬如说我们想表示GOOD这个词
Synonyms of “Good” in WordNet:
(n)good,goodness
(n)commodity,trade_good,good
(s)full,good
(s)adept,expert,good,practiced,proficient,skillful
(s)estimable,good,honorable,respectable
但这种方法存在问题
- Missing nuance
e.g. (“proficient”, “good”) are synonyms only in some contexts - Missing new meanings of words
e.g. Apple (fruit → IT company) - Subjective主观性问题,受限于原本的词源标注
- Data sparsity
- Requires human labor to create and adapt
1.3 One-Hot Representation
对于计算机来说, 更好的办法仍然是将一个词表示为一个唯一的符号(向量)
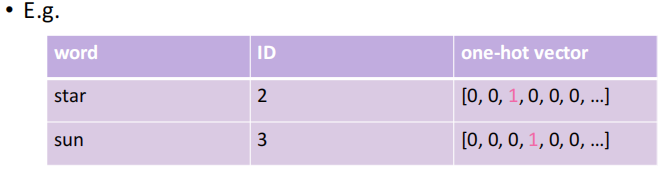 每个词对应的向量都是独一无二的
每个词对应的向量都是独一无二的
- Vector dimension = # words in vocabulary
- Order is not important
但这种方法存在问题
- All the vectors are orthogonal. No natural notion of similarity for one-hot vectors.
因此, 根本无法计算相似度
1.4 Represent Word by Context
核心思想是用词的上下文来表示这个词
- The meaning of a word is given by the words that frequently appear close-by
- One of the most successful ideas of modern statistical NLP
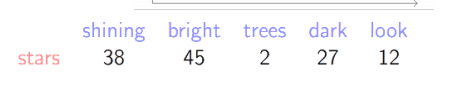
e.g. Use context words to represent stars

1.5 Count-Based Representation
在Represent Word by Context 的基础上, 仍然对 n 个词的文本创建一个 n 维向量 ,
并且对其他词与词 A 同时出现的次数进行计数( Co-Occurrence Counts ), 写入A的向量中
这样我们能得到一个稠密向量, 对稠密向量之间进行相似度计算是可行的
 但这种方法存在问题
但这种方法存在问题
- Increase in size with vocabulary, require a lot of storage
- sparsity issues for those less frequent words
1.6 Word Embedding
运用分布式表达的方法Distributed Representation
尝试用一个低维的空间就将文本全集装载, 然后在这个低维空间中进行相似度运算
- Build a dense vector for each word learned from large-scale text corpora
- 一个比较知名的方法 : Word2Vec (We will learn it in the next class)\
1.7 Language Model
- Language Modeling is the task of predicting the upcoming word
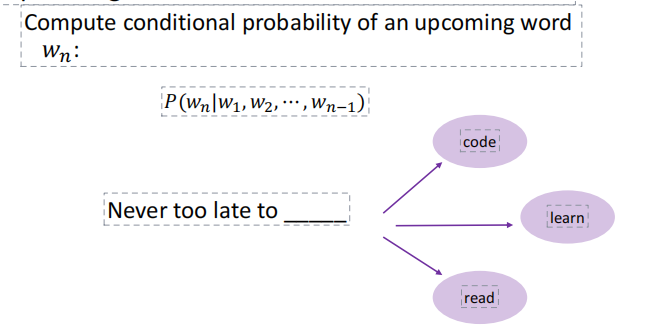
- A language model is a probability distribution over a sequence of words\
语言模型的两个任务
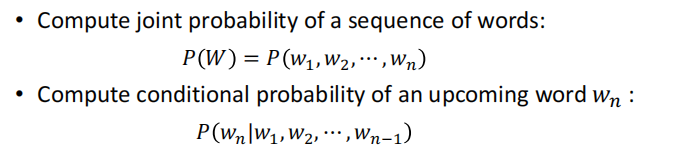 由此引出一个问题 : 如何计算概率?
由此引出一个问题 : 如何计算概率?
引入一个假设
Assumption: the probability of an upcoming word is only determined by all its previous words
以此就能将句子的概率拆解为条件概率
e.g. 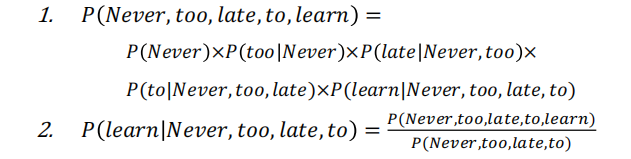
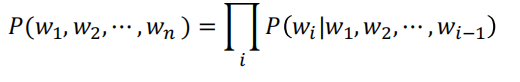 即对于语言模型来说
即对于语言模型来说
一个句子的联合概率 = 每个词相对于整体的条件概率再取积
1.8 N-gram Model
Collect statistics about how frequent different ngrams are, and use these to predict next word.
例如 , 对于 4-gram, 统计三个词too late to 之后接不同的词的概率
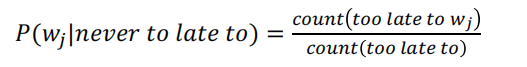

但这种方法存在问题
- Need to store count for all possible n-grams. So model size is O ( e^n )
- Not considering contexts farther than 1 or 2 words
- Not capturing the similarity between words
最简单的例子, 如果以整个互联网的文本去统计, 而每次仅统计两三个词连在一起的概率, 最终统计结果会相当稀疏
e.g.
• The cat is walking in the bedroom
• A dog was running in a room
3-gram 也无法认识到 cat 和 dog 的相似度, walking 和 running 的相似度
1.9 Neural Language Model
A neural language model is a language model based on neural networks to learn distributed representadons of words
- Associate words with distributed vectors
- Compute the joint probability of word sequences in terms of the feature vectors
- Optimize the word feature vectors (embedding matrix E) and the parameters of the loss function (map matrix W)
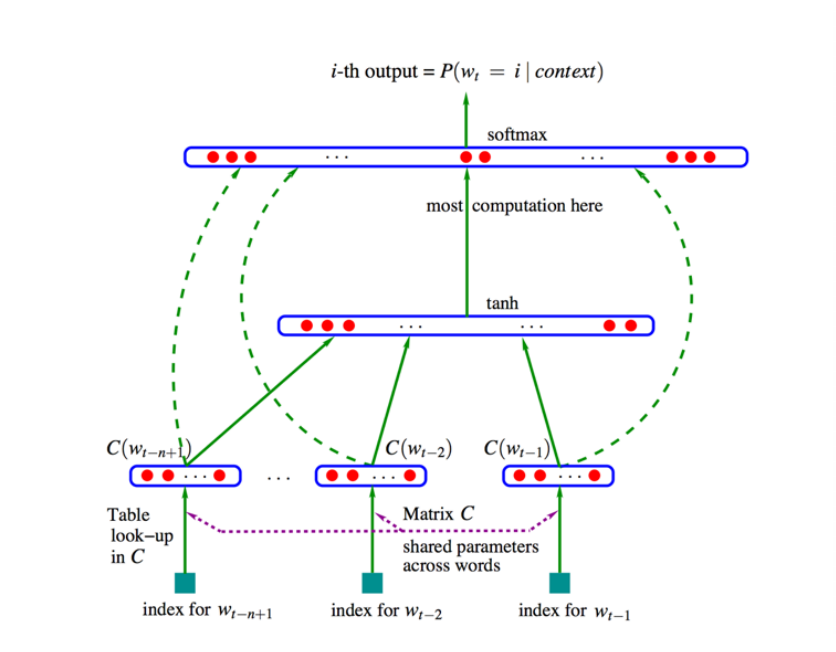
求Wt在Context下的条件概率, 可以利用前几个词( 这里取3 )的向量, 拼成一个高维的上下文向量, 再经过非线性转换tanh , 就可以预测下一个词.
整个的匹配过程是通过 神经网络 , 在可调的过程中完成的.
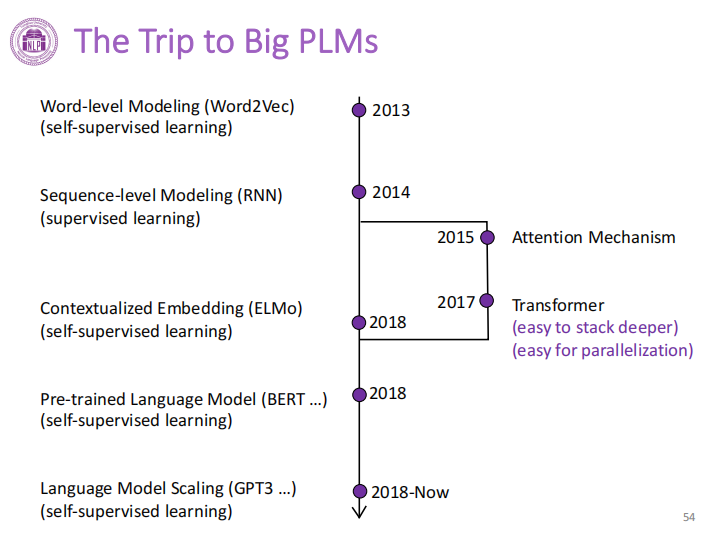
2. Big Model Basics Development
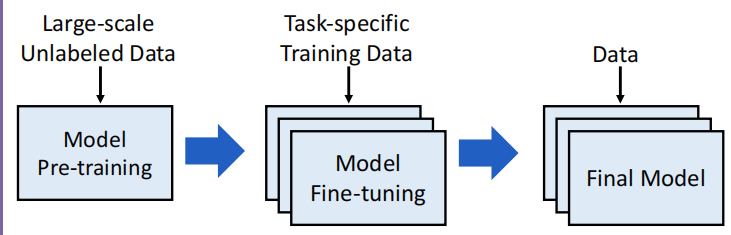
3 Paradigms behind Big Models 大模型背后的范式
- 对于预训练模型来说, 很关键的一点是 模型会从无标注的数据中学习, 通过自监督的任务获取通用知识.
- 在预训练完毕的模型上引入任务相关数据, 帮助具体的任务做适配
- 最终得到解决具体任务的模型
The breakthrough of NLP: Transformer
Based on Transformer, a series of deep pretraining models are developed instead of shallow RNNs, which is more powerful
)




Web后端之MySQL语法使用详解-01)





)







