在指针的类型中我们知道有⼀种指针类型为字符指针 char*
1.一般使用方法如下:
int main()
{
char ch = 'w';
char *pc = &ch;
*pc = 'w';
return 0;
}2.还有⼀种使⽤⽅式如下:
int main()
{
const char* pstr = "hello world.";
printf("%s\n", pstr);
return 0;
}
注意:
代码 const char* pstr = "hello world."; 特别容易让人以为是把字符串 hello world放
到字符指针 pstr ⾥了,但是本质是把字符串 hello world. ⾸字符的地址放到了pstr中
这里是把⼀个常量字符串的⾸字符 h 的地址存放到指针变量 pstr 中
3.《剑指offer》中收录的⼀道和字符串相关的笔试题
int main()
{char str1[] = "hello bit.";char str2[] = "hello bit.";const char* str3 = "hello bit.";const char* str4 = "hello bit.";if (str1 == str2)printf("str1 and str2 are same\n");elseprintf("str1 and str2 are not same\n");if (str3 == str4)printf("str3 and str4 are same\n");elseprintf("str3 and str4 are not same\n");return 0;
}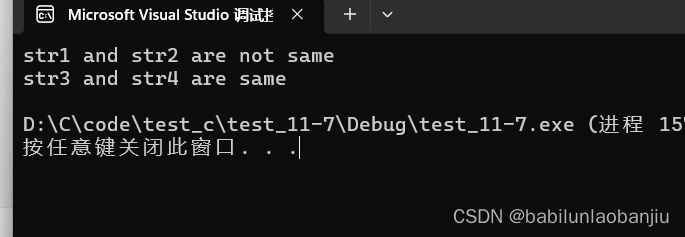
原因:
这⾥str3和str4指向的是⼀个同⼀个常量字符串。
C/C++会把常量字符串存储到单独的⼀个内存区域,当⼏个指针指向同⼀个字符串的时候,他们实际会指向同⼀块内存。
但是⽤相同的常量字符串去初始化不同的数组的时候就会开辟出不同的内存块。所以str1和str2不同,str3和str4相同





详细教程)
)





)

)

![[Electron]中screen屏幕](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Electron]中screen屏幕)


bootmem引导内存分配)