SpringBoot
- SpringBoot
- 概述
- 依赖管理
- 自动配置
- SpringBoot 注解使用
- @Configuration
- @Import(value = {Cat.class,Dog.class})
- @ImportResource(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
- yaml 标记语言
- 概述
- 基本语法
- 数据类型
- 字面量
- 对象
- 数组
- 使用细节
- Rest 风格请求处理
- 概述
- 注意事项
- 接收参数注解
- @CookieValue
- 自定义转换器
- 概述
- 创建自定义转换器的步骤
- 代码实现
- 前端提交的表单
- 实体类 Car
- 自定义转换器
- 注意
- 内容协商
- 概述
- 示例
- 注意
- 服务器渲染技术 Thymeleaf
- 概述
- 基本语法
- 表达式
- 字面量
- 文本操作
- 运算符
- th 属性
- 使用 th 属性需要注意点
- 综合案例
- 需求说明
- 思路分析
- 代码实现
- 1、配置 pom.xml 引入 thymeleaf-start
- 2、转发到登录页面 - IndexController
- 3、登录页面 - login.html
- 4、创建 model
- 5、验证用户信息 - CheckUserController
- 6、管理用户页面 - manage.html
- 拦截器 Interceptor
- 概述
- 实现步骤
- 文件上传
- 需求说明
- 综合案例
- 单个文件上传
- 1、上传文件页面
- 2、添加依赖
- 3、编写控制器
- 多个文件上传
- 1、上传文件页面
- 2、依赖如上
- 3、编写控制器方法
- 注意事项
SpringBoot
大家好呀!我是小笙,我接下来继续分享一些自己学习韩老师 Java课程的笔记,由于 SpringBoot 这部分内容较多,我分成二部分进行总结,以下是第一部分,希望内容对你有所帮助!
概述
SpringBoot 可以轻松创建独立的、生产级的基于 Spring 的应用程序
SpringBoot 直接嵌入 Tomcat、Jetty 或者 Undertow,可以直接运行应用程序
约定优于配置理念
简便来说就是你所期待的配置与约定的配置一致,那么就可以不做任何配置,约定不符合期待的时候,才需要对约定进行替换配置
依赖管理
自动依赖仲裁,即如果没有指定某个依赖的版本号,则以父项目指定的版本号为准(就近原则)
修改版本仲裁的两种方式如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.Al_tair</groupId><artifactId>springboot_lns</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><parent><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><version>2.5.3</version></parent><dependencies><!-- Web 场景启动器:会自动引入 Web 开发相关的依赖 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><!-- 1、直接指定 mysql 的版本 --><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.49</version></dependency></dependencies><!-- 2、属性里面指定对应key的版本号 --><properties><mysql.version>5.4.19</mysql.version></properties><!-- 3、如果没有指定mysql版本则以父项目的版本为准 -->
</project>
自动配置
扫描包:默认为执行的主程序所在的包及其子包下的所有文件都会被扫描
// 修改默认配置
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"",""})
public class MainApp {}
配置文件
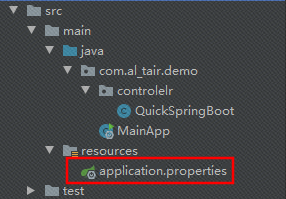
配置文件的读取路径以及配置文件名的默认值如下
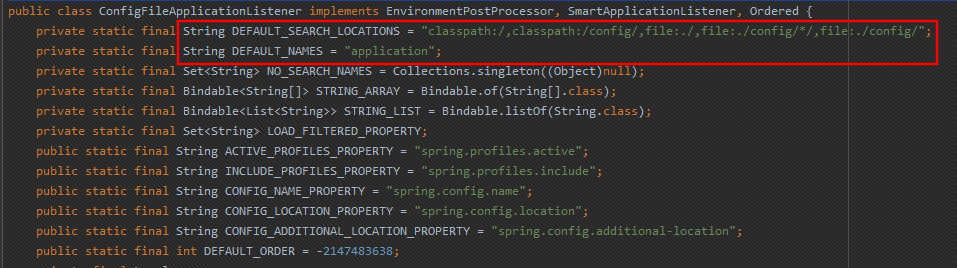
自定义配置
// 自定义类中获取 application.properties 中的配置信息
class Test {@Value("${配置文件里的名称}")private String properties
}
SpringBoot 注解使用
@Configuration
类似于 Spring 里面的 Bean 对象创建
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {/*1、默认Bean对象的 name/id 为方法名 usero1如果想要设置 name/id,通过 @Bean(name = "")2、User: 为注入的类型3、默认为单例注入 @Scope("prototype") 设置为多实例注入*/@Beanpublic User usero1(){return new User(100,18,"lns","1079936@qq.com",1);}
}
@Import(value = {Cat.class,Dog.class})
注入 Bean 对象,value 值传入的是 Bean对象的 Class 数组
@Import(value = {User.class})
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {@Beanpublic User usero1(){return new User(100,18,"lns","1079936@qq.com",1);}
}
@ImportResource(locations = “classpath:beans.xml”)
将 Spring 框架中使用的 beans.xml 文件导入到 Java 配置文件里(指定 beans.xml 的类路径)
@Configuration
@ImportResource(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
public class BeanConfig {
}
yaml 标记语言
注意:格式很重要!!!
概述
一种以数据为中心,而不是以标记语言为重点的标记语言(适合用作配置文件 .yml .yam 后缀文件)
基本语法
-
形式为 key: value (注意冒号后面有空格)
-
区分大小写
-
使用缩进形式表示层级关系(注意缩进最好只用空格,相同层级的元素之间要对齐)
User: Name: xxxSex: yyySchool: zzz -
字符串不需要加单/双引号(加上也没影响)
-
注释符号 #
数据类型
字面量
类似于 Java 里面的数据类型,是不可再分割的值
value 值的字面值为:date、boolean、string、number、null
对象
键值对的集合,如:map、hash、set、object
# 行内写法 object
User: {Name: xxx,Sex: yyy,School: zzz}
# 换行形式 object
User: Name: xxx Sex: yyy School: zzz
数组
一组按次序排列的值,如: array、list、queue
# 行内写法 array
User: [v1,v2,v3]
# 换行形式 array
k: - v1 - v2 - v3
使用细节
-
application.properties 和 application.yml 有相同的前缀值绑定时候,application.properties 优先级较高
-
添加相关依赖可以是 application.yml 和 application.properties 有提示(只提示没有填的数据)
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><!-- optional 为 true,防止将此依赖传递给其他模块 --><optional>true</optional> </dependency> -
实体类要对应 yml 文件的对象数据,需要添加注解 @ConfigurationProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
Rest 风格请求处理
概述
请求方法:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等等(如果需要请求为 PUT、DELETE,需要配置相关内容如下)
Rest 风格请求处理核心:HiddenHttpMethodFilter
-
首先表单请求会被 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 拦截,获取到表单里 _method 的值
-
判断是否是 PUT/DELETE/PATCH(PATCH 可以理解为是对PUT 方法的补充)来进行对应的跳转
-
配置文件 .yml 文件
spring:mvc:hiddenmethod:filter:enabled: true # 开启页面表单的 Rest 功能
注意事项
-
分析如下控制层方法为啥是返回字符串而不是对应的资源文件
// 如果没有配置如下的试图解析器参数,则会默认查询字符串下地址 /hello,如果还是没有,则会在页面上直接输出字符串 hello @RestController public class HiController {@RequestMapping("/hi")public String hi() {return "hello";} } @RestController public class HiController {@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hi() {return "find it";} } -
需要添加配置文件
# 需要注意静态资源是否加前缀 static-path-pattern,prefix 需要与其保持一致性 spring:mvc:static-path-pattern: /lns/** # 修改静态资源访问的路径/前缀view:suffix: .htmlprefix: /lns
接收参数注解
@RequestMapping、@RequestHeader、@PathVariable等等已经在SprignMVC 中讲解,接下来讲一些其他的注解
@CookieValue
概述
@CookieValue是Spring框架中用于获取HTTP请求中的Cookie值的注解
示例
使用@CookieValue注解将名为cookieKey的Cookie值绑定到方法参数cookieValue上。当客户端发起GET请求到"/demo"路径时,Spring会自动从请求中获取名为cookieKey的Cookie的值,并将其作为字符串赋值给cookieValue参数
@GetMapping("/demo")
public String exampleMethod(@CookieValue("cookieKey") String cookieValue) {System.out.println(cookieValue);return "example";
}
注意:注解可以通过设置属性 required 来控制请求参数 cookieKey 是否需要时必填的
@RequestAtrribute、@SessionAtrribute等相关注解用法类似
自定义转换器
概述
自定义转换器通常是指根据特定的需求编写的一段代码,用于将一种数据类型转换为另一种数据类型。这种转换器在多种情况下非常有用,比如数据迁移、系统整合、不同格式之间的数据交换等(SpringBoot在响应客户端请求时,将提交的数据封装成对象时,使用了内置的转换器 )
底层 org.springframework.core.convert.converter 包下的类 ConvertiblePair
创建自定义转换器的步骤
- 确定需要转换的数据类型
- 设计转换逻辑,处理任何可能出现的异常情况
- 编写单元测试来验证转换器的正确性
- 在适当的地方使用或集成这个转换器
代码实现
要求:自定义转换器用于将级联对象通过一个字符串里包含多个参数定制化转换成对象的实现形式
前端提交的表单
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>添加车</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/savemonster" method="post"><!-- 使用自定义转换器关联car(对应实体类), 使用,号间隔 -->交通工具:<input name="car" value="比亚迪秦,79888"><br/><input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
实体类 Car
@Data
public class Car {private String name;private Double price;
}
自定义转换器
/*** @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)* 1. 表示 WebConfig 是一个配置类* 2. proxyBeanMethods = false 使用Lite模式*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class WebConfig {/*** 1. 在addFormatters 方法中,增加一个自定义的转换器* 2. 增加自定义转换器 String -> Car,会注册到 converters 容器中*/@Beanpublic WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {return new WebMvcConfigurer() {@Overridepublic void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {// 使用匿名内部类的方式增加自定义转换器registry.addConverter(new Converter<String, Car>() {// source就是 传入的字符串 比亚迪秦,79888@Overridepublic Car convert(String source) {// 自定义的转换业务代码if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(source)) {Car car = new Car();String[] split = source.split(",");car.setName(split[0]);car.setPrice(Double.parseDouble(split[1]));return car;}return null;}});}};}
}
注意
-
converters 底层结构是 ConcurrentHashMap,key 为 源类型 —> 目标类型,如果添加相同的源类型以及目标类型的自定义转换器,则会覆盖前面的转换器
-
网页默认返回 Json 格式数据底层也是转换器进行转换的,只需要控制层的方法上添加注解 @Responsebody,可以将目标方法返回的数据格式为 json 格式
<!-- SpringBoot 中引入场景启动器 spring-boot-starter-web,已经引入了 处理 Json 格式数据的 jar包Web 场景启动器:会自动引入 Web 开发相关的依赖 --> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
内容协商
概述
内容协商在计算机科学领域通常指的是在互联网通信中,服务端与客户端之间就数据交换格式、语言或其他特性达成一致的过程,主要有类型协商(服务器根据客户端发送的Accept头部信息提供相应的数据格式,如JSON、XML或HTML等)、编码协商(服务器根据客户端的Accept-Encoding头部提供压缩或未压缩的版本)等等,本节主要讲解类型协商
示例
使用 Postman 发送 Http 请求,根据不同请求头参数,返回对应的 json 或者 xml 数据
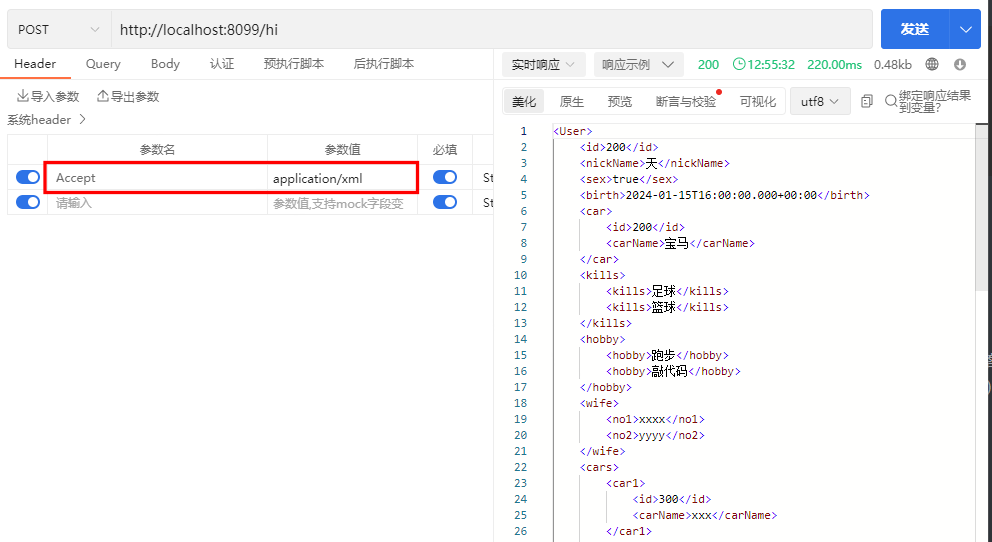
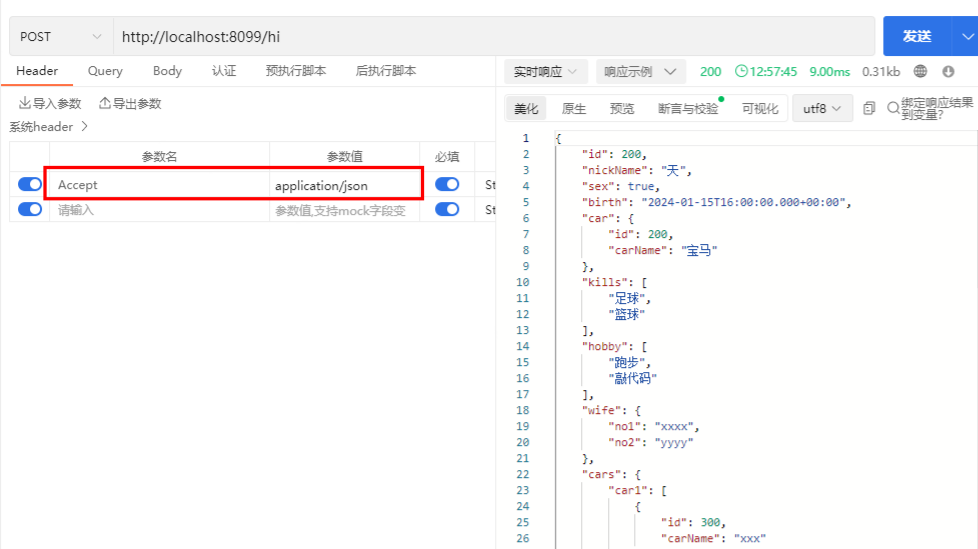
注意:返回 xml 数据需要下载相关依赖
<!-- 引入xml格式处理依赖 -->
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId><artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
注意
-
为啥没下载 xml 处理依赖的时候默认是 Json 格式,而下载了依赖之后默认的是 xml 格式了呢?
客户端请求头 Accept 会给出返回数据格式的权重,根据权重来解析,如下图
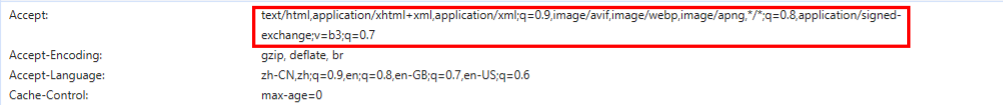
-
浏览器已经固定内容协商的类型,如果想要返回不同的格式,有解决方法吗?
-
配置 yml 文件
spring:mvc:contentnegotiation:favor-parameter: true # 开启基于请求参数的内容协商parameter-name: format # 指定接收参数名,默认是 format -
浏览器访问的时候携带 ?format = json 或者 ?format = xml 来决定返回什么格式的数据
-
服务器渲染技术 Thymeleaf
概述
在线文档
Thymeleaf 是一个用于 Web 和独立环境的现代服务器端 Java 模板引擎。它能够处理 HTML、XML、JavaScript、CSS 等多种类型的模板,并且能够让开发者在浏览器中直接查看模板的静态原型,无需启动服务器或构建整个应用程序(和 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模版引擎,可替代 JSP)
优点
- 浏览器兼容性:Thymeleaf 模板可以直接在浏览器中打开,无需服务器渲染,这对于前端开发者来说是一个很大的便利。
- 与 Spring Boot 的集成:Thymeleaf 与 Spring Boot 框架有很好的集成,Spring Boot 提供了自动配置,使得在 Spring 应用程序中使用 Thymeleaf 变得很简单
- 丰富的表达式支持:Thymeleaf 支持丰富的表达式语法,包括文本、消息、链接、片段等,提供了强大的数据绑定能力
缺点
- 性能问题:Thymeleaf 在处理大型模板时可能会遇到性能瓶颈,特别是在模板中包含大量表达式和逻辑时
- XML/HTML 限制:Thymeleaf 模板必须符合 XML 或 HTML 规范,这可能会限制模板的灵活性,特别是在使用非标准化的 HTML 代码时
- 与前端框架的集成:虽然 Thymeleaf 可以与前端框架(如 Angular、React 等)集成,但与纯前端模板引擎(如 Handlebars、Mustache 等)相比,集成可能会更加复杂。
- 依赖 Spring:Thymeleaf 与 Spring 的紧密集成意味着在非 Spring 应用程序中使用它可能会更加困难
基本语法
表达式
| 表达式名字 | 语法 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 变量取值 | ${…} | 获取请求域、session 域、对象等值 |
| 选择变量 | *{…} | 获取上下文对象值 |
| 消息 | #{…} | 获取国际化等值 |
| 链接 | @{…} | 生成链接 |
| 片段表达式 | ~{…} | jsp:include 作用,引入公共页面片段 |
字面量
- 数字: 10 , 7 , 36.8 , …
- 文本值: ‘hsp edu’ , ‘hello’ ,…
- 布尔值: true , false
- 空值: null
- 变量: name,age,… (变量不能有空格)
文本操作
- 字符串拼接: +
- 变量替换: |age= ${age}|
运算符
- 数学运算: + , - , * , / , %**
- 布尔运算: and , or**
- 一元运算: ! , not
- 比较运算: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )等式: == , != ( eq , ne )**
- 条件运算
- If-then: (if) ? (then)
- If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
- Default: (value) ?: (default value)
th 属性
- th:text :设置当前元素的文本内容,相同功能的还有 th:utext,两者的区别在于前者不会转义 html 标签,后者会。优先级不高:order=7
- th:value:设置当前元素的 value 值,类似修改指定属性的还有 th:src,th:href。优先级不高:order=6
- th:each:遍历循环元素,和 th:text 或 th:value 一起使用。注意该属性修饰的标签位置,详细往后看。优先级很高:order=2
- th:if:条件判断,类似的还有 th:unless,th:switch,th:case。优先级较高:order=3
- th:insert:代码块引入,类似的还有 th:replace,th:include,三者的区别较大,若使用不恰当会破坏 html 结构,常用于公共代码块提取的场景。优先级最高:order=1
- th:fragment:定义代码块,方便被 th:insert 引用。优先级最低:order=8
- th:object:声明变量,一般和*{}一起配合使用,达到偷懒的效果。优先级一般:order=4
- th:attr:修改任意属性,实际开发中用的较少,因为有丰富的其他 th 属性帮忙,类似的还有 th:attrappend,th:attrprepend。优先级一般:order=5
使用 th 属性需要注意点
- 若要使用 Thymeleaf 语法,首先要声明名称空间:xmlns:th=“http://www.thymeleaf.org”
- 设置文本内容 th:text,设置 input 的值 th:value,循环输出 th:each,条件判断 th:if,插入代码块 th:insert,定义代码块 th:fragment,声明变量 th:object
- th:each 的用法需要格外注意,打个比方:如果你要循环一个 div 中的 p 标签,则 th:each属性必须放在 p 标签上。若你将 th:each 属性放在 div 上,则循环的是将整个 div
- 变量表达式中提供了很多的内置方法,该内置方法是用#开头,请不要与#{}消息表达式弄混
综合案例
需求说明
实现简单的用户登录页面,登录成功则跳转到管理页面,登录失败则提示错误信息(主要以实现 SpringBoot 引入 Thymeleaf 为主,不实现三层架构)
思路分析
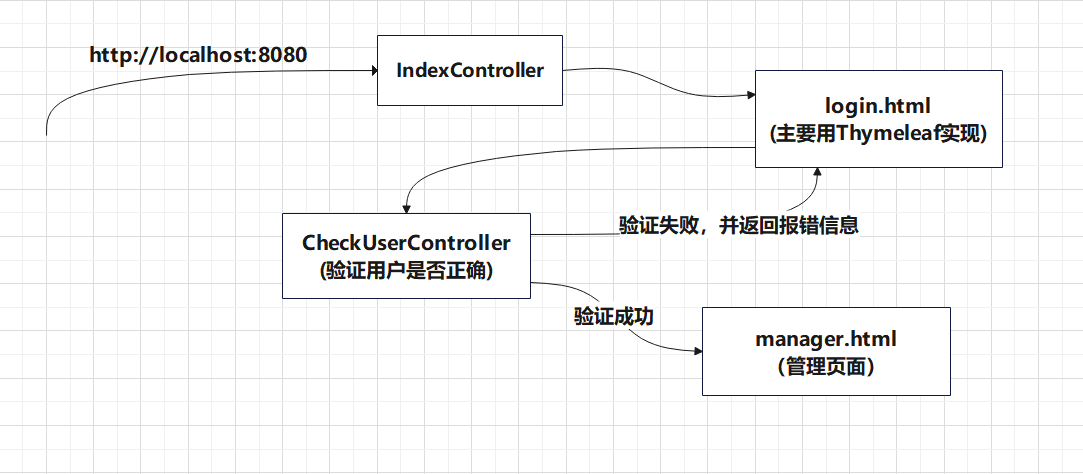
代码实现
1、配置 pom.xml 引入 thymeleaf-start
<!--引入thymeleaf-start: 会进行默认配置-->
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
注意: thymeleaf 配置默认路径在 templates 下后缀为 html 文件中
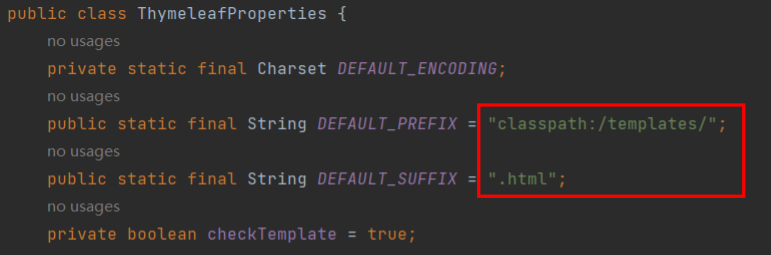
2、转发到登录页面 - IndexController
@Controller
public class IndexController {// 编写方法,转发到登录页面@GetMapping(value = {"/", "/login"})public String login() {/*** 直接使用视图解析到 thymeleaf下的模板文件 login.html*/return "login";}
}
3、登录页面 - login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>login</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#CED3FE"><hr/><div style="text-align: center"><h1>用户登陆</h1><form action="#" th:action="@{/login}" method="post"><label style="color: red" th:text="${msg}"></label><br/>用户名:<input type="text" style="width:150px" name="name"/><br/><br/>密 码:<input type="password" style="width:150px" name="password"/><br/><br/><input type="submit" value="登录"/><input type="reset" value="重新填写"/></form></div><hr/>
</body>
</html>
4、创建 model
@Data
public class Admin {private String name;private String password;
}@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {private Integer id;private String name;private String password;private Integer age;private String email;
}
5、验证用户信息 - CheckUserController
@Controller
@Slf4j
public class CheckUserController {// 响应用户的登录请求@PostMapping("/login")public String login(Admin admin, HttpSession session, Model model) {// 验证用户是否合法(默认密码为:admin)if (StringUtils.hasText(admin.getName()) && "admin".equals(admin.getPassword())) {// 将登录用户保存到sessionsession.setAttribute("loginAdmin", admin);// 验证成功则重定向到 manage.html// 不使用请求转发是防止刷新页面会重复提交return "redirect:/manage.html";} else {// 验证失败则重新登录, 请求转发model.addAttribute("msg", "账号/用户密码错误");return "login";}}// 处理用户的请求 manage.html@GetMapping("/manage.html")public String managePage(Model model, HttpSession session) {Object loginAdmin = session.getAttribute("loginAdmin");if(null != loginAdmin) {//可以这里集合-模拟用户数据, 放入到request域中,并显示ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();users.add(new User(1, "关羽", "123", 43, "11@sohu.com"));users.add(new User(2, "张飞", "234", 54, "22@sohu.com"));users.add(new User(3, "赵云", "345", 43, "33@sohu.com"));users.add(new User(4, "马超", "5645", 24, "44@sohu.com"));users.add(new User(5, "黄忠", "7657", 43, "55@sohu.com"));// 将数据放入到request域model.addAttribute("users", users);return "manage";} else {// 这里就返回登录页,并给出提示model.addAttribute("msg","你没有登录/请登录");return "login";}}
}
6、管理用户页面 - manage.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>管理后台</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#CED3FE"><a href='#'>返回管理界面</a> <a href='#' th:href="@{/}">安全退出</a> 欢迎您:[[${session.loginAdmin.name}]]<hr/><div style="text-align: center"><h1>管理用户~</h1><table border="1px" cellspacing="0" bordercolor="green" style="width:800px;margin: auto"><tr bgcolor="pink"><td>id</td><td>name</td><td>pwd</td><td>email</td><td>age</td></tr><tr bgcolor="#ffc0cb" th:each="user:${users}"><td th:text="${user.id}">a</td><td th:text="${user.name}">b</td><td th:text="${user.password}">c</td><td th:text="${user.email}">d</td><td th:text="${user.age}">e</td></tr></table><br/></div><hr/>
</body>
</html>
拦截器 Interceptor
概述
在 Spring Boot 应用程序中,拦截器是一种 AOP(面向切面编程)工具,用于在处理 HTTP 请求和响应的过程中插入特定的逻辑。拦截器可以用于多种用途,例如日志记录、权限校验、请求验证等
示意图
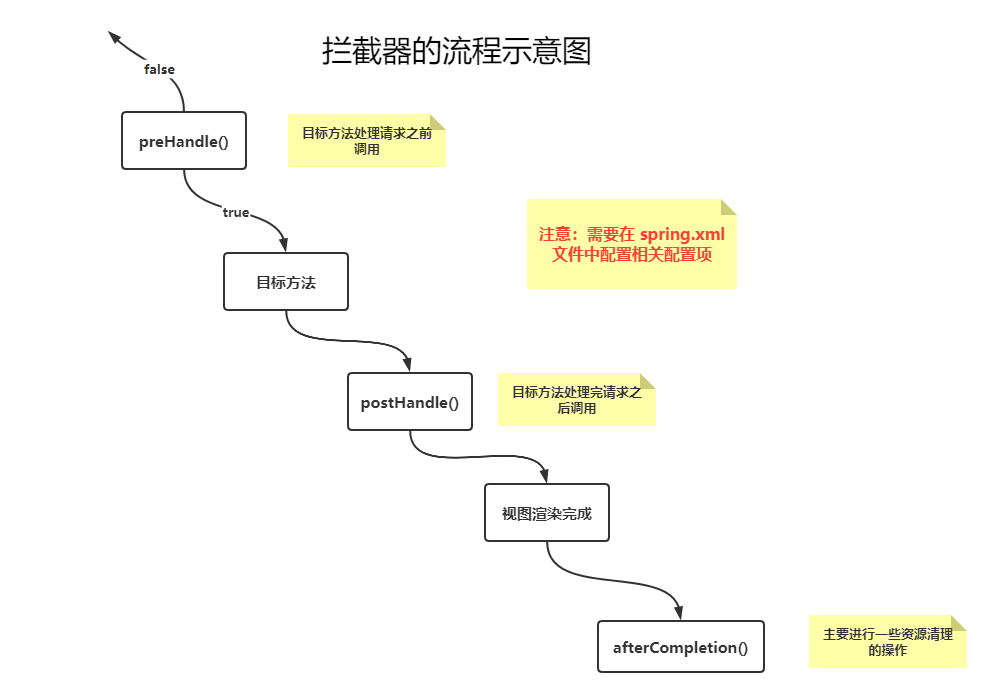
实现步骤
-
创建拦截器类:实现
HandlerInterceptor接口,并重写其中的方法preHandle():在请求处理之前进行调用(Controller 方法调用之前)postHandle():在请求处理之后立即调用,但是在视图被渲染之前(Controller 方法调用之后)afterCompletion():在整个请求结束之后,也就是在视图被渲染之后进行调用
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {// 在请求处理之前进行调用(Controller方法调用之前)return true; // 返回 true 继续执行,返回 false 则取消当前请求}@Overridepublic void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {// 在请求处理之后立即调用,但是在视图被渲染之前(Controller方法调用之后)}@Overridepublic void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {// 在整个请求结束之后调用,也就是在DispatcherServlet渲染了对应的视图之后执行(主要用于资源清理工作)} } -
注册拦截器:创建一个配置类,实现
WebMvcConfigurer接口,并重写addInterceptors()方法,以注册拦截器 -
配置拦截规则:在
addInterceptors()方法中,可以配置拦截器的拦截路径和排除路径import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;@Configuration public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**") // 表示拦截所有请求.excludePathPatterns("/","/login", "/static/**"); // 排除登录和静态资源} }
文件上传
需求说明
实现简单的单个文件上传以及多个文件上传的功能
综合案例
单个文件上传
1、上传文件页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>File Upload</title>
</head>
<body><form method="POST" action="/upload" enctype="multipart/form-data"><input type="file" name="file" /><input type="submit" value="Upload" /></form>
</body>
</html>
2、添加依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
3、编写控制器
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;@RestController
public class FileUploadController {@PostMapping("/upload")public String uploadFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {// 处理文件保存逻辑...return "File uploaded successfully";}
}
多个文件上传
1、上传文件页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>File Upload</title>
</head>
<body><form method="POST" action="/uploadMultiple" enctype="multipart/form-data"><input type="file" name="files" multiple /><input type="submit" value="Upload" /></form>
</body>
</html>
2、依赖如上
3、编写控制器方法
@PostMapping("/uploadMultiple")
public String uploadMultipleFiles(@RequestParam("files") MultipartFile[] files) {// 处理多个文件保存逻辑for (MultipartFile file : files) {String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();String filePath = "savePath/" + fileName;File dest = new File(filePath);try {file.transferTo(dest);} catch (IOException e) {log.info("多个文件上传失败!")}}// ...return "Files uploaded successfully";
}
注意事项
-
处理异常情况,如文件大小限制、文件类型检查等。在 Spring Boot 中,可以通过配置
application.properties或application.yml文件来设置文件上传的相关属性# 根据项目需求修改文件上传的参数,否测文件上传会抛出异常 spring:servlet:multipart:max-file-size: 5MB # 单个文件大小,max-request-size: 50MB # 一次请求最大上传大小(多个文件)
















)


