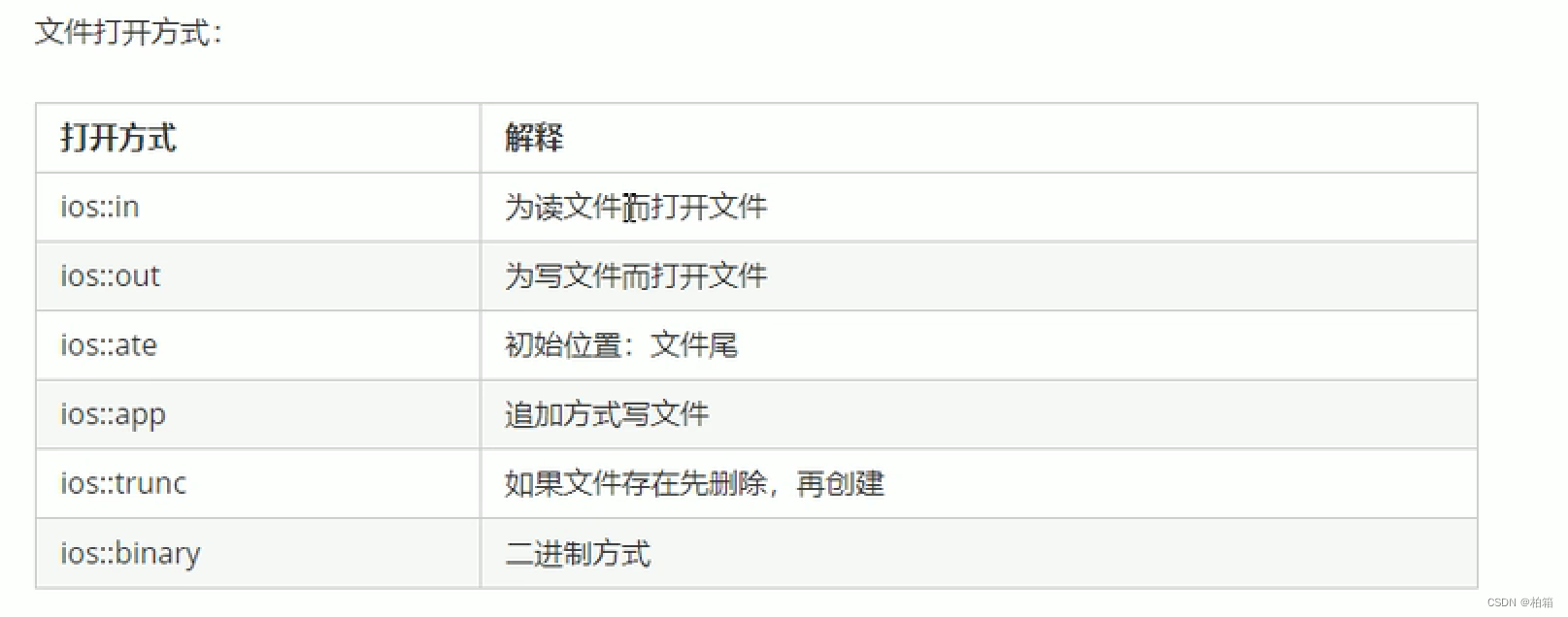
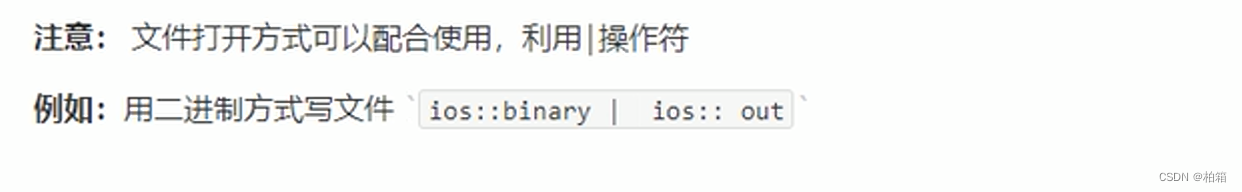
目录
1.文本文件
1.写文件
2.读文件
2.二进制文件
1.写文件
2.读文件
1.文本文件



1.写文件

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;int main()
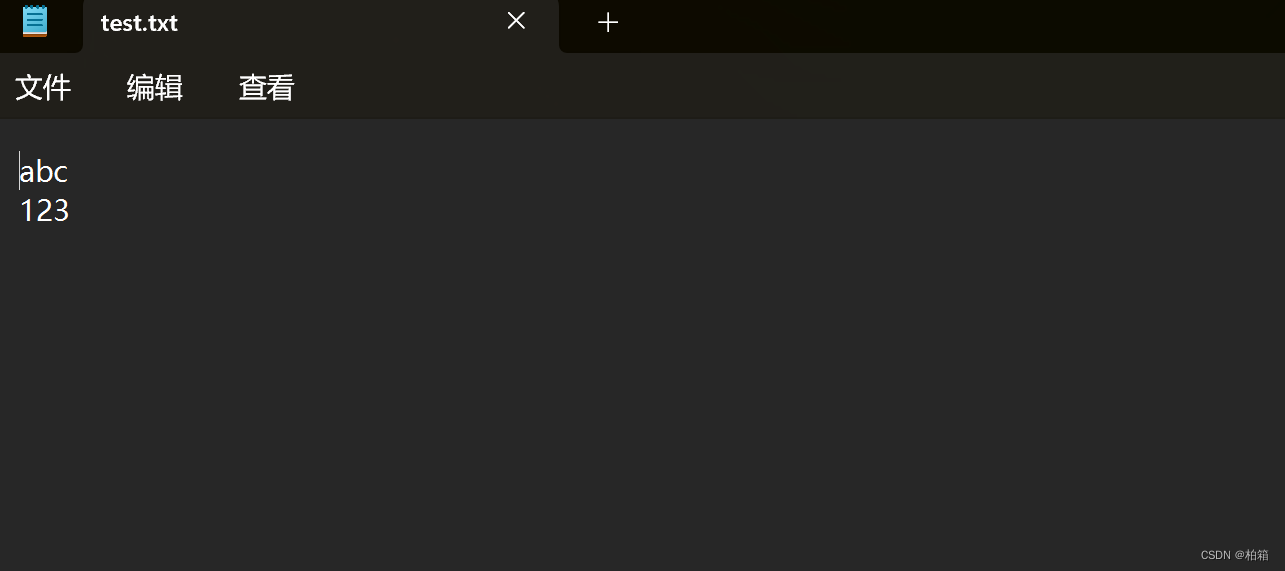
{ofstream ofs;ofs.open("text.txt",ios::out);ofs << "abc" << endl;ofs << 123 << endl;ofs.close();return 0;
}打开文件所在的文件夹即可发现一个新文件

2.读文件

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;int main()
{ifstream ifs;ifs.open("test.txt",ios::in);//如果成功打开了返回真,否则返回假ifs.is_open();if(!ifs.is_open()){cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;return 0;}//读数据//第一种// char buf[1024] = {0};// while(ifs >> buf)// {// cout << buf << endl;// } //一行一行读入,只要文件中还有有文字输入就将它输出//第二种// char buf[1024] = {0};// while(ifs.getline(buf,sizeof(buf)))// {// cout << buf << endl;// }//第三种// string buf;//getline里第一个空是输入流对象,也就是ifs//第二个是准备好的字符串,这里为buf// while(getline(ifs,buf))// {// cout << buf << endl;// }//第四种,效率低,不太推荐char c;//没有读到尾就一直读,EOF代表文件尾end of filewhile((c = ifs.get()) != EOF){cout << c;}ifs.close();return 0;
}

 2.二进制文件
2.二进制文件
1.写文件


#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;class person
{
public://写入文件时最好用字符数组而不是c++里的字符串char name[10];int id;
};
int main()
{ofstream ofs("person.txt",ios::out | ios::binary);//先创建ofs再这样写也行//ofs.open("person.txt",ios::out | ios::binary);person p = {"xiaoming",1};ofs.write((const char *)&p,sizeof(person));ofs.close();return 0;
}打开文件所在文件夹
以二进制的方式写入,所以会有乱码存在


2.读文件
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;class person
{
public://写入文件时最好用字符数组而不是c++里的字符串char name[10];int id;
};int main()
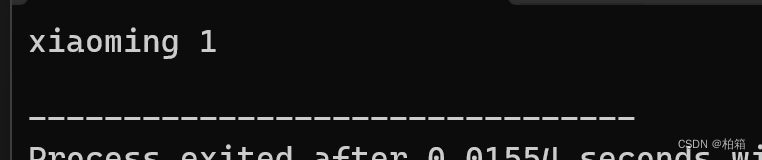
{ifstream ifs;ifs.open("person.txt",ios::in | ios::binary);if(!ifs.is_open()){cout << "打开失败" << endl;}person p;ifs.read((char *)&p, sizeof(person));cout << p.name << ' ' << p.id << endl;ifs.close();return 0;
}


)
)

)

36)






,nodejs新手到高手,(八)NodeJS入门——http模块)


)

 验证模块 页面配置)
