

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
//vector容器构造
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1; //默认构造 无参构造
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//通过区间方式进行构造
vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v2);
//n个elem方式构造
vector<int> v3(10, 100);
printVector(v3);
//拷贝构造
vector<int> v4(v3);
printVector(v4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//vector赋值操作
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1; //无参构造
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//赋值 operator=
vector<int>v2;
v2 = v1;
printVector(v2);
//assign赋值
vector<int>v3;
v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v3);
//n个elem方式赋值
vector<int>v4;
v4.assign(10, 100);
printVector(v4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
//vector容器的容量和大小操作
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
if (v1.empty())//为真 代表容器为空
{
cout << "v1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v1不为空" << endl;
cout << "v1的容量 = " << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v1的大小 = " << v1.size() << endl;
}
//重新指定大小
//resize 重新指定大小 ,若指定的更大,默认用0填充新位置,可以利用重载版本替换默认填充
v1.resize(15,10);//利用重载版本,可以指定默认填充值,参数2
printVector(v1);
//resize 重新指定大小 ,若指定的更小,超出部分元素被删除
v1.resize(5);
printVector(v1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
//vector插入和删除
/*
* `push_back(ele);` //尾部插入元素ele
* `pop_back();` //删除最后一个元素
* `insert(const_iterator pos, ele);` //迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
* `insert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele);` //迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
* `erase(const_iterator pos);` //删除迭代器指向的元素
* `erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);` //删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素
* `clear();` //删除容器中所有元素
*/
//遍历
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
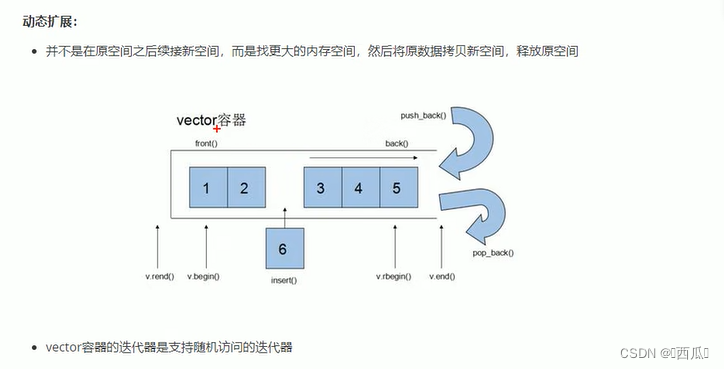
//插入和删除
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
//尾插
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(20);
v1.push_back(30);
v1.push_back(40);
v1.push_back(50);
printVector(v1);
//尾删
v1.pop_back();
printVector(v1);
//插入 第一个参数是迭代器
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 100);
printVector(v1);
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 2, 1000);
printVector(v1);
//删除 参数也是迭代器
v1.erase(v1.begin());
printVector(v1);
//清空
v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end());
v1.clear();
printVector(v1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
//vector容器 数据存取
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
//利用[]方式访问数组中元素
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//利用at方式访问元素
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//获取第一个元素
cout << "v1的第一个元素为: " << v1.front() << endl;
//获取最后一个元素
cout << "v1的最后一个元素为: " << v1.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
//vector容器互换
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//1.基本使用
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
cout << "互换前" << endl;
printVector(v1);
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--)
{
v2.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v2);
//互换容器
cout << "互换后" << endl;
v1.swap(v2);
printVector(v1);
printVector(v2);
}
//2.实际用途
//巧用swap可以收缩内存空间
void test02()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
//重新指定大小
v.resize(3);
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
//收缩内存
vector<int>(v).swap(v); //匿名对象
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
//vector容器 预留空间
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
//预留空间
v.reserve(100000);
int num = 0;//统计开辟次数
int* p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
if (p != &v[0])
{
p = &v[0];
num++;
}
}
cout << "num:" << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}









和BaseHTTPRequestHandler self.wfile在Web 服务器中的应用)










