今天是二零二四年二月十八,农历正月初九。同时今天也是农历新年假期后的第一个工作日。我的内心既兴奋,又担忧,更急躁。兴奋是因为假期后的第一个工作日工作轻松;担忧是因为经过了这么长时间,我依旧没搞明白Spring事务,总觉得有些东西没搞懂,却又不知道是哪里,所以只能在这里徘徊不前;急躁是因为许多事情都要用钱去解决,自己那微薄的收入根本就是杯水车薪,而自己又不知道用哪种方式去筹集足够的资金来解决问题,所以只能整日急不可耐,而问题依旧。到底该怎么办呢?∙∙∙∙∙∙
针对第二种心理,我觉得没有其他办法,只能继续梳理,但也不能因此而放弃后面知识点的梳理。今天就让我们来聊一下Spring事务的几个面试题吧!我想围绕下面这样几个问题展开:
- 《Spring事务原理总结四》这篇文章中提到的将TransactionInfo绑定到当前线程的意义是什么呢?
- Spring是如何解决事务嵌套的?
首先回忆一下前面几篇文章的主要内容:《Spring事务原理总结一》主要梳理了事务的基本概念及特征,同时也梳理了Spring事务的基本用法;《Spring事务原理总结二》则主要梳理了Spring框架解析及注册事务代理的流程;《Spring事务原理总结三》则主要梳理了Spring事务的一些核心组件及其继承结构;《Spring事务原理总结四》梳理了Spring事务的执行流程;《Spring事务原理总结五》主要梳理并回答了前一篇文章中遗留的几个问题;《Spring事务原理总结六》主要梳理了Spring事务的异常回滚流程。接着让我们试着利用这些文章梳理的内容来回答这两个问题。
首先看第一个问题,将TransactionInfo对象绑定到当前线程的操作,在《Spring事务原理总结四》这篇文章中有提到,如下图所示:

当时只是说了这些代码位于TransactionAspectSupport类中,不过并没有深究其意义。现在让我们细化一下这个说法,然后在梳理完第二个问题后来回答这个问题。TransactionInfos是TransactionAspectSupport类中的最终静态内部类(该类内部定义了bindToThread()方法和restoreThreadLocalStatus()方法。所以截图中说前者位于TransactionAspectSupport类的说法也是对的,因为其所在的类位于TransactionAspectSupport类中),其源码如下所示:
protected static final class TransactionInfo {@Nullableprivate final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;@Nullableprivate final TransactionAttribute transactionAttribute;private final String joinpointIdentification;@Nullableprivate TransactionStatus transactionStatus;@Nullableprivate TransactionInfo oldTransactionInfo;public TransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager,@Nullable TransactionAttribute transactionAttribute, String joinpointIdentification) {this.transactionManager = transactionManager;this.transactionAttribute = transactionAttribute;this.joinpointIdentification = joinpointIdentification;}public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {Assert.state(this.transactionManager != null, "No PlatformTransactionManager set");return this.transactionManager;}@Nullablepublic TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute() {return this.transactionAttribute;}/*** Return a String representation of this joinpoint (usually a Method call)* for use in logging.*/public String getJoinpointIdentification() {return this.joinpointIdentification;}public void newTransactionStatus(@Nullable TransactionStatus status) {this.transactionStatus = status;}@Nullablepublic TransactionStatus getTransactionStatus() {return this.transactionStatus;}/*** Return whether a transaction was created by this aspect,* or whether we just have a placeholder to keep ThreadLocal stack integrity.*/public boolean hasTransaction() {return (this.transactionStatus != null);}private void bindToThread() {// Expose current TransactionStatus, preserving any existing TransactionStatus// for restoration after this transaction is complete.this.oldTransactionInfo = transactionInfoHolder.get();transactionInfoHolder.set(this);}private void restoreThreadLocalStatus() {// Use stack to restore old transaction TransactionInfo.// Will be null if none was set.transactionInfoHolder.set(this.oldTransactionInfo);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return (this.transactionAttribute != null ? this.transactionAttribute.toString() : "No transaction");}
}
这个类上有bindToThread()方法和restoreThreadLocalStatus()两个方法,它们的主要作用就是更改当前线程持有的ThreadLocal上的TransactionInfo值。
下面让我们来看一下第二个问题,要回答这个问题,需要从TransactionInterceptor的invoke(MethodInvocation)方法看起,这个方法的代码如下所示:
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);// ……
// 这里删除了一些无用代码PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager cpptm)) {// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);Object retVal;try {// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();}catch (Throwable ex) {// target invocation exceptioncompleteTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);throw ex;}finally {cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);}if (retVal != null && txAttr != null) {TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();if (status != null) {if (retVal instanceof Future<?> future && future.isDone()) {try {future.get();}catch (ExecutionException ex) {if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex.getCause())) {status.setRollbackOnly();}}catch (InterruptedException ex) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}}else if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);}}}commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);return retVal;}else {Object result;final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.try {result = cpptm.execute(txAttr, status -> {TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);try {Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);}return retVal;}catch (Throwable ex) {if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.if (ex instanceof RuntimeException runtimeException) {throw runtimeException;}else {throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);}}else {// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.throwableHolder.throwable = ex;return null;}}finally {cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);}});}catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {throw ex.getCause();}catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);}throw ex2;}catch (Throwable ex2) {if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);}throw ex2;}// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {throw throwableHolder.throwable;}return result;}
}
当调用事务代理对象时,程序会经过判断后,走进if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager cpptm))分支。首先让我们考虑一下非事务嵌套的操作场景,if分支中的retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();就表示业务代码执行完成了,后面就是释放资源(即调用cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo)方法)、提交事务(则是指调用commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo)方法)等一系列常规操作。这样整个事务和业务处理逻辑就执行完成了。接着再来考虑一下事务嵌套的处理场景(即需要事务的业务处理代码中调用了另外一个需要事务的业务代码),这个时候第一次进入if分支的程序执行完retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();后,会再次进入到if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager cpptm))分支,这个时候我们需要关注if分支中的TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification)这句,先来看一下这个被调用的方法(createTransactionIfNecessary())及其关联方法(prepareTransactionInfo())的源码:
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {@Overridepublic String getName() {return joinpointIdentification;}};}TransactionStatus status = null;if (txAttr != null) {if (tm != null) {status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);}else {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +"] because no transaction manager has been configured");}}}return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
//
protected TransactionInfo prepareTransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, String joinpointIdentification,@Nullable TransactionStatus status) {TransactionInfo txInfo = new TransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);if (txAttr != null) {// We need a transaction for this method...if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Getting transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");}// The transaction manager will flag an error if an incompatible tx already exists.txInfo.newTransactionStatus(status);}else {// The TransactionInfo.hasTransaction() method will return false. We created it only// to preserve the integrity of the ThreadLocal stack maintained in this class.if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("No need to create transaction for [" + joinpointIdentification +"]: This method is not transactional.");}}// We always bind the TransactionInfo to the thread, even if we didn't create// a new transaction here. This guarantees that the TransactionInfo stack// will be managed correctly even if no transaction was created by this aspect.txInfo.bindToThread();return txInfo;
}
这时我们主要关注prepareTransactionInfo()方法中的txInfo.bindToThread(),关于这个被调用的方法的详情可以看参看前面的源码。这里再贴一下图片:

从图中不难看出,这个方法会先从当前线程的ThreadLocal中拿出一个TransactionInfo对象,并将其赋值给TransactionInfo的oldTransactionInfo属性,然后将新的TransactionInfo对象重新赋值到当前线程的ThreadLocal中。接着就是就是继续调用retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(),然后调用cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo)方法,最后再调用commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo)方法。这里我们再啰嗦一下cleanupTransactionInfo ()方法,其源码如下图所示:
protected void cleanupTransactionInfo(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {if (txInfo != null) {txInfo.restoreThreadLocalStatus();}
}
该方法最终调用的是TransactionInfo类中的restoreThreadLocalStatus()方法,其源码如下图所示:
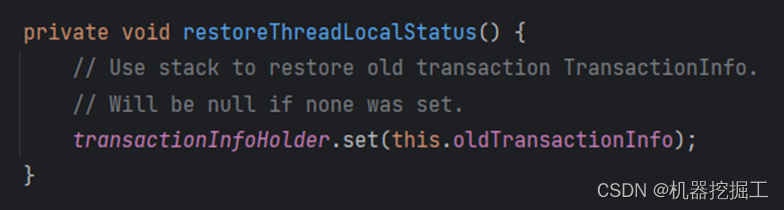
说白了就是将当前TransactionInfo对象中的oldTransactionInfo对象重新赋值到当前线程的ThreadLocal对象中,这个对象就是嵌套事务的上一层事务。至此我们就可以用自己的语言来回答前面的两个问题了!
总的来看,将TransactionInfo绑定到当前线程的主要目的就是解决嵌套事务的。Spring解决嵌套的主要思路就是先将当前的TransactionInfo对象绑定到当前线程,当当前TransactionInfo对应的业务处理代码调用其他事务代理时,会将当前线程中保存的TransactionInfo对象赋值给新的TransactionInfo对象的oldTransactionInfo属性,然后将新的TransactionInfo对象重新绑定到当前线程的ThreadLocal上,这样就实现了前后两个事务的关联,并完成对事务传播行为的处理。

:SORA已来,AI将开启新纪元)














-根据RequestBody的内容来区分使用哪个资源)


