朋友们、伙计们,我们又见面了,本期来给大家解读一下set和map的封装,如果看完之后对你有一定的启发,那么请留下你的三连,祝大家心想事成!
C 语 言 专 栏:C语言:从入门到精通
数据结构专栏:数据结构
个 人 主 页 :stackY、
C + + 专 栏 :C++
Linux 专 栏 :Linux

目录
1. stl库中的封装
2. 模拟实现的红黑树改进
2.1 存储数据的类型
2.2 添加提取类型的仿函数
2.2.1 改进红黑树的插入
3. 封装红黑树的迭代器
3.1 operator++逻辑
代码实现:
3.2 operator--逻辑
3.3 其他接口
4. 添加红黑树的迭代器
代码实现:
5. set的封装
5.1 set的插入
set封装代码:
6. map的封装
6.1 operator[]
map封装代码:
7. 添加迭代器之后的红黑树完整代码
1. stl库中的封装
set和map底层封装采用了红黑树,如果不了解红黑树的铁铁可以去:【C++】:红黑树
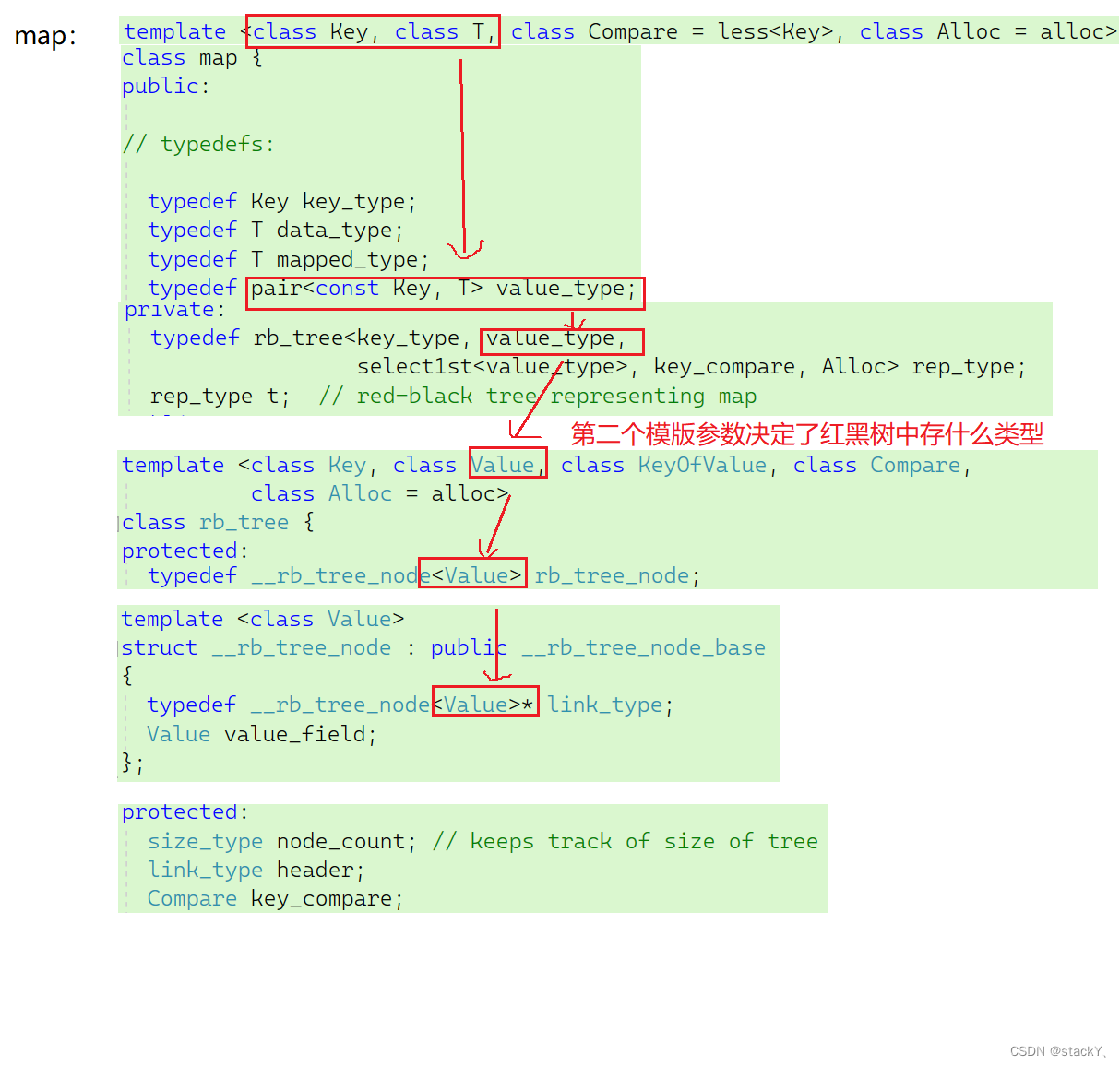
那么我们可以简单的来看一看库中对set和map的封装:
从库中可以看到,在传参的时候红黑树中的第二个模版参数决定的是红黑树中存的是什么类型的数据,这样就可以通过传参调用使set与map用一个红黑树即可,根据库中的红黑树,为了实现set与map的封装,首先对我们自己实现的红黑树做个简单的改进。
2. 模拟实现的红黑树改进
模拟实现红黑树代码:https://blog.csdn.net/Yikefore/article/details/134885925?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
2.1 存储数据的类型
因为要根据第二个模版参数来构造红黑树的节点,所以需要将红黑树的节点结构做一变化:
只需要用一个模版参数来构造即可:
#pragma once//枚举定义节点颜色 enum Color {RED, //红色BLACK //黑色 };//红黑树节点的定义 template<class T> struct RBTreeNode {RBTreeNode<T>* _left; //左子树节点RBTreeNode<T>* _right; //右子树节点RBTreeNode<T>* _parent; //父节点Color _col; //节点颜色T _data; //节点的数据//节点的构造RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_col(RED),_data(data){} };
2.2 添加提取类型的仿函数
由于红黑树种存储的数据类型是通过传参来决定的,由于红黑树的插入是需要通过比较大小的,那么在接下来的插入逻辑中我们并不知道是key模型还是key_value模型。
① 假设是key模型 -> 那么只比较这一个key的大小即可。
② 假设是key_value模型 -> 那么是需要比较key与key的大小,不需要关心value的大小。
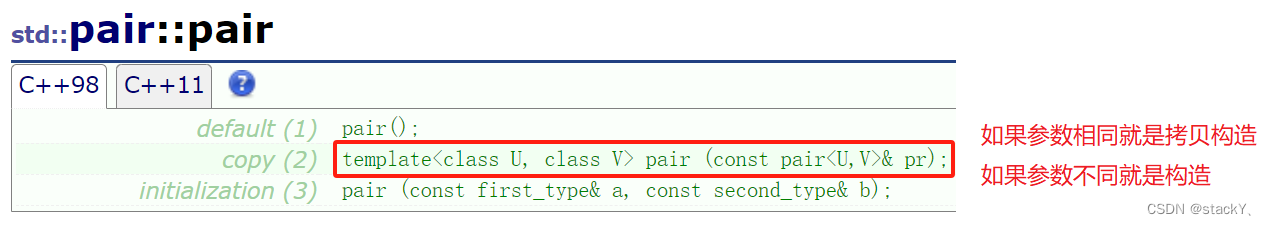
如果我们使用的是map,那么就会传递一个pair,我们不妨来看一下pair默认的比较逻辑:
first和second有一个小就表示小,因此pair的默认比较逻辑是不符合我们的要求的,所以我们需要自己使用仿函数来获取key来进行比较。
template<class K>class set{public://提取set的keystruct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _tree;};template<class K, class V>class map{public://提取map的keystruct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};private:RBTree<K, V, MapKeyOfT> _tree;};为了让set与key都可以使用同一个红黑树,所以也需要对set的key做以提取,这里就可以保证在红黑树的插入结构中的比较逻辑都用的key进行比较。
2.2.1 改进红黑树的插入
由于我们是根据第二个模板参数来确认红黑树节点的类型,所以再插入比较时需要用提取key的仿函数进行提取,再进行比较:
//插入bool Insert(const T& data){//为空可以直接插入,并将根节点置为黑色if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;KeyOfT kot;//不为空找到合适的插入位置while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}elsereturn false;}//链接//新插入的节点默认为红色节点cur = new Node(data);if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}//判断节点的颜色,是否破坏了平衡//......}
3. 封装红黑树的迭代器
红黑树的迭代器封装是一种类似于链表迭代器的样式,不熟悉的铁铁可以去看看:【STL】:list模拟实现
我们使用一份代码,通过传递参数控制const迭代器和非const迭代器。
3.1 operator++逻辑
红黑树的遍历是一种二叉树的中序遍历: 左子树 根 右子树
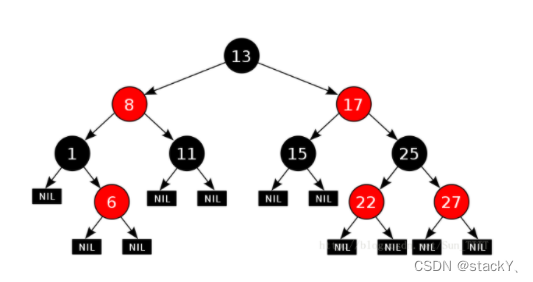
因此红黑树遍历出的结果是一个升序。我们以下面这棵红黑树为例来演示一下:
中序遍历的第一个节点是1, 最后一个节点是27
中序遍历结果是 1 6 8 11 13 15 17 22 25 27
中序遍历的第一个节点便是这棵红黑树的最左节点;
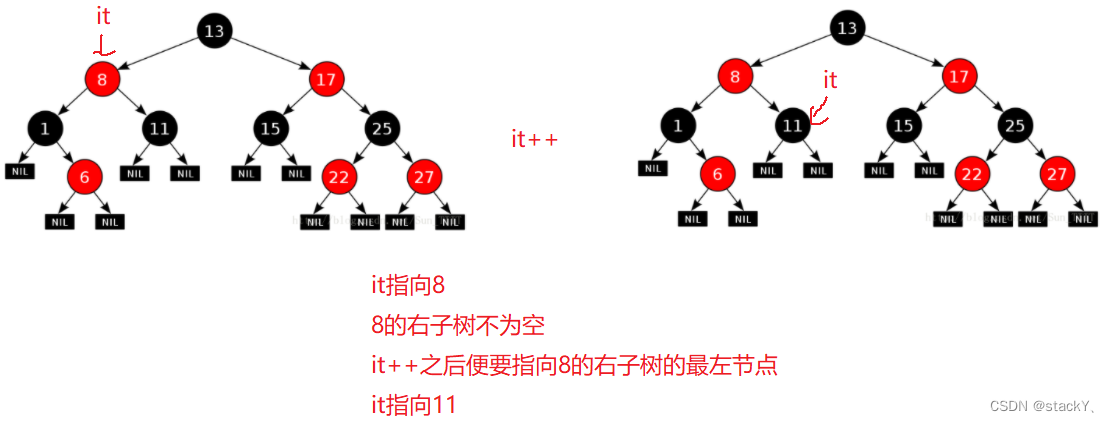
++it的核心:找中序遍历的下一个节点;
有两种情况:
1. it指向的当前节点,如果右子树不为空,那么下一个节点就是该右子树的最左节点。
2. it指向的当前节点,如果右子树为空,那么分两种情况:
① it指向的当前节点是父节点的左,那么就表明父节点的左子树已经访问完了,接下来直接访问父节点即可。
② it指向的当前结点是父节点的右,那么就表明以父节点为根的这棵子树全部访问完毕,需要访问下一棵子树,那么就要往上找孩子是父亲左的那个祖先节点。
代码实现:
// 红黑树迭代器 template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr> struct __TreeIterator {typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right) //右子树不为空,下一个节点就是右子树的最左节点{Node* cur = _node->_right;while (cur->left){cur = cur->_left;}_node = cur;}else //右子树为空,下一个节点就是孩子为父亲左的那个祖先节点{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent; }return *this;} };
3.2 operator--逻辑
operator--的逻辑和operator++逻辑正好相反: 右子树 根 左子树
1. it指向的当前节点,如果左子树不为空,那么下一个节点就是该左子树的最右节点。
2. it指向的当前节点,如果右子树为空,那么分两种情况:
① it指向的当前节点是父节点的右,那么就表明父节点的右子树已经访问完了,接下来直接访问父节点即可。
② it指向的当前结点是父节点的左,那么就表明以父节点为根的这棵子树全部访问完毕,需要访问下一棵子树,那么就要往上找孩子是父亲右的那个祖先节点。
代码就不实现了,只需对operator++代码稍微改动即可。
3.3 其他接口
operator*、operator->、operator==、operator!=
// 红黑树迭代器 template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr> struct __TreeIterator {typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){//......}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;} };
4. 添加红黑树的迭代器
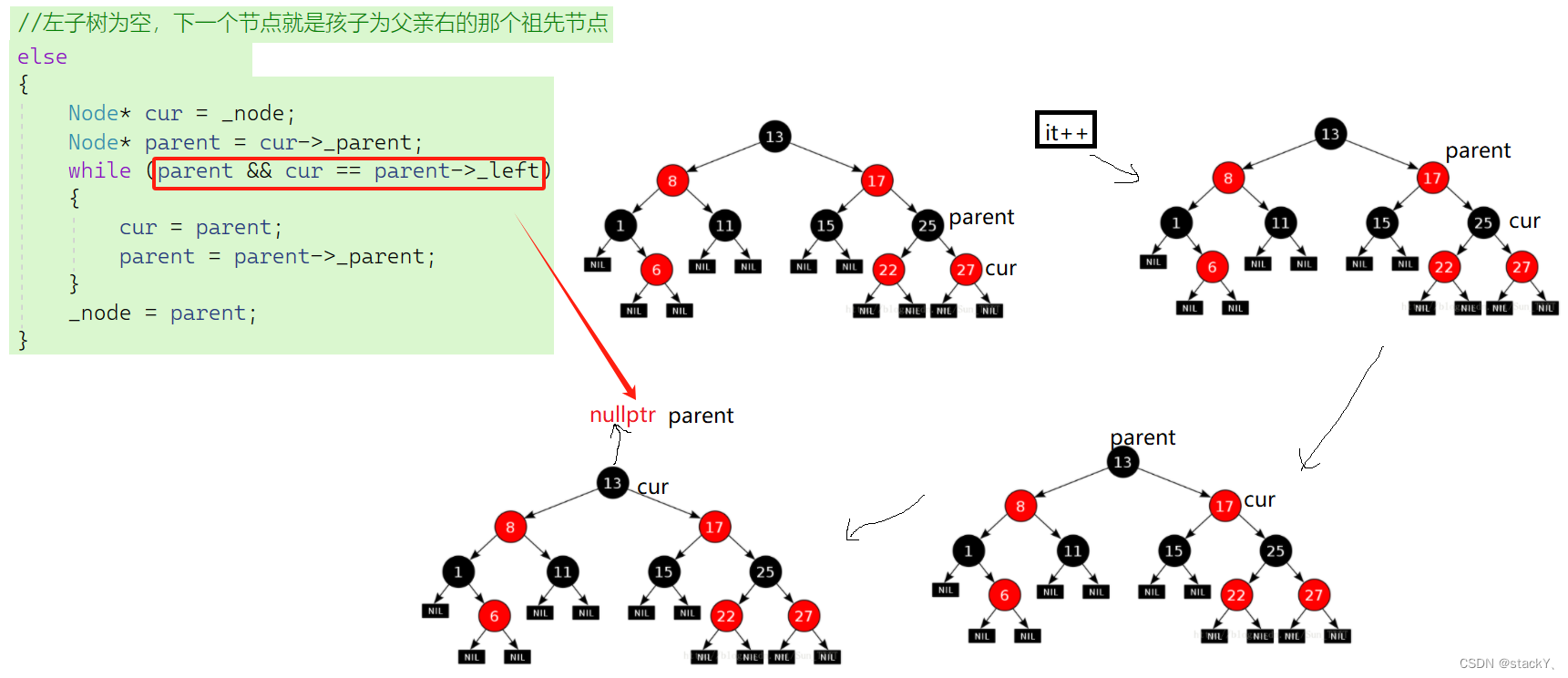
根据我们上面实现的operator++原理来看的话:begin()是最左节点, end()是nullptr,那么为什么end()是nullptr呢?我们接下来看一下:
还是这一棵红黑树
当我们访问到了最后一个节点27时,它的左右子树都为空,并且它是父亲节点的右子树,再进行一步it++时,它就会往上面找孩子是父亲左的祖先节点,因此就会一直循环往上走,直到走到了13,但是13为根节点,没有父亲节点。
因此,当访问最后一个节点27时,再进行it++,找到的就是nullptr,所以需要将end()设置为nullptr。
代码实现:
//红黑树的实现 // set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t; // map->RBTree<K, pair<K, T>, MapKeyOfT> _t; template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT> class RBTree { public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;//插入bool Insert(const T& data)//......//中序遍历void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}//判断是否平衡//......//高度//......//节点个数//......//查找//...... private://判断是否平衡//......//右单旋//......//左单旋//...... private:Node* _root = nullptr; };
5. set的封装
在封装之前我们需要了解一个内嵌类型的细节:
对类模板取内嵌类型需要加上typename
因为编译器在编译的时候不确定是模板还是类型,不能取到内嵌类型,加上typename就表明是一个类型。
根据set的属性:数据是不允许修改的,所以我们直接将普通迭代器和const迭代器都封装为const迭代器:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator; typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
5.1 set的插入
set和map的插入的返回值是一个pair,其中pair第一个参数是迭代器,插入成功表示新插入节点的迭代器,插入失败表示已存在节点的迭代器,第二个参数是bool值,表示插入是否成功。
那么我们就需要对我们的Insert再稍作调整:
我们使用pair的特性,用一个Node*类型的去构造一个iterator类型,这样就保证了iterator到const_iterator的转化:
set封装代码:
#pragma once #include "RBTree.h"namespace ywh {template<class K>class set{public://提取set的keystruct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:iterator begin() const{return _tree.begin();}iterator end() const{return _tree.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){_tree.Insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _tree;}; }
6. map的封装
map的封装需要实现operator[],返回的pair的second,需要借助于Insert。
6.1 operator[]
关于operator[]的详细介绍和原理都在【C++】:set和map 中,需要的可以去看一看。
V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = Insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}
map封装代码:
#pragma once #include "RBTree.h"namespace ywh {template<class K, class V>class map{public://提取map的keystruct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:iterator begin(){return _tree.begin();}const_iterator begin() const{return _tree.begin();}iterator end(){return _tree.end();}const_iterator end() const {return _tree.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _tree.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _tree;}; }
7. 添加迭代器之后的红黑树完整代码
#pragma once//枚举定义节点颜色 enum Color {RED, //红色BLACK //黑色 };//红黑树节点的定义 template<class T> struct RBTreeNode {RBTreeNode<T>* _left; //左子树节点RBTreeNode<T>* _right; //右子树节点RBTreeNode<T>* _parent; //父节点Color _col; //节点颜色T _data; //节点的数据//节点的构造RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_col(RED),_data(data){} };// 红黑树迭代器 template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr> struct __TreeIterator {typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right) //右子树不为空,下一个节点就是右子树的最左节点{Node* cur = _node->_right;while (cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}_node = cur;}else //右子树为空,下一个节点就是孩子为父亲左的那个祖先节点{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent; }return *this;}Self& operator--(){if (_node->_left) //左子树不为空,下一个节点就是右子树的最右节点{Node* cur = _node->left;while (cur->_right){cur = cur->_right;}_node = cur;}else //左子树为空,下一个节点就是孩子为父亲右的那个祖先节点{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;} };//红黑树的实现 // set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t; // map->RBTree<K, pair<K, T>, MapKeyOfT> _t; template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT> class RBTree { public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;//插入//pair<iterator, bool> Instrt(const T& data)pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const T& data){//为空可以直接插入,并将根节点置为黑色if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(_root, true);}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;KeyOfT kot;//不为空找到合适的插入位置while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}elsereturn make_pair(cur, false);}//链接//新插入的节点默认为红色节点cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur; //保存当前节点防止丢失cur->_col = RED;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}//判断节点的颜色,是否破坏了平衡while (parent && parent->_col == RED){//祖父节点Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;//判断父亲与叔叔的位置if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;//叔叔节点存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){//变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//将grandfather变为新的cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else //叔叔节点不存在或者存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_left) //该路径的parent已经是grandfather的左{//旋转+变色Rotate_right(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else //cur是parent的右{//双旋+变色Rotate_left(parent);Rotate_right(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else //parent == grandfather->_right{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;//叔叔节点存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){//变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//将grandfather变为新的cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right) //该路径的parent已经是grandfather的右{//旋转+变色Rotate_left(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else //cur是parent的左{Rotate_right(parent);Rotate_left(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}//将根节点再次置黑保持红黑树的平衡_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(newnode, true);}//中序遍历void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}//判断是否平衡bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;//1.判断根是否为黑if (_root->_col == RED)return false;int standard_val = 0; //最左路径的黑色节点个数Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK)standard_val++;cur = cur->_left;}int Black_size = 0;return Check(_root,standard_val,Black_size);}//高度int Height(){return _Height(_root);}//节点个数size_t Size(){return _Size(_root);}//查找Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return NULL;} private:size_t _Size(Node* root){if (root == NULL)return 0;return _Size(root->_left)+ _Size(root->_right) + 1;}int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;}//判断是否平衡bool Check(Node* root, const int standard_val, int Black_size){if (root == nullptr){if (Black_size != standard_val) //比较黑色节点的个数{cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}elsereturn true;}//判断它与它父亲的颜色if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << "有连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}//黑色节点计数器++if (root->_col == BLACK){Black_size++;}//递归它的左右子树return Check(root->_left, standard_val, Black_size)&& Check(root->_right, standard_val, Black_size);}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}//右单旋void Rotate_right(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if(subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppNode->_left == parent){ppNode->_left = subL;subL->_parent = ppNode;}else{ppNode->_right = subL;subL->_parent = ppNode;}}}//左单旋void Rotate_left(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right; Node* subRL = subR->_left; Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;if (_root == parent){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppNode->_left == parent)ppNode->_left = subR;elseppNode->_right = subR;subR->_parent = ppNode;}} private:Node* _root = nullptr; };
朋友们、伙计们,美好的时光总是短暂的,我们本期的的分享就到此结束,欲知后事如何,请听下回分解~,最后看完别忘了留下你们弥足珍贵的三连喔,感谢大家的支持!








)
)






一面笔试算法原题)


鉴权组件插槽-登入检测)



-- 详解)



