目录
- 2.2 链表
- 1) 概述
- 2) 单向链表
- 3) 单向链表(带哨兵)
- 4) 双向链表(带哨兵)
- 5) 环形链表(带哨兵)

2.2 链表
1) 概述
定义
在计算机科学中,链表是数据元素的线性集合,其每个元素都指向下一个元素,元素存储上并不连续
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next.
可以分类为[^5]
- 单向链表,每个元素只知道其下一个元素是谁

- 双向链表,每个元素知道其上一个元素和下一个元素

- 循环链表,通常的链表尾节点 tail 指向的都是 null,而循环链表的 tail 指向的是头节点 head

链表内还有一种特殊的节点称为哨兵(Sentinel)节点,也叫做哑元( Dummy)节点,它不存储数据,通常用作头尾,用来简化边界判断,如下图所示

随机访问性能
根据 index 查找,时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
插入或删除性能
- 起始位置: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
- 结束位置:如果已知 tail 尾节点是 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),不知道 tail 尾节点是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- 中间位置:根据 index 查找时间 + O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
2) 单向链表
根据单向链表的定义,首先定义一个存储 value 和 next 指针的类 Node,和一个描述头部节点的引用
public class SinglyLinkedList {private Node head; // 头部节点private static class Node { // 节点类int value;Node next;public Node(int value, Node next) {this.value = value;this.next = next;}}
}
- Node 定义为内部类,是为了对外隐藏实现细节,没必要让类的使用者关心 Node 结构
- 定义为 static 内部类,是因为 Node 不需要与 SinglyLinkedList 实例相关,多个 SinglyLinkedList实例能共用 Node 类定义
头部添加
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void addFirst(int value) {this.head = new Node(value, this.head);}
}
- 如果 this.head == null,新增节点指向 null,并作为新的 this.head
- 如果 this.head != null,新增节点指向原来的 this.head,并作为新的 this.head
- 注意赋值操作执行顺序是从右到左
while 遍历
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void loop() {Node curr = this.head;while (curr != null) {// 做一些事curr = curr.next;}}
}
for 遍历
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void loop() {for (Node curr = this.head; curr != null; curr = curr.next) {// 做一些事}}
}
- 以上两种遍历都可以把要做的事以 Consumer 函数的方式传递进来
- Consumer 的规则是一个参数,无返回值,因此像 System.out::println 方法等都是 Consumer
- 调用 Consumer 时,将当前节点 curr.value 作为参数传递给它
迭代器遍历
public class SinglyLinkedList implements Iterable<Integer> {// ...private class NodeIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {Node curr = head;public boolean hasNext() {return curr != null;}public Integer next() {int value = curr.value;curr = curr.next;return value;}}public Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new NodeIterator();}
}
- hasNext 用来判断是否还有必要调用 next
- next 做两件事
- 返回当前节点的 value
- 指向下一个节点
- NodeIterator 要定义为非 static 内部类,是因为它与 SinglyLinkedList 实例相关,是对某个 SinglyLinkedList 实例的迭代
递归遍历
public class SinglyLinkedList implements Iterable<Integer> {// ...public void loop() {recursion(this.head);}private void recursion(Node curr) {if (curr == null) {return;}// 前面做些事recursion(curr.next);// 后面做些事}
}
尾部添加
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...private Node findLast() {if (this.head == null) {return null;}Node curr;for (curr = this.head; curr.next != null; ) {curr = curr.next;}return curr;}public void addLast(int value) {Node last = findLast();if (last == null) {addFirst(value);return;}last.next = new Node(value, null);}
}
- 注意,找最后一个节点,终止条件是 curr.next == null
- 分成两个方法是为了代码清晰,而且 findLast() 之后还能复用
尾部添加多个
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void addLast(int first, int... rest) {Node sublist = new Node(first, null);Node curr = sublist;for (int value : rest) {curr.next = new Node(value, null);curr = curr.next;}Node last = findLast();if (last == null) {this.head = sublist;return;}last.next = sublist;}
}
- 先串成一串 sublist
- 再作为一个整体添加
根据索引获取
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...private Node findNode(int index) {int i = 0;for (Node curr = this.head; curr != null; curr = curr.next, i++) {if (index == i) {return curr;}}return null;}private IllegalArgumentException illegalIndex(int index) {return new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("index [%d] 不合法%n", index));}public int get(int index) {Node node = findNode(index);if (node != null) {return node.value;}throw illegalIndex(index);}
}
- 同样,分方法可以实现复用
插入
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void insert(int index, int value) {if (index == 0) {addFirst(value);return;}Node prev = findNode(index - 1); // 找到上一个节点if (prev == null) { // 找不到throw illegalIndex(index);}prev.next = new Node(value, prev.next);}
}
- 插入包括下面的删除,都必须找到上一个节点
删除
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void remove(int index) {if (index == 0) {if (this.head != null) {this.head = this.head.next;return;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}Node prev = findNode(index - 1);Node curr;if (prev != null && (curr = prev.next) != null) {prev.next = curr.next;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}
}
- 第一个 if 块对应着 removeFirst 情况
- 最后一个 if 块对应着至少得两个节点的情况
- 不仅仅判断上一个节点非空,还要保证当前节点非空
3) 单向链表(带哨兵)
观察之前单向链表的实现,发现每个方法内几乎都有判断是不是 head 这样的代码,能不能简化呢?
用一个不参与数据存储的特殊 Node 作为哨兵,它一般被称为哨兵或哑元,拥有哨兵节点的链表称为带头链表
public class SinglyLinkedListSentinel {// ...private Node head = new Node(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
}
- 具体存什么值无所谓,因为不会用到它的值
加入哨兵节点后,代码会变得比较简单,先看几个工具方法
public class SinglyLinkedListSentinel {// ...// 根据索引获取节点private Node findNode(int index) {int i = -1;for (Node curr = this.head; curr != null; curr = curr.next, i++) {if (i == index) {return curr;}}return null;}// 获取最后一个节点private Node findLast() {Node curr;for (curr = this.head; curr.next != null; ) {curr = curr.next;}return curr;}
}
- findNode 与之前类似,只是 i 初始值设置为 -1 对应哨兵,实际传入的 index 也是 [ − 1 , ∞ ) [-1, \infty) [−1,∞)
- findLast 绝不会返回 null 了,就算没有其它节点,也会返回哨兵作为最后一个节点
这样,代码简化为
public class SinglyLinkedListSentinel {// ...public void addLast(int value) {Node last = findLast();/*改动前if (last == null) {this.head = new Node(value, null);return;}*/last.next = new Node(value, null);}public void insert(int index, int value) {/*改动前if (index == 0) {this.head = new Node(value, this.head);return;}*/// index 传入 0 时,返回的是哨兵Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev != null) {prev.next = new Node(value, prev.next);} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}public void remove(int index) {/*改动前if (index == 0) {if (this.head != null) {this.head = this.head.next;return;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}*/// index 传入 0 时,返回的是哨兵Node prev = findNode(index - 1);Node curr;if (prev != null && (curr = prev.next) != null) {prev.next = curr.next;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}public void addFirst(int value) {/*改动前this.head = new Node(value, this.head);*/this.head.next = new Node(value, this.head.next);// 也可以视为 insert 的特例, 即 insert(0, value);}
}
- 对于删除,前面说了【最后一个 if 块对应着至少得两个节点的情况】,现在有了哨兵,就凑足了两个节点
4) 双向链表(带哨兵)
public class DoublyLinkedListSentinel implements Iterable<Integer> {private final Node head;private final Node tail;public DoublyLinkedListSentinel() {head = new Node(null, 666, null);tail = new Node(null, 888, null);head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;}private Node findNode(int index) {int i = -1;for (Node p = head; p != tail; p = p.next, i++) {if (i == index) {return p;}}return null;}public void addFirst(int value) {insert(0, value);}public void removeFirst() {remove(0);}public void addLast(int value) {Node prev = tail.prev;Node added = new Node(prev, value, tail);prev.next = added;tail.prev = added;}public void removeLast() {Node removed = tail.prev;if (removed == head) {throw illegalIndex(0);}Node prev = removed.prev;prev.next = tail;tail.prev = prev;}public void insert(int index, int value) {Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null) {throw illegalIndex(index);}Node next = prev.next;Node inserted = new Node(prev, value, next);prev.next = inserted;next.prev = inserted;}public void remove(int index) {Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null) {throw illegalIndex(index);}Node removed = prev.next;if (removed == tail) {throw illegalIndex(index);}Node next = removed.next;prev.next = next;next.prev = prev;}private IllegalArgumentException illegalIndex(int index) {return new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("index [%d] 不合法%n", index));}@Overridepublic Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new Iterator<Integer>() {Node p = head.next;@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return p != tail;}@Overridepublic Integer next() {int value = p.value;p = p.next;return value;}};}static class Node {Node prev;int value;Node next;public Node(Node prev, int value, Node next) {this.prev = prev;this.value = value;this.next = next;}}
}
5) 环形链表(带哨兵)
双向环形链表带哨兵,这时哨兵既作为头,也作为尾
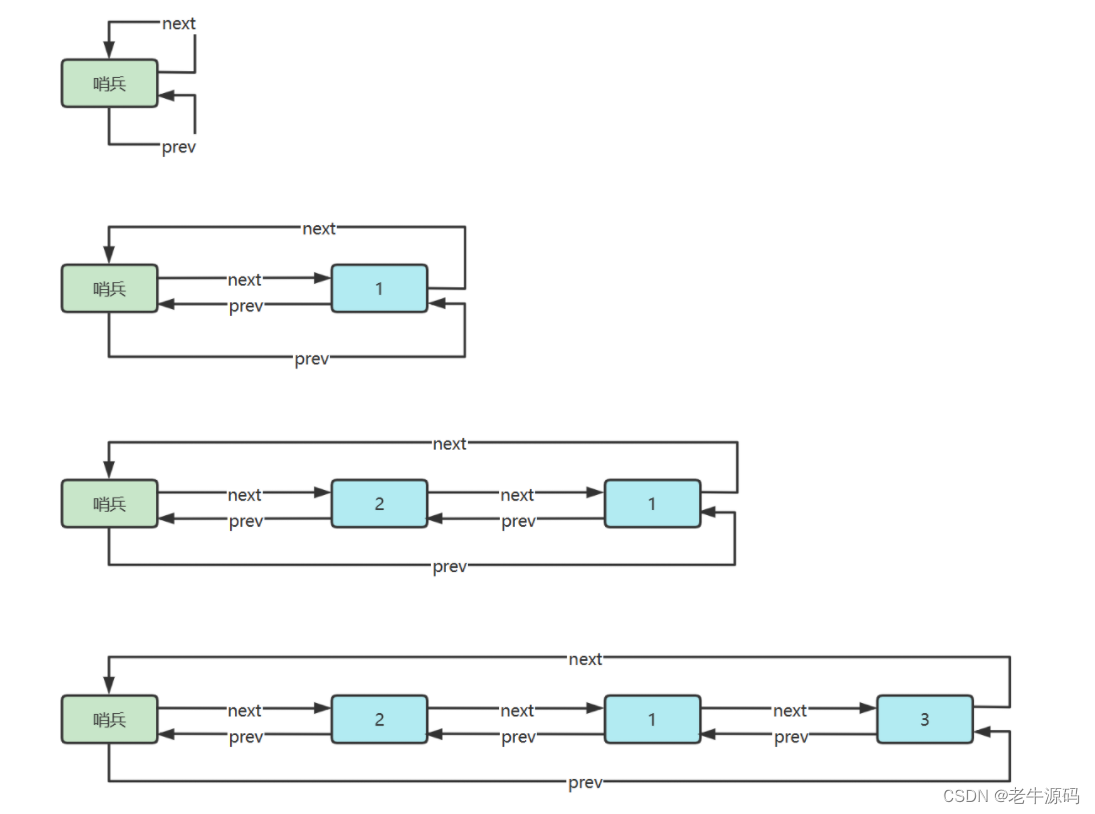
参考实现
public class DoublyLinkedListSentinel implements Iterable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new Iterator<>() {Node p = sentinel.next;@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return p != sentinel;}@Overridepublic Integer next() {int value = p.value;p = p.next;return value;}};}static class Node {Node prev;int value;Node next;public Node(Node prev, int value, Node next) {this.prev = prev;this.value = value;this.next = next;}}private final Node sentinel = new Node(null, -1, null); // 哨兵public DoublyLinkedListSentinel() {sentinel.next = sentinel;sentinel.prev = sentinel;}/*** 添加到第一个* @param value 待添加值*/public void addFirst(int value) {Node next = sentinel.next;Node prev = sentinel;Node added = new Node(prev, value, next);prev.next = added;next.prev = added;}/*** 添加到最后一个* @param value 待添加值*/public void addLast(int value) {Node prev = sentinel.prev;Node next = sentinel;Node added = new Node(prev, value, next);prev.next = added;next.prev = added;}/*** 删除第一个*/public void removeFirst() {Node removed = sentinel.next;if (removed == sentinel) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法");}Node a = sentinel;Node b = removed.next;a.next = b;b.prev = a;}/*** 删除最后一个*/public void removeLast() {Node removed = sentinel.prev;if (removed == sentinel) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法");}Node a = removed.prev;Node b = sentinel;a.next = b;b.prev = a;}/*** 根据值删除节点* <p>假定 value 在链表中作为 key, 有唯一性</p>* @param value 待删除值*/public void removeByValue(int value) {Node removed = findNodeByValue(value);if (removed != null) {Node prev = removed.prev;Node next = removed.next;prev.next = next;next.prev = prev;}}private Node findNodeByValue(int value) {Node p = sentinel.next;while (p != sentinel) {if (p.value == value) {return p;}p = p.next;}return null;}}


)

:将Node.js和UI能力(app/BrowserWindow/dialog)等注入html)
)
)






:这一篇基本能满足Git基本的使用需求了!)
)



