*本文是博主对Java各种实验的再整理与详解,除了代码部分和解析部分,一些题目还增加了拓展部分(⭐)。拓展部分不是实验报告中原有的内容,而是博主本人自己的补充,以方便大家额外学习、参考。
目录
一、实验目的
二、实验内容
1、判断E盘指定目录下是否有后缀名为.jpg的文件,如果有就输出此文件名称。
2、分别使用字节流和字节缓冲流的两种读取方式实现对图片文件的复制操作并比较两种方式在复制时间上的效率。
3、编写一个程序,分别使用转换流、字符流和缓冲字符流拷贝一个文本文件。
4、编程序实现下列功能
5、复制指定目录中的指定类型(如.java)的文件到另一个目录中。
6、已知s.txt文件中有这样的一个字符串:“hcexfgijkamdnoqrzstuvwybpl”,请编写程序读取数据内容,把数据排序后写入ss.txt中。
三、实验总结
一、实验目的
1、理解字节流和字符流的含义,掌握IO流的分类;
2、掌握File类的使用;
3、掌握文件字节流FileInputStream、FileOutputStream和文件字符流FileReader、FileWriter的使用;
4、掌握字符缓冲流BufferedReader、BufferedWriter的使用;
5、了解转换流OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader的使用;
6、能够灵活使用IO流完成数据的处理。
二、实验内容
1、判断E盘指定目录下是否有后缀名为.jpg的文件,如果有就输出此文件名称。
由于博主电脑没设E盘,因此路径改为D盘。路径下内容为:

通过Java的文件操作来实现。File类是 Java 中抽象表示文件和目录路径名的一个类,它提供了一系列方法,可以用于创建、删除、重命名等文件和目录的基本操作,以及获取文件信息。在实现该练习时,用到了如下几个方法:
- File directory = new File(directoryPath) 这是根据目录路径创建File对象,目录路径是我们事先指定的目标路径,指定的路径是哪个,后续就对哪个路径进行操作。可以把File对象理解成我们要进行文件操作的遥控器。操作系统是对文件系统的直接管理,而我们用户要操作文件,是通过创建File对象、调用File对象中的各种方法实现的。(这个形式和socket操作网卡,thread操作线程类似。)
- File[] files = directory.listFiles() 获取目录下的所有文件,用File数组来接收。在博主本人的程序中,获取到的就是test.jpg和fox.png这两个文件。获取目录下所有文件的操作往往和遍历数组配合使用,以搭配条件语句对目录下的文件进行过滤,如:
File[] files = directory.listFiles(); // 获取目录下的文件和子目录列表 for (File file : files) {// 处理每个文件或目录 } - file.isFile() 用于判断file对象是否是一个文件。
- file.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".jpg") 用于判断file对象名是否以“.jpg”结尾。getName()获取到file对象的文件名(是一个字符串),后面的toLowerCase().endsWith(".jpg")是字符串String的方法。
源代码:
import java.io.File;public class S7_1 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 指定目录路径String directoryPath = "D:\\ASSIGNMENT\\code\\javacode\\leetcode-test\\imgdir";// 创建File对象File directory = new File(directoryPath);// 获取目录下所有文件File[] files = directory.listFiles();// 遍历文件列表if (files != null) {for (File file : files) {// 判断文件是否以.jpg结尾if (file.isFile() && file.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".jpg")) {// 输出文件名称System.out.println(file.getName());}}} else {System.out.println("指定目录不存在或不是一个目录!");}}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:

2、分别使用字节流和字节缓冲流的两种读取方式实现对图片文件的复制操作并比较两种方式在复制时间上的效率。
字节流和字节缓冲流是 Java 中用于处理二进制数据的输入输出流类,用于进行字节级别的数据读写操作。
1、字节流:
- 字节流以字节为单位进行数据传输,适用于处理二进制数据,如图片、音频、视频等文件。
InputStream和OutputStream是 Java 中用于操作字节流的抽象基类。- 常见的字节流类包括
FileInputStream、FileOutputStream、ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream等。
2、字节缓冲流:
- 字节缓冲流是对字节流的一种包装,在读写过程中加入了缓冲区,以提高读写效率。
- 通过使用缓冲区,可以减少实际读写硬盘的次数,从而提高了数据传输的效率。
- 常见的字节缓冲流类包括
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream。
理解一下“缓冲区”:可以想象有一个工人正在开卡车搬运箱子,他的任务是把箱子从A厂转移到B厂。箱子有很多,如果此时他一个一个搬运,每在A厂将一个箱子放上卡车就开车运到B厂,这样的效率是非常低的且有很多不必要的开销;而如果他先在A厂把所有要搬的箱子都放到一辆卡车上,等要搬运的箱子都放上卡车后一趟直接开到B厂,那么这样他只需要跑一趟就能一块搬运完所有的箱子,这样是效率更高也更节约资源的。
使用字节缓冲流相比直接使用字节流,可以提高读写效率(特别是在处理大文件时)。因为字节缓冲流会将数据先写入内存缓冲区,待缓冲区满或达到一定条件时再一次性写入文件,减少了频繁的硬盘读写操作。
如果需要处理二进制数据且关注性能和效率,通常会选择使用字节缓冲流来进行文件读写操作。
其他细节处理如下:
- 如何比较时间效率?经典的方法是分别记录下程序执行前的时间戳和程序执行完毕后的时间戳,二者的时间间隔即程序运行的时间。常用代码如下:
long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); // do something... long endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); long timeByByteStream = endTime1 - startTime1; - 分别定义方法copyFileByByteStream(字节流复制文件)和copyFileByBufferedStream(字节缓冲流)复制文件。两个方法的逻辑相同,即分别创建输入对象in和输出对象out,通过调用in的read方法读取source.jpg到一个变量,再通过out的write方法将该变量中的内容写入输出目录。
- 在try中申请资源,这样在在try块结束时会自动关闭这些资源,以确保资源被正确释放,避免资源泄露。
- source.jpg存放的位置:必须在工程项目Project目录下时,创建文件对象才能直接使用文件名(也即相对路径),否则必须使用绝对路径。如:

源代码:
import java.io.*;public class S7_2 {public static void main(String[] args) {String sourceFilePath = "source.jpg"; // 源文件路径String destFilePath1 = "dest1.jpg"; // 目标文件路径(字节流复制)String destFilePath2 = "dest2.jpg"; // 目标文件路径(字节缓冲流复制)// 使用字节流复制图片文件并计时long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();copyFileByByteStream(sourceFilePath, destFilePath1);long endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();long timeByByteStream = endTime1 - startTime1;// 使用字节缓冲流复制图片文件并计时long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();copyFileByBufferedStream(sourceFilePath, destFilePath2);long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();long timeByBufferedStream = endTime2 - startTime2;// 输出复制时间System.out.println("使用字节流复制图片文件耗时:" + timeByByteStream + " 毫秒");System.out.println("使用字节缓冲流复制图片文件耗时:" + timeByBufferedStream + " 毫秒");}// 使用字节流复制文件的方法private static void copyFileByByteStream(String sourcePath, String destPath) {try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(sourcePath);OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destPath)) {int byteRead;while ((byteRead = in.read()) != -1) {out.write(byteRead);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 使用字节缓冲流复制文件的方法private static void copyFileByBufferedStream(String sourcePath, String destPath) {try (InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(sourcePath));OutputStream out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destPath))) {byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];int bytesRead;while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:

3、编写一个程序,分别使用转换流、字符流和缓冲字符流拷贝一个文本文件。
要求:
• 分别使用InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter类和FileReader、FileWriter类用两种方式(字符和字符数组)进行拷贝。
• 使用BufferedReader、BufferedWriter类的特殊方法进行拷贝。
源代码:
import java.io.*;public class S7_3 {public static void main(String[] args) {String sourceFilePath = "source.txt";String destFilePath = "destination.txt";// 使用转换流拷贝文件(字符方式)copyFileWithInputStreamReader(sourceFilePath, destFilePath);// 使用转换流拷贝文件(字符数组方式)copyFileWithInputStreamReaderAndCharArray(sourceFilePath, destFilePath);// 使用字符流拷贝文件copyFileWithFileReader(sourceFilePath, destFilePath);// 使用字符流拷贝文件(字符数组方式)copyFileWithFileReaderAndCharArray(sourceFilePath, destFilePath);// 使用缓冲字符流拷贝文件copyFileWithBufferedReader(sourceFilePath, destFilePath);}// 使用转换流拷贝文件(字符方式)private static void copyFileWithInputStreamReader(String sourceFilePath, String destFilePath) {try (InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(sourceFilePath));OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(destFilePath))) {int data;while ((data = reader.read()) != -1) {writer.write(data);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 使用转换流拷贝文件(字符数组方式)private static void copyFileWithInputStreamReaderAndCharArray(String sourceFilePath, String destFilePath) {try (InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(sourceFilePath));OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(destFilePath))) {char[] buffer = new char[1024];int length;while ((length = reader.read(buffer)) != -1) {writer.write(buffer, 0, length);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 使用字符流拷贝文件private static void copyFileWithFileReader(String sourceFilePath, String destFilePath) {try (FileReader reader = new FileReader(sourceFilePath);FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(destFilePath)) {int data;while ((data = reader.read()) != -1) {writer.write(data);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 使用字符流拷贝文件(字符数组方式)private static void copyFileWithFileReaderAndCharArray(String sourceFilePath, String destFilePath) {try (FileReader reader = new FileReader(sourceFilePath);FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(destFilePath)) {char[] buffer = new char[1024];int length;while ((length = reader.read(buffer)) != -1) {writer.write(buffer, 0, length);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 使用缓冲字符流拷贝文件private static void copyFileWithBufferedReader(String sourceFilePath, String destFilePath) {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sourceFilePath));BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destFilePath))) {String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {writer.write(line);writer.newLine();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
生成的目标文件:

建议:同学们在完成该程序时,让每种方法保存的文件名都不相同。我这里因为所有的目标文件名都指定成了destination.txt,所以存在覆盖保存的情况,最终就只有一个目标文件了。
4、编程序实现下列功能
• 向指定的txt文件中写入键盘输入的内容,然后再重新读取该文件的内容,显示到控制台上。
• 键盘录入5个学生信息(姓名, 成绩),按照成绩从高到低追加存入上述的文本文件中。
首先进行准备工作,在Project目录下创建两个txt文件备用:

确保这两个文件是空的,然后编写代码。几个关键步骤说明:
- 为了让代码更加规范,建议将文件名定义成只读常量,以static final修饰。
- 定义writeToFile()和readFromFile()方法,分别用于向指定的txt文件中写入键盘输入的内容以及重新读取文件内容并显示到控制台上(题目的第一个要求)。代码如下:
// 向指定的txt文件中写入键盘输入的内容private static void writeToFile() {try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(FILE_PATH1))) {BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String line;System.out.println("请输入要写入文件的内容(输入exit结束):");while (!(line = reader.readLine()).equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {writer.write(line);writer.newLine();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 重新读取文件内容并显示到控制台上private static void readFromFile() {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(FILE_PATH1))) {System.out.println("\n从文件中读取的内容:");String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(line);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}} -
题干第二个要求:如何实现成绩排序?推荐使用自定义的Comparator比较器。首先定义List<String>用于接收读取出来的结果,然后调用List对象的sort()进行排序,这里要传入的就是比较器。比较器中可以定义比较规则。
lines.sort(new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {int score1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.split(" ")[1]);int score2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.split(" ")[1]);return Integer.compare(score2, score1);}});注意,由于我们要比较的学生的成绩,也即我们输入内容的第2列,因此比较器或者说比较规则是一定要设置的,否则sort()方法并不知道我们要依据哪个内容来进行排序。关于比较器的内容这里不作补充,有需要的同学可以自行搜索Java的Comparator类进行了解。
源代码:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;public class S7_4 {private static final String FILE_PATH1 = "test.txt";private static final String FILE_PATH2 = "students.txt";public static void main(String[] args) {// 向指定的txt文件中写入键盘输入的内容writeToFile();// 重新读取文件内容并显示到控制台上readFromFile();// 键盘录入5个学生信息,并按成绩从高到低追加存入文件appendStudentInfoToFile();}// 向指定的txt文件中写入键盘输入的内容private static void writeToFile() {try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(FILE_PATH1))) {BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String line;System.out.println("请输入要写入文件的内容(输入exit结束):");while (!(line = reader.readLine()).equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {writer.write(line);writer.newLine();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 重新读取文件内容并显示到控制台上private static void readFromFile() {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(FILE_PATH1))) {System.out.println("\n从文件中读取的内容:");String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(line);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 键盘录入5个学生信息,并按成绩从高到低追加存入文件private static void appendStudentInfoToFile() {try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(FILE_PATH2, true))) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("\n请输入学生信息(姓名 成绩):");String name = scanner.next();int score = scanner.nextInt();writer.write(name + " " + score);writer.newLine();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 按成绩从高到低排序学生信息sortStudentInfoByScore();}// 按成绩从高到低排序学生信息private static void sortStudentInfoByScore() {List<String> lines = new ArrayList<>();try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(FILE_PATH2))) {String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {lines.add(line);}// 使用自定义的比较器按成绩从高到低排序lines.sort(new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {int score1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.split(" ")[1]);int score2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.split(" ")[1]);return Integer.compare(score2, score1);}});} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 将排序后的学生信息重新写入文件try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(FILE_PATH2))) {for (String line : lines) {writer.write(line);writer.newLine();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
注意每次运行前,最好都确认一下两个提前准备好的文件是空的,或者没有格式非法的数据。
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
控制台

文件

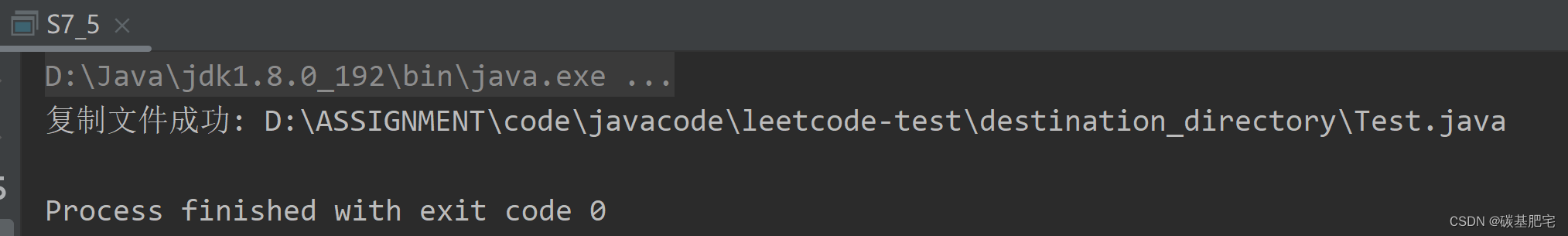
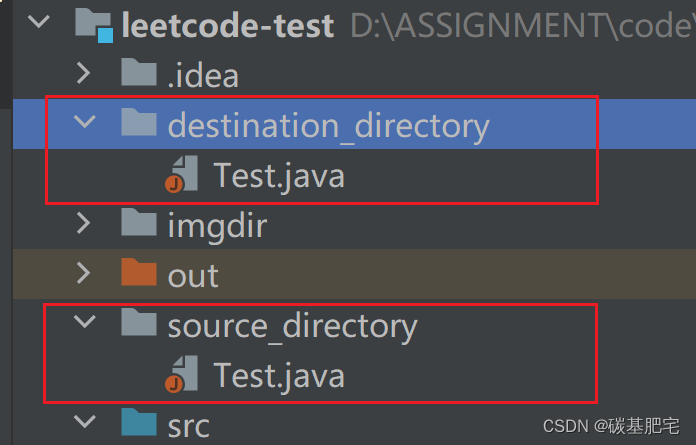
5、复制指定目录中的指定类型(如.java)的文件到另一个目录中。
提前在Project目录下准备好要复制的文件:

源代码:
import java.io.*;public class S7_5 {public static void main(String[] args) {String sourceDirectory = "source_directory"; // 源目录路径String destinationDirectory = "destination_directory"; // 目标目录路径String fileExtension = ".java"; // 要复制的文件类型copyFilesByExtension(sourceDirectory, destinationDirectory, fileExtension);}// 复制指定目录中指定类型的文件到另一个目录中private static void copyFilesByExtension(String sourceDirectory, String destinationDirectory, String fileExtension) {File sourceDir = new File(sourceDirectory);File destDir = new File(destinationDirectory);// 确保目标目录存在if (!destDir.exists()) {destDir.mkdirs();}// 检查源目录是否存在if (sourceDir.exists() && sourceDir.isDirectory()) {File[] files = sourceDir.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {@Overridepublic boolean accept(File dir, String name) {return name.endsWith(fileExtension);}});if (files != null) {for (File file : files) {File destFile = new File(destDir, file.getName());try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destFile)) {byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];int length;while ((length = in.read(buffer)) > 0) {out.write(buffer, 0, length);}System.out.println("复制文件成功: " + destFile.getAbsolutePath());} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("复制文件失败: " + file.getAbsolutePath());e.printStackTrace();}}} else {System.out.println("源目录中没有指定类型的文件");}} else {System.out.println("源目录不存在或不是目录");}}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
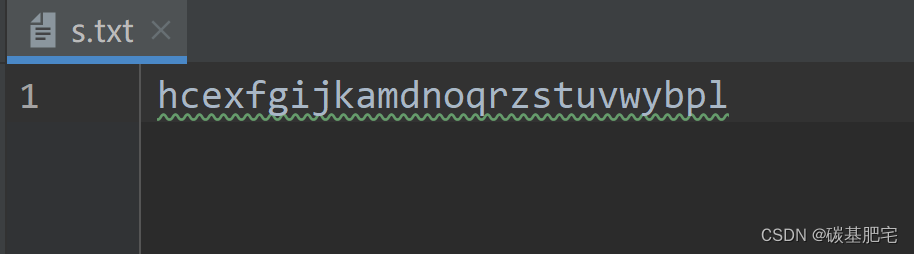
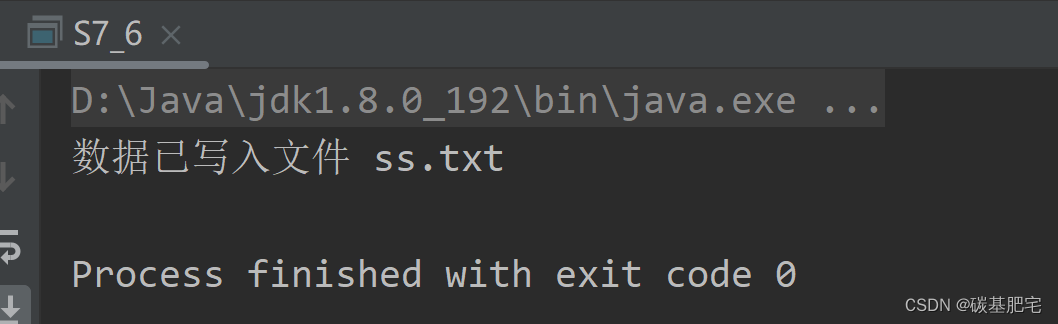
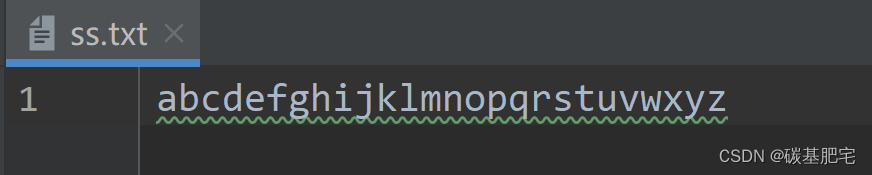
6、已知s.txt文件中有这样的一个字符串:“hcexfgijkamdnoqrzstuvwybpl”,请编写程序读取数据内容,把数据排序后写入ss.txt中。
s.txt内容:
源代码:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;public class S7_6 {public static void main(String[] args) {String sourceFileName = "s.txt"; // 源文件名String destinationFileName = "ss.txt"; // 目标文件名// 读取数据内容String data = readDataFromFile(sourceFileName);if (data != null && !data.isEmpty()) {// 排序数据内容String sortedData = sortString(data);// 写入到目标文件中writeDataToFile(destinationFileName, sortedData);} else {System.out.println("源文件中没有数据或文件不存在");}}// 读取数据内容private static String readDataFromFile(String fileName) {StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName))) {String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {content.append(line);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return content.toString();}// 对字符串进行排序private static String sortString(String input) {char[] chars = input.toCharArray();Arrays.sort(chars);return new String(chars);}// 将数据写入文件中private static void writeDataToFile(String fileName, String data) {try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fileName))) {writer.write(data);System.out.println("数据已写入文件 " + fileName);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
三、实验总结
本次实验中我编写了Java程序实现IO控制,如利用File类和FileInputStream/FileOutputStream类实现了复制指定目录中指定类型的文件到另一个目录中的功能;使用BufferedReader/BufferedWriter类和OutputStreamWriter/InputStreamReader类完成从指定文件中读取数据内容,对其进行排序后写入到另一个文件中的任务的功能等。以下是我的总结:
1. 我学会了如何使用Java中的File类来进行文件和目录的操作,包括创建文件、删除文件、获取文件信息等。
2. 我掌握了如何使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream类来进行文件的读取和写入操作,实现了文件的复制功能。
3. 我理解了BufferedReader和BufferedWriter类的作用,学会了如何利用它们来提高文件读写的效率。
4. 我了解了OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader的使用方法,学会了如何使用转换流来进行字符流和字节流之间的转换操作。
5. 初次接触OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader时,我对字符流和字节流之间的转换操作不太理解,特别是如何正确地使用转换流进行转换的过程。在实验中我也遇到了一些异常处理方面的问题,如捕获并处理文件操作出现的IOException。
6. 我通过阅读官方文档和查阅相关资料加深了对OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader的理解,解决了以上遇到的困难,同时结合实际代码练习,逐步掌握了它们的正确使用方法。




软件介绍)
)

,利弊分析)



】第二层: 中心缓存的具体实现(上))



)

)

