组函数
-
以组为操作单位,一组数据得到一个结果。
-
在没有手动分组的前提下,整张表默认为一组数据
-
max(列名):获取最大值
-
min(列名):获取最小值
-
sum(列名):获取总和
-
avg(列名):获取平均值
-
count(列名):统计值的个数
-
所有组函数都会自动忽略null值
-- 查看员工的最高薪资
select max(salary) from employees
-- 查看员工的最低薪资、平均薪资、月薪资总和
select min(salary),avg(salary),sum(salary) from employees
-- 统计总共有多少名员工
select count(*) from employees
select count(employee_id) from employees
-- 统计员工表中部门的个数
-- 先对整张表的部门id进行去重,再count统计结果
select count(distinct department_id) from employees分组
-
在某些情况下,我们需要根据需要对表中数据进行手动分组
-
规则:值相同的为同一组数据
select 列名 from 表名 group by 列名
执行顺序:from-->group by-->select
先确定从哪张表进行操作-->对表中数据进行分组-->基于分组结果进行查询操作
-- 查询各个部门的平均薪资 select department_id,avg(salary) from employees group by department_id
where+group by
-
先where,再group by
先筛选出符合要求的数据,再对符合要求的数据进行分组时,分组的工作量会被减少,效率更高
where 条件 group by 列名
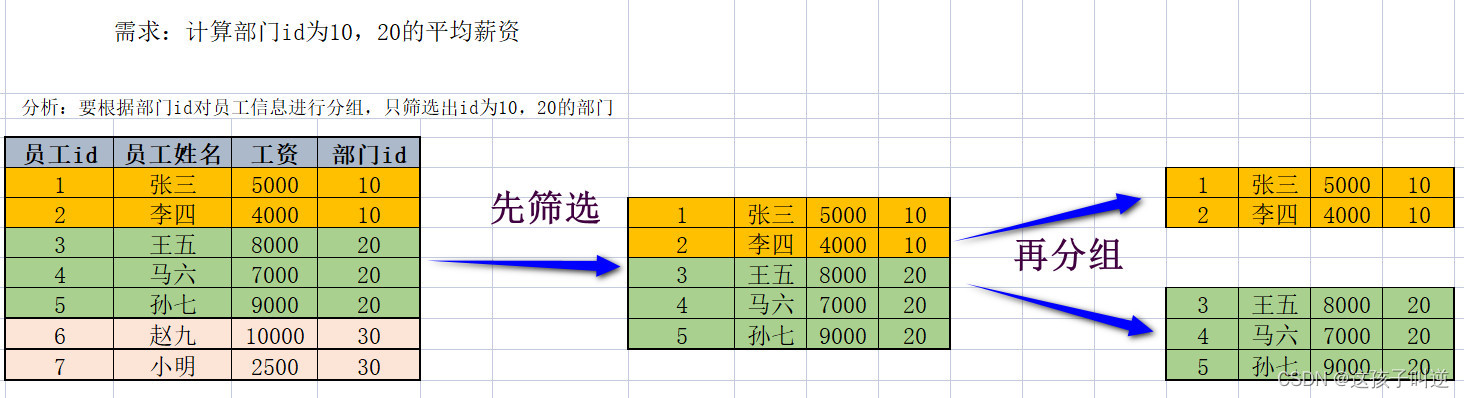
-- 查询部门id为10,20,30的部门的平均薪资
select department_id,avg(salary)
from employees
where department_id in(10,20,30)
group by department_id-
执行顺序:from-->where-->group by-->select
having子句
-
和where类似,也是用来做数据筛选,在分组之后执行
group by 列名 having 条件
-- 查询部门平均薪资>=7000的部门id
select department_id,avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id -- 先分组
having avg(salary)>=7000 -- 后筛选
和where子句的区别
-
where在分组前执行,having在分组后执行
-
where子句存在分组时不能使用组函数,但是having可以
-
当既可以使用where,又能使用having时,优先使用where,效率更高
limit关键字
-
作用:限制查询结果显示的条目数,通常用于分页
select 列名.. from 表名 limit 显示的起始下标,显示的条数
-
使用:
-
该关键字是基于查询的最终结果进行限制显示,所以其与其他查询关键字使用时,必须最后执行,所以一定写在最后
-
下标为0时,可以省略不写
-
-- 查询工资最高的前十名员工信息
select employee_id,salary
from employees
order by salary desc -- 先根据工资进行降序排序
limit 0,10 -- 显示前十行
-- 查看前十条员工信息
select * from employees limit 10
-- 查询部门平均薪资最高的前3个部门id
-- 分析:-- 部门平均薪资:根据部门id分组 group by -- 最高:根据平均薪资进行降序排序 order by avg(salary)-- 前三个:limit从最终查询结果中提取出前三条
select department_id,avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id -- 根据部门id分组
order by avg(salary) desc -- 根据平均薪资进行降序排序
limit 3 -- 从最终查询结果中提取出前三条查询关键字的顺序
-
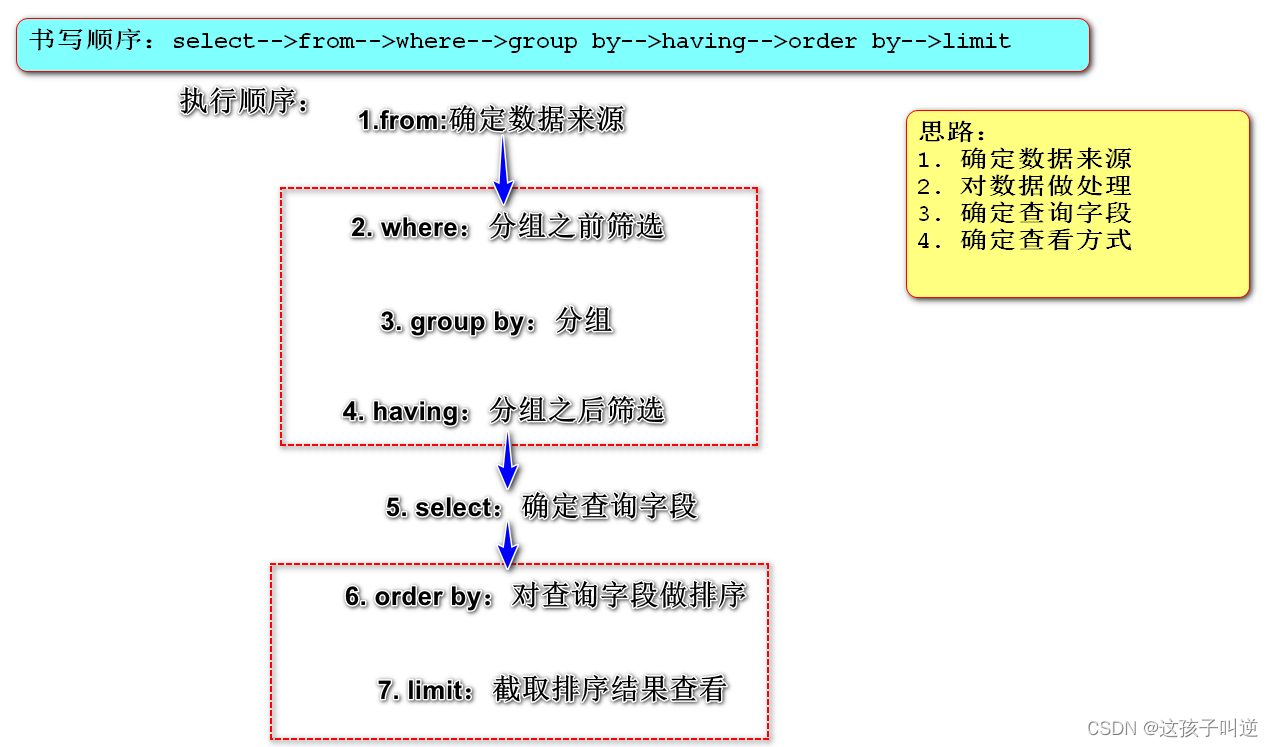
select 、 from 、where 、 order by 、 group by 、 having 、 limit
语法顺序: select 、 from 、where、 group by、having 、order by 、limit
子查询
-
当一个SQL的执行需要借助另一个SQL的执行结果时,则需要进行SQL嵌套,该语法结构称之为子查询
select 列名... from 表名 where 列名 =|in (子SQL语句)
-
执行顺序:优先执行小括号内的子SQL,根据子SQL的执行结果再执行外层SQL
-
只要逻辑完整,对SQL的嵌套层数不做要求
-
执行:从内向外执行
-
where单值子查询
-
子SQL(被嵌套的SQL)返回的时一行一列的单个结果
-- 查询员工id为101号员工的领导信息
-- 先查询员工id为101号员工的直接领导的id
select manager_id from employees where employee_id=101
-- 拼装
select * from employees
where employee_id=(select manager_id from employees where employee_id=101
)
-- 查询员工id为100的员工所在的部门信息
-- 查询员工id为100的员工所在的部门id
select department_id from employees where employee_id=100
-- 拼装
select * from departments
where department_id =(select department_id from employees where employee_id=100)where多值子查询
-
子SQL返回的是多个结果
-- 查询工资>10000的员工所在的部门信息 select * from departments where department_id in(select department_id from employees where salary>10000)
from子查询(了解)
-
将子SQL的查询结果临时看作一张表进行后续操作
-
为了符合语法要求,需要给子查询的结果起别名充当临时表的表名
-- 查询工资最高的前十名员工的总薪资
-- 分析:1. 把工资最高的前十名员工的薪资查出来-- 2. 对这十个工资进行求和
-- 查询SQL的基本语法:select 列名 from 表名
select sum(salary)
from (select salary from employees order by salary desc limit 10) as e
-- 子SQL:把工资最高的前十名员工的薪资查出来
select salary from employees order by salary desc limit 10


)
)


)

)









