一 std::function 与 std::bind 的介绍
1. std::function
std::function 是 c++ 11 的新特性 ,包含在头文件<functional>中,为了更方便的调用函数而引入。
std::function 是一个函数包装器(function wrapper),可以包装任何可调用实体,包括如下几种:
普通函数、函数指针、成员函数、静态函数、lambda 表达式 与 仿函数对象。
std::function 对象实例可以拷贝与移动,可以使用指定的调用特征来调用目标元素。当 std::function 对象实例未包含任何实体时,调用该 std::function 对象实例时,会抛出std::bad_function_call异常。
2. std::bind
std::bind 是 c++ 11 的新特性,其作用与其字面名称相似,是为了绑定函数的某些参数。
std::bind 是一种延迟计算的思想,将可调用函数对象保存起来,在需要调用时再去调用。可以绑定
仿函数对象、普通函数与成员函数,其参数可以支持占位符。
占位符:
std::placeholders::_1 是一个占位符,绑定函数的第一个参数,std::placeholders::_2 是一个占位符,绑定函数的第二个参数,std::placeholders::_n 是一个占位符,绑定函数的第 n 个参数。
二 源码
2.1 std::function
template<typename _Signature>class function;/*** @brief Primary class template for std::function.* @ingroup functors** Polymorphic function wrapper.*/template<typename _Res, typename... _ArgTypes>class function<_Res(_ArgTypes...)>: public _Maybe_unary_or_binary_function<_Res, _ArgTypes...>,private _Function_base{template<typename _Func,typename _Res2 = typename result_of<_Func&(_ArgTypes...)>::type>struct _Callable : __check_func_return_type<_Res2, _Res> { };// Used so the return type convertibility checks aren't done when// performing overload resolution for copy construction/assignment.template<typename _Tp>struct _Callable<function, _Tp> : false_type { };template<typename _Cond, typename _Tp>using _Requires = typename enable_if<_Cond::value, _Tp>::type;public:typedef _Res result_type;// [3.7.2.1] construct/copy/destroy/*** @brief Default construct creates an empty function call wrapper.* @post @c !(bool)*this*/function() noexcept: _Function_base() { }/*** @brief Creates an empty function call wrapper.* @post @c !(bool)*this*/function(nullptr_t) noexcept: _Function_base() { }/*** @brief %Function copy constructor.* @param __x A %function object with identical call signature.* @post @c bool(*this) == bool(__x)** The newly-created %function contains a copy of the target of @a* __x (if it has one).*/function(const function& __x);/*** @brief %Function move constructor.* @param __x A %function object rvalue with identical call signature.** The newly-created %function contains the target of @a __x* (if it has one).*/function(function&& __x) noexcept : _Function_base(){__x.swap(*this);}/*** @brief Builds a %function that targets a copy of the incoming* function object.* @param __f A %function object that is callable with parameters of* type @c T1, @c T2, ..., @c TN and returns a value convertible* to @c Res.** The newly-created %function object will target a copy of* @a __f. If @a __f is @c reference_wrapper<F>, then this function* object will contain a reference to the function object @c* __f.get(). If @a __f is a NULL function pointer or NULL* pointer-to-member, the newly-created object will be empty.** If @a __f is a non-NULL function pointer or an object of type @c* reference_wrapper<F>, this function will not throw.*/template<typename _Functor,typename = _Requires<__not_<is_same<_Functor, function>>, void>,typename = _Requires<_Callable<_Functor>, void>>function(_Functor);/*** @brief %Function assignment operator.* @param __x A %function with identical call signature.* @post @c (bool)*this == (bool)x* @returns @c *this** The target of @a __x is copied to @c *this. If @a __x has no* target, then @c *this will be empty.** If @a __x targets a function pointer or a reference to a function* object, then this operation will not throw an %exception.*/function&operator=(const function& __x){function(__x).swap(*this);return *this;}/*** @brief %Function move-assignment operator.* @param __x A %function rvalue with identical call signature.* @returns @c *this** The target of @a __x is moved to @c *this. If @a __x has no* target, then @c *this will be empty.** If @a __x targets a function pointer or a reference to a function* object, then this operation will not throw an %exception.*/function&operator=(function&& __x) noexcept{function(std::move(__x)).swap(*this);return *this;}template<typename _Functor>_Requires<_Callable<typename decay<_Functor>::type>, function&>operator=(_Functor&& __f){function(std::forward<_Functor>(__f)).swap(*this);return *this;}/// @overloadtemplate<typename _Functor>function&operator=(reference_wrapper<_Functor> __f) noexcept{function(__f).swap(*this);return *this;}/*** @brief Invokes the function targeted by @c *this.* @returns the result of the target.* @throws bad_function_call when @c !(bool)*this** The function call operator invokes the target function object* stored by @c this.*/_Res operator()(_ArgTypes... __args) const;};2.2 std::bind
// Trait type used to remove std::bind() from overload set via SFINAE// when first argument has integer type, so that std::bind() will// not be a better match than ::bind() from the BSD Sockets API.template<typename _Tp, typename _Tp2 = typename decay<_Tp>::type>using __is_socketlike = __or_<is_integral<_Tp2>, is_enum<_Tp2>>;template<bool _SocketLike, typename _Func, typename... _BoundArgs>struct _Bind_helper: _Bind_check_arity<typename decay<_Func>::type, _BoundArgs...>{typedef typename decay<_Func>::type __func_type;typedef _Bind<__func_type(typename decay<_BoundArgs>::type...)> type;};// Partial specialization for is_socketlike == true, does not define// nested type so std::bind() will not participate in overload resolution// when the first argument might be a socket file descriptor.template<typename _Func, typename... _BoundArgs>struct _Bind_helper<true, _Func, _BoundArgs...>{ };/*** @brief Function template for std::bind.* @ingroup binders*/template<typename _Func, typename... _BoundArgs>inline typename_Bind_helper<__is_socketlike<_Func>::value, _Func, _BoundArgs...>::typebind(_Func&& __f, _BoundArgs&&... __args){typedef _Bind_helper<false, _Func, _BoundArgs...> __helper_type;return typename __helper_type::type(std::forward<_Func>(__f),std::forward<_BoundArgs>(__args)...);}template<typename _Result, typename _Func, typename... _BoundArgs>struct _Bindres_helper: _Bind_check_arity<typename decay<_Func>::type, _BoundArgs...>{typedef typename decay<_Func>::type __functor_type;typedef _Bind_result<_Result,__functor_type(typename decay<_BoundArgs>::type...)>type;};/*** @brief Function template for std::bind<R>.* @ingroup binders*/template<typename _Result, typename _Func, typename... _BoundArgs>inlinetypename _Bindres_helper<_Result, _Func, _BoundArgs...>::typebind(_Func&& __f, _BoundArgs&&... __args){typedef _Bindres_helper<_Result, _Func, _BoundArgs...> __helper_type;return typename __helper_type::type(std::forward<_Func>(__f),std::forward<_BoundArgs>(__args)...);}三 使用例子
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>int (*func_ptr)(int);int func(int a)
{std::cout << "func: " << a << endl;return a;
}void f(int n1, int n2, int n3, const int& n4, int n5) {std::cout << n1 << ' ' << n2 << ' ' << n3 << ' ' << n4 << ' ' << n5 << std::endl;
}template<typename T>
T fun2(T a){return a + 2;
}struct my_add{int operator()(int x){return x + 9;}
};struct Foo
{static void func11(){std::cout << "static void func1......" << std::endl;}static void func12(int val){std::cout << "static void func1( val "<< val << "......" << std::endl;}void func2(int val){std::cout << "void func2(val "<< val << ")......" << std::endl;}};int main()
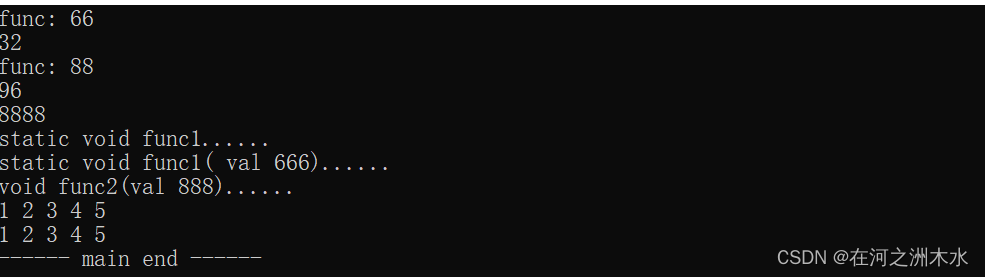
{// 1. 包装函数std::function<int(int)> f1 = func;f1(66);std::cout << sizeof (f1) << std::endl;// 2. 包装函数指针func_ptr = func;func_ptr(88);// 3. 包装模板函数f1 = fun2<int>;f1(688);// 4. 包装仿函数f1 = my_add();std::cout << f1(87) << std::endl;// 5. 包装lambda 函数auto tmp_func = [](int a)->int{return a;};f1 = tmp_func;std::cout << f1(8888) << std::endl;// 6 包装静态函数std::function<void(void)> f61 = Foo::func11;f61();std::function<void(int)> f62 = Foo::func12;f62(666);// 7 包装类成员函数Foo foo;std::function<void(int)> f7 = std::bind(&Foo::func2, foo, std::placeholders::_1);f7(888);// bindauto f2 = std::bind(f, std::placeholders::_3, std::placeholders::_2, std::placeholders::_1, 4, 5);f2(3, 2, 1);std::function<void(int, int, int)> ff = f2;ff(3, 2, 1);std::cout << "------ main end ------" << std::endl;return 0;
}
输出:



 MySQL数据库分库分表方案)


)










)

