origin/<branch>
远程分支在本地以 origin/<branch>格式存在,他指向上次和远程分支通过时的记录
git checkout origin/<branch> 会出现HEAD分离的情况
与远程通讯
git fetch —— 从远端获取数据(实际上将本地仓库中的远程分支更新成了远程仓库相应分支最新的状态)
- 从远程仓库下载本地仓库中缺失的提交记录
- 更新远程分支指针(如 o/main)
使用 http:// 或 git:// 协议从远端获取数据
注意:git fetch 不会修改你本地的分支
牢记下面两个公式,以后经常会使用到
git pull = git fetch + git merge o/<branch>
git pull --rebase = git fetch + git rebase o/<branch>
提交的技巧:
git checkout branchName commitID 将branchName指向指定的提交记录
跟踪远程分支
git checkout -b totallyNotMain o/main 通过远程分支切换到一个新的分支
翻译: 新创建一个分支为totallyNotMain分支并设置它的remote tracking为: o/main
意味着为 totallyNotMain分支指定了推送的目的地以及拉取后合并的目标为o/main
上面的是设置远程追踪分支的其中一只方法,接下来介绍另外一种方法:
git branch -u o/main foo
如果当前就在 foo 分支上, 还可以省略 foo:
git branch -u o/main
详细介绍几个操作远程分支的命令的参数
git push
git push不加参数时:根据上面我们说的追踪分支来确定远程的目的地git push <remote> <place><place>同时指定了提交记录的来源和去向git push origin <source>:<destination><source>:<destination>分别指定了提交记录的来源和去向(<source>可以是commitID)
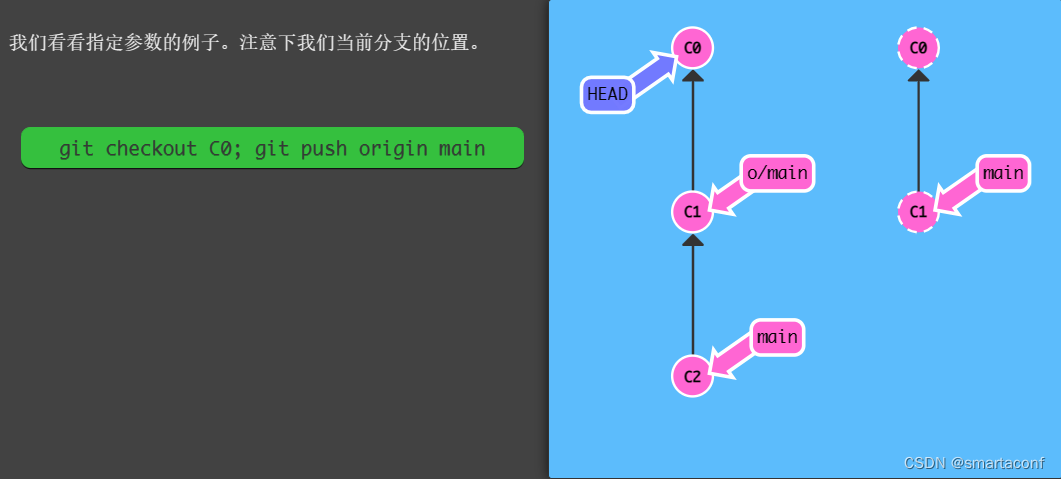
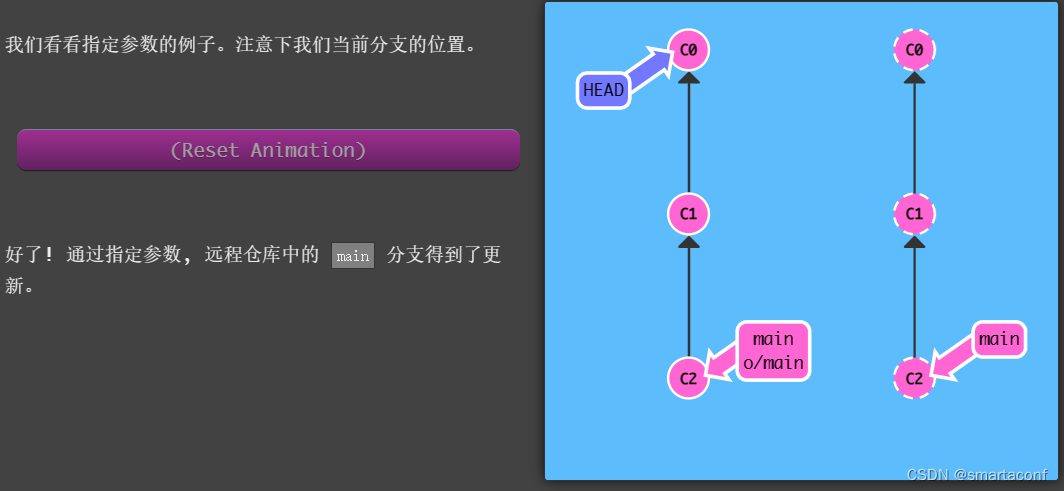
举例:git push origin main
翻译: 本地仓库中的“main”分支,获取所有的提交,再到远程仓库“origin”中找到“main”分支,将远程仓库中没有的提交记录都添加上去,搞定之后告诉我。
注意:我们执行push命令的过程中,当前分支(HEAD)不会移动。
git fetch
– 类似于git push的参数,但操作的对象和push刚好相反
git fetch没有参数,它会下载所有的提交记录到各个远程分支git fetch <origin> <place>:到远程仓库的 <place>分支上,然后获取所有本地不存在的提交,放到本地的 o/<place> 上 (注意可不是本地的<place>上)git fetch <origin> <source>:<destination>source 指的是远程仓库中的位置,而 才是要放置提交的本地仓库的位置(<destination> 不能是当前切换的分支,但是其它分支是可以的)
神奇的<source>
git push origin :<destination> 删除远端的分支<destination>
git fetch origin :<destination> 基于当前的分支创建新的分支<destination>
git pull
git pull= git fetch +git merge o/<upstream>
git pull <remote> <place>= git fetch <remote> <place> + git merge o/<place>
git pull <remote> <source>:<destination> = git fetch <remote> <source>:<destination> + git merge <destination>












)



_糗事百科案例)


