关于man的使用
man 系统参考手册
man n name 在系统手册第n章查看name
1.
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>int main() {int x = 100;int rc = fork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {printf("child pid: x = %d\n", x);} else {wait(NULL);}return 0;
}
输出:

子进程会保持和父进程一样的值100,当子进程和父进程都改变x的值时,变量会各自单独保持一份互不影响,相互隔离。
2.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {int fd = open("./tmp.txt", O_CREAT | O_APPEND | O_RDWR, S_IRWXU);int rc = fork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {int i;for (i = 0; i < atoi(argv[1]); i++) write(fd, "child\n", 6);} else {int i;for (i = 0; i < atoi(argv[1]); i++) write(fd, "parent\n", 7);wait(NULL);close(fd);}return 0;
}
结果如下:
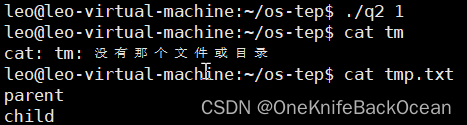
1次并没有发现并发问题,试过1000次也没什么问题
3.
可以使用vfork来做到等待子进程结束,具体可见系统手册:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>int main() {int rc = vfork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {printf("hello\n");} else {printf("goodbye\n");}return 0;
}
另一种实现方式:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int flag = 0;int main() {int rc = vfork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {printf("hello\n");flag = 1;exit(1);} else {while(flag == 0);printf("goodbye\n");wait(NULL);}return 0;
}
最终输出如下:
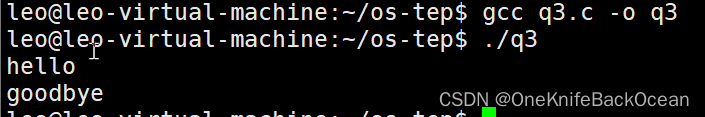
4.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main() {int i; for (i = 1; i <= 6; ++i) {int rc = fork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");exit(1);} else if (rc == 0) {char* path = "/bin/ls";char* pro = "ls";char* target = ".";char* ev[] = {pro, target, NULL};switch (i){case 1:execl(path, pro, target, NULL);break;case 2:execle(path, pro, target, NULL);break;case 3:execlp(pro, pro, target, NULL);break;case 4:execv(path, ev);break;case 5:execvp(pro, ev);break;case 6:execvpe(pro, ev);break;default:break;}} else {wait(NULL);}}return 0;
}
结果如下:
5.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main() {int rc = vfork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {wait(NULL);printf("child pid is %d\n", getpid());exit(1);} else {int result = wait(NULL);printf("the return value is %d\n", result);exit(1);}return 0;
}
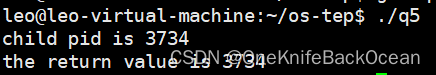
从上图中可见,wait返回的是子进程的进程号,而子进程中使用wait并不会发生什么,它会等待子进程自己的子进程结束。
6.
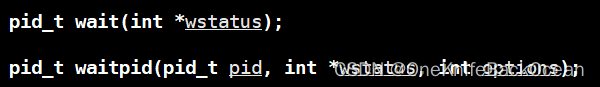
同样是返回pid,但是waitpid传入的参数不同,需要传入子进程的id、状态参数以及额外的选项。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
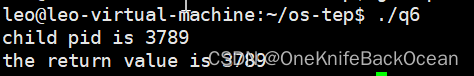
#include <stdlib.h>int main() {int rc = vfork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {printf("child pid is %d\n", getpid());exit(1);} else {int result = waitpid(rc, NULL, 0);printf("the return value is %d\n", result);exit(1);}return 0;
}
结果如下图所示:
7.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>int main() {int rc = fork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {close(STDOUT_FILENO);int res = printf("output something\n");fprintf(stderr, "%d\n", res);res = fflush(stdout);fprintf(stderr, "%d %s\n", res, strerror(errno));} else {wait(NULL);}return 0;
}
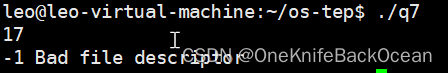
会把数据先写在缓存块内,具体可参考:在关闭stdout之后调用printf会发生什么?
8.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>int main() {int fds[2];pipe(fds);int rc = fork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {close(STDOUT_FILENO);close(fds[1]);dup(fds[0]);close(fds[0]);}rc = fork();if (rc == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");} else if (rc == 0) {close(STDIN_FILENO);close(fds[1]);dup(fds[1]);close(fds[1]);printf("hello\n");}close(fds[1]);close(fds[0]);wait(NULL);return 0;
}
结果如下图所示:








是什么?)




![【Dart】=> [06] Dart初体验-类Class-构造函数-继承-mixin-异步编程-链式调用-泛型-异常](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【Dart】=> [06] Dart初体验-类Class-构造函数-继承-mixin-异步编程-链式调用-泛型-异常)
斯坦福CS231n学习笔记:DL与CV教程 (1) | 引言与知识基础)





