ES中的查询操作分为两种:查询和过滤。查询即是之前提到的query查询,它默认会计算每个返回文档的得分,然后根据得分排序。而过滤只会筛选出符合条件的文档,并不计算得分,并且可以缓冲记录。所以我们在大范围筛选数据时,应先使用过滤操作过滤数据,然后使用查询匹配数据。

1.使用
1.1初始化创建商品索引
#创建商品索引
#id,title,price,created_at,description
PUT /products
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type":"integer"
},
"title":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"price":{
"type":"double"
},
"created_at":{
"type":"date"
},
"description":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word" #使用ik分词器
}
}
}
}
1.2插入数据
POST /products/_doc/1
{
"id":1,
"title":"库迪咖啡",
"price":"10.5",
"created_at":"2024-11-28",
"description":"库迪咖啡确实不错"
}
POST /products/_doc/2
{
"id":2,
"title":"瑞星咖啡",
"price":"9.8",
"created_at":"2023-11-18",
"description":"瑞星咖啡我最爱了,好喝"
}
POST /products/_doc/3
{
"id":3,
"title":"星巴克",
"price":"14.5",
"created_at":"2024-11-18",
"description":"太苦了,咖啡不好喝"
}
1.3过滤类型——term
GET products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "咖啡"
}
}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"term": {
"description": "瑞星"
}
}
]
}
}
}

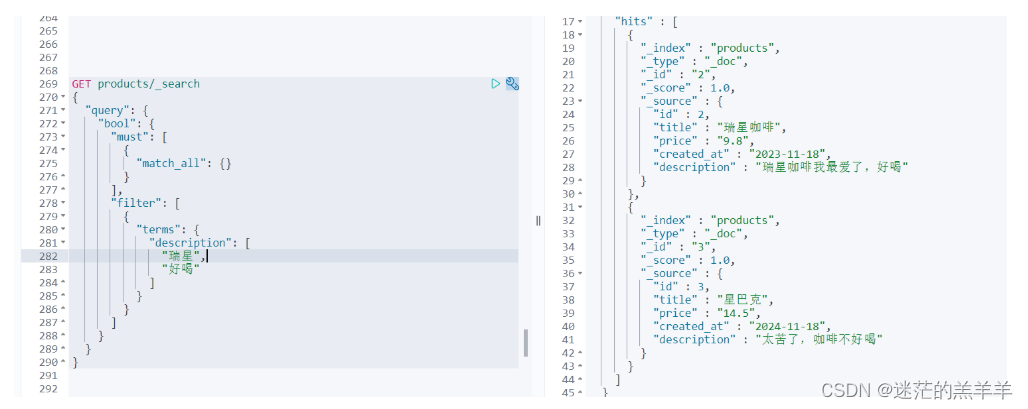
1.4过滤类型——terms
GET products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_all": {}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"terms": {
"description": [
"瑞星",
"好喝"
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
1.5过滤类型——range
GET products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_all": {}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 20
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
1.6过滤类型——exists
GET products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_all": {}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"exists": {
"field": "title" #过滤出带某个字段的数据,比如先拿到有title字段的数据
}
}
]
}
}
}
1.7过滤类型——ids
GET products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"description": {
"value": "好喝"
}
}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"ids": { #根据数据id过滤出在ids里面的数据
"values": [
"1",
"2"
]
}
}
]
}
}
}



——AllSafe App wp)









而想到的(下))





三)