一、 Retrofit是什么
Retrofit是Android用来接口请求的网络框架,内部是基于OkHttp实现的,retrofit负责接口请求的封装,retrofit可以直接将接口数据解析为Bean类、List集合等,直接简化了中间繁琐的数据解析过程
二、 Retrofit的简单使用
- Retrofit在github的地址 :https://github.com/square/retrofit
- Retrofit官方使用介绍 :https://square.github.io/retrofit/
2.1 在项目中引入retrofit
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.9.0'implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.9.0'//解析json字符所用
2.2 清单文件AndroidManifest.xml中添加网络权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
Google在Android p为了安全起见,已经明确规定禁止http协议额,接口都是https请忽略,如果接口有http请在清单文件AndroidManifest.xml中application先添加networkSecurityConfig配置
<applicationandroid:name=".App"android:allowBackup="true"android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"android:label="@string/app_name"android:networkSecurityConfig="@xml/network_security_config"android:requestLegacyExternalStorage="true"android:supportsRtl="true"android:theme="@style/AppTheme"tools:ignore="UnusedAttribute">
res文件夹下新建xml文件夹,xml文件夹中新建network_security_config文件,文件内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<network-security-config><base-config cleartextTrafficPermitted="true" />
</network-security-config>
2.3 创建Retrofit
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl("https://api.github.com/").addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())//设置数据解析器.build();
2.4 创建RetrofitApi
//定义 网络API 地址
public interface RetrofitApi{@GET("users/{user}/repos")Call<List<User>> getData(@Path("user") String user);
}
2.5 请求接口
//获取API
GitHubService service = retrofit.create(RetrofitApi.class);Call<List<User>> call= service.getData("user");
2.6 发送请求数据
//异步call.enqueue(new Callback<List<User>>() {@Overridepublic void onResponse(Call<List<User>> call, Response<List<User>> response) {//处理请求数据}@Overridepublic void onFailure(Call<List<User>> call, Throwable throwable) {}});//同步try {Response<List<User>> execute = call.execute();execute.body().toString();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
三、Retrofit注解参数类型
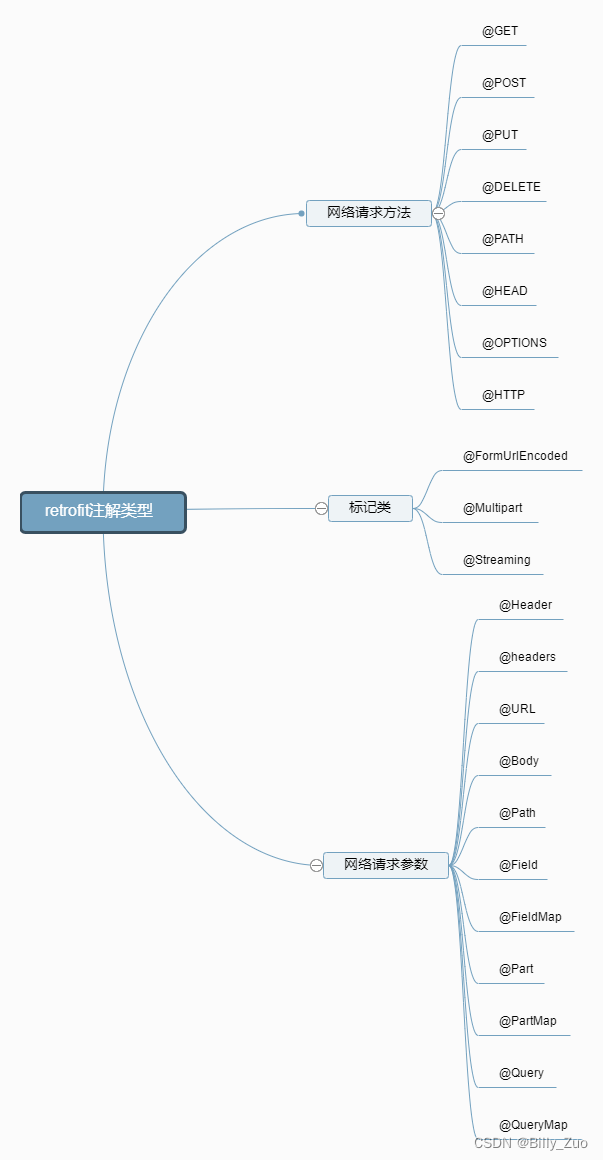
3.1 网络请求方法
3.1.1 GET请求
//简单的get请求(没有参数)@GET("user")Call<UserInfo> getItem();
//简单的get请求(URL中带有参数)@GET("News/{userId}")Call<TradesBean> getItem(@Path("userId") String userId);
//参数在url问号之后@GET("trades")Call<TradesBean> getItem(@Query("userId") String userId);
//get请求,多个请求参数@GET("trades")Call<TradesBean> getItem(@QueryMap Map<String, String> map);@GET("trades")Call<TradesBean> getItem(@Query("userId") String userId,@QueryMap Map<String, String> map);
//get请求,不使用baseUrl,直接请求url地址@GETCall<TradesBean> getItem(@Url String url,@QueryMap Map<String, Object> params);
3.1.2 POST请求
http://192.168.43.173/api/trades/{userId}
//需要补全URL,post的数据只有一条reason@FormUrlEncoded@POST("trades/{userId}")Call<TradesBean> postResult(@Path("userId") String userId,@Field("reason") String reason;
http://192.168.43.173/api/trades/{userId}?token={token}
//需要补全URL,问号后需要加token,post的数据只有一条reason@FormUrlEncoded@POST("trades/{userId}")Call<TradesBean> postResult(@Path("userId") String userId,@Query("token") String token,@Field("reason") String reason;//post一个对象@POST("trades/{userId}")Call<TradesBean> postResult(@Path("userId") String userId,@Query("token") String token,@Body TradesBean bean;
//post请求,不使用baseUrl,直接请求url地址@FormUrlEncoded@POSTCall<TradesBean> postResultl(@Url String url,@FieldMap Map<String, Object> params);
3.2 标记类
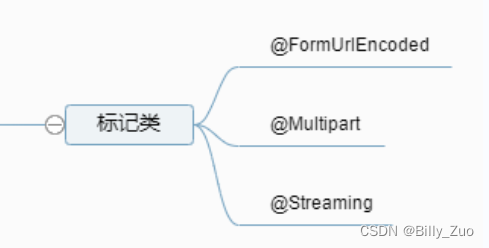
3.2.1 @FormUrlEncoded
- 作用:表示发送form-encoded的数据
- @FieldMap必须与 @FormUrlEncoded 一起配合使用
3.2.2 @Multipart
- 作用:表示发送form-encoded的数据(适用于 有文件 上传的场景)
- 每个键值对需要用@Part来注解键名,随后的对象需要提供值。
@Multipart@POSTCall<ResponseBody> uploadFiles(@Url String uploadUrl,@Part MultipartBody.Part file);
3.2.3 @Steaming
- 表示数据以流的形式返回
- 大文件官方建议用 @Streaming 来进行注解,不然会出现IO异常,小文件可以忽略不注入
/*** 大文件官方建议用 @Streaming 来进行注解,不然会出现IO异常,小文件可以忽略不注入** @param fileUrl 地址* @return ResponseBody*/@Streaming@GETCall<ResponseBody> downloadFile(@Url String fileUrl);
3.3 网络请求类

3.3.1 @Header & @Headers
- 添加请求头 &添加不固定的请求头
// @Header
@GET("user")
Call<User> getUser(@Header("Authorization") String authorization)// @Headers
@Headers("Authorization: authorization")
@GET("user")
Call<User> getUser()// 以上的效果是一致的。
// 区别在于使用场景和使用方式
// 1. 使用场景:@Header用于添加不固定的请求头,@Headers用于添加固定的请求头
// 2. 使用方式:@Header作用于方法的参数;@Headers作用于方法3.3.2 @Body
- 以 Post方式 传递 自定义数据类型 给服务器,@Body会将请求参数放到请求体中,所以适用于POST请求
- Body相当于多个@Field,以对象的方式提交,@Body 提交的提交的Content-Type 为application/json; charset=UTF-8
- @Body标签不能和@FormUrlEncoded或@Multipart标签同时使用,会报错
3.3.3 @Field & @FieldMap
- 发送 Post请求 时提交请求的表单字段
- @FieldMap必须与 @FormUrlEncoded 一起配合使用
- 提交的Content-Type 为application/x-www-form-urlencoded
3.3.4 @Part & @PartMap
- 发送 Post请求 时提交请求的表单字段
与@Field的区别:功能相同,但携带的参数类型更加丰富,包括数据流,所以适用于 有文件上传 的场景,与 @Multipart 注解配合使用
3.3.5 @Query和@QueryMap
- 用于 @GET 方法的查询参数(Query = Url 中 ‘?’ 后面的 key-value)
//参数在url问号之后@GET("trades")Call<TradesBean> getItem(@Query("userId") String userId);
3.3.6 @Path
- URL地址的缺省值
@GET("users/{user}/repos")Call<ResponseBody> getBlog(@Path("user") String user );// 访问的API是:https://api.github.com/users/{user}/repos// 在发起请求时, {user} 会被替换为方法的第一个参数 user(被@Path注解作用)
3.3.7 @Url
- 直接传入一个请求的 URL变量 用于URL设置
@GETCall<ResponseBody> testUrlAndQuery(@Url String url, @Query("showAll") boolean showAll);// 当有URL注解时,@GET传入的URL就可以省略// 当GET、POST...HTTP等方法中没有设置Url时,则必须使用 {@link Url}提供
下一篇文章总结一下Retrofit+Rxjava封装成网络请求库


)









)




)

