目录
- 一、回顾C语言文件操作
- 二、文件系统调用接口
- 1. open
- 2.write
- 3.read
- 三、文件描述符
- 四、重定向
- 1.输出重定向
- 2.输入重定向
- 五、dup2
一、回顾C语言文件操作
1 #include<stdio.h>2 #include<stdlib.h>3 4 #define LOG "log.txt"5 6 int main()7 {8 //w 默认写方式打开文件,如果文件不在,就创建它9 //默认如果是打开,内容会被自动清空10 //同时,每次进行写入的时候,都会从最开始写入11 FILE* fp=fopen(LOG,"w"); //"r"只读 ,"a"追加12 if(fp==NULL)13 {14 perror("fopen"); //判断是否创建成功15 return 1;16 }17 18 //文件打开成功,进行文件操作19 const char* msg="hello linux!";20 int cnt=5;21 while(cnt)22 {23 fprintf(fp,"%s: %d: tzc\n",msg,cnt); //打印到文件中 24 //fprintf(stdout,"%s: %d: tzc\n",msg,cnt); //stdout 打印到显示器文件中 25 //fputs(msg,fp);26 cnt--;27 }28 fclose(fp); //关闭文件29 30 return 0;31 }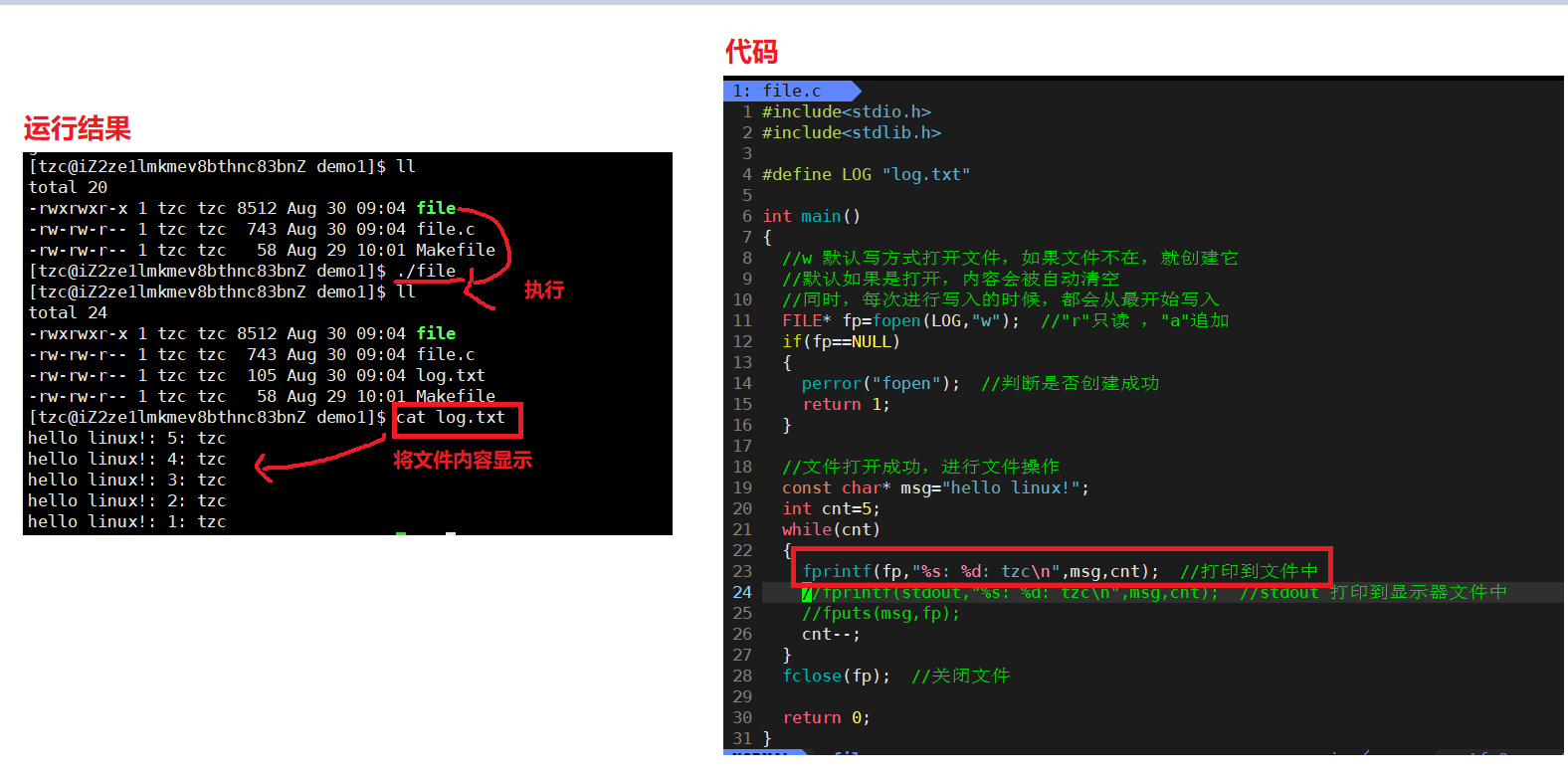
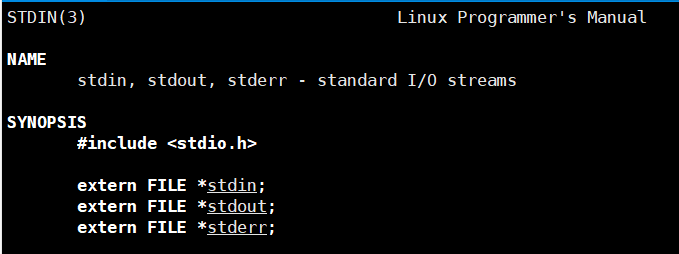
C语言有三个默认输入输出流,分别是 stdin,stdout,stderr.将他们分别称为:标准输入,标准输出,标准错误;他们分别对应 键盘、显示器、显示器。
代码
#include<stdio.h>int main()
{ const char* str = "hello wrold!\n";fputs(str,stdout); // 向标准输出中打印,即打印在显示器上fputs(str,stdout);fputs(str,stdout);
}
运行结果

二、文件系统调用接口
1. open
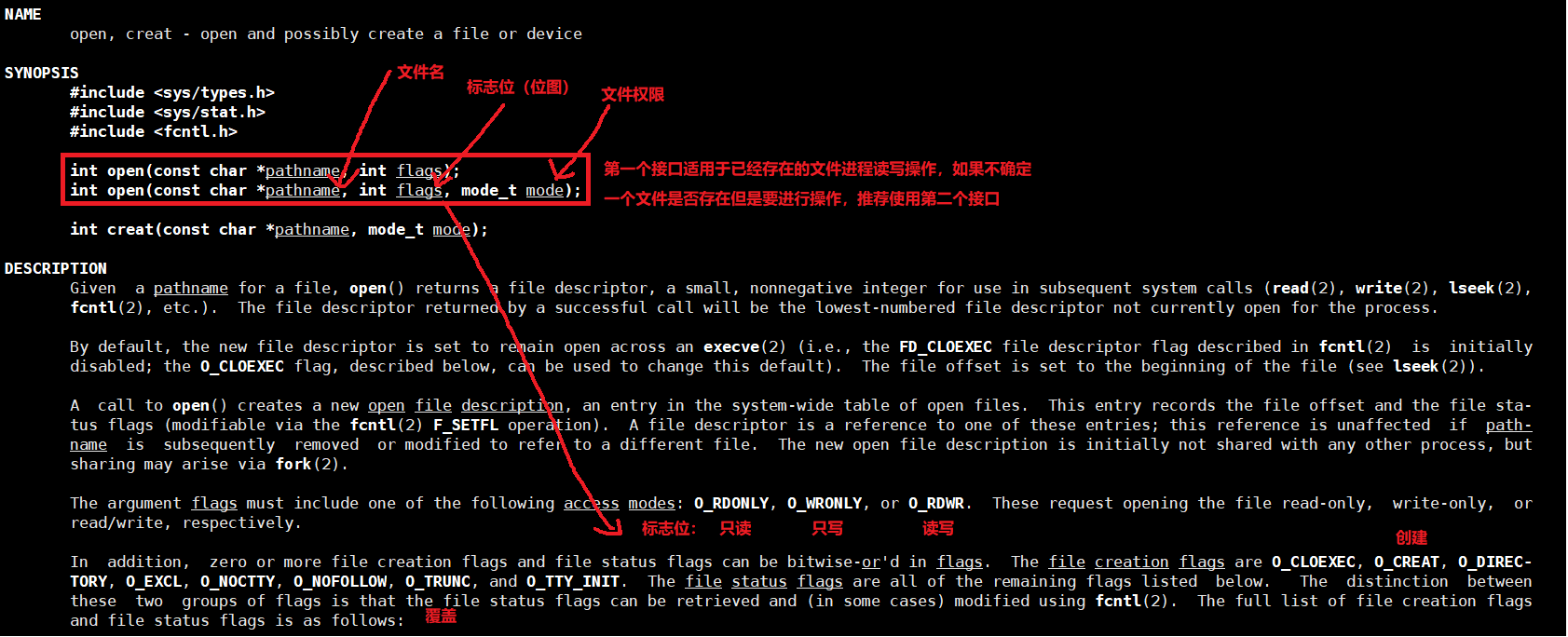
open打开文件后会返回一个文件描述符,用来后续进行文件操作
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<fcntl.h>int main()
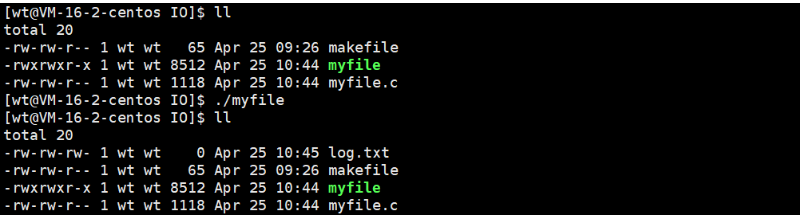
{umask(0); // 防止umask码&设置权限,影响期望权限int fd = open("./log.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0666); // 以只写方式打开,如果没有该文件就创建,权限为666if(fd<0) // 打开失败{perror("open");return 1;}close(fd);return 0;
}
2.write
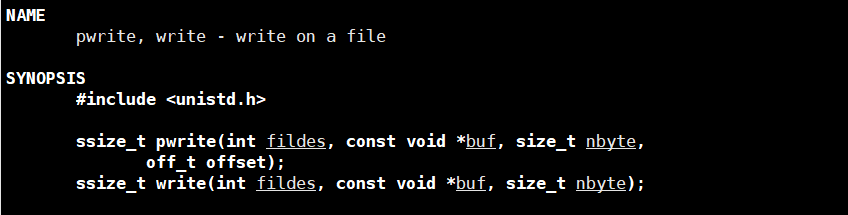
第一个参数是需要填写文件描述符,需要操作哪一个文件就将哪一个文件的文件描述符填到第一个参数,第二个参数是要写入的内容,第三个参数是写入的大小
返回值:返回值为实际写入文件数据大小。
1 #include<stdio.h>2 #include<unistd.h>3 #include<sys/stat.h>4 #include<sys/types.h>5 #include<fcntl.h>6 #include<string.h>7 8 int main()9 {10 int fd = open("./log.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0644);11 if(fd<0)12 {13 perror("open");14 return 1;15 }16 17 const char* msg = "hello linux!\n";18 int count = 5;19 while(count--)20 {21 char line[256]; //缓存数组22 snprintf(line,sizeof(line),"%s, %d\n",msg,count); //写入line 23 write(fd, msg,strlen(msg));// 写入时不需要写入'\0',字符串以'\0'结束只是C语言的规定,文件中字符串不需要'\0'24 }25 close(fd);26 return 0;27 }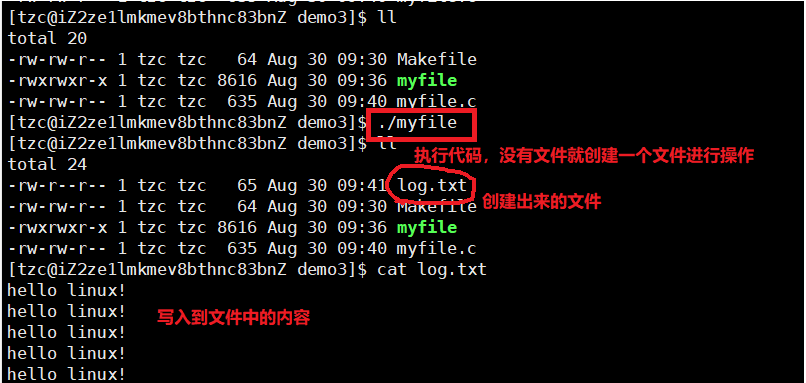
3.read
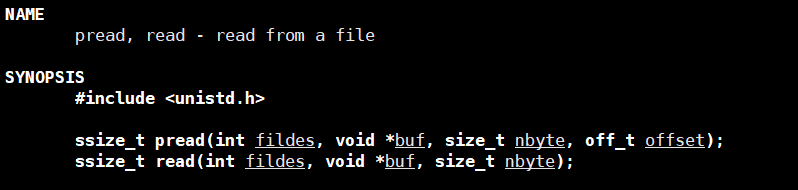
第一个参数是文件描述符,第二个参数是读取到哪个位置,第三个参数是读取多大
需要注意的是读取的时候直接全文进行读取,不会按行读取。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<unistd.h>3 #include<sys/stat.h>4 #include<sys/types.h>5 #include<fcntl.h>6 #include<string.h>7 8 9 int main()10 {11 int fd = open("./log.txt",O_RDONLY);12 if(fd<0)13 {14 perror("open");15 return 1;16 }17 18 char buf[1024];19 ssize_t s = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)-1);// 将文件内容读出,需将字符串末尾加'\0'20 if(s>0)21 {22 buf[s] = 0;23 printf("%s\n",buf); //将读取到的字符串打印出来24 }25 else26 {27 printf("read failed\n");28 }29 return 0;30 }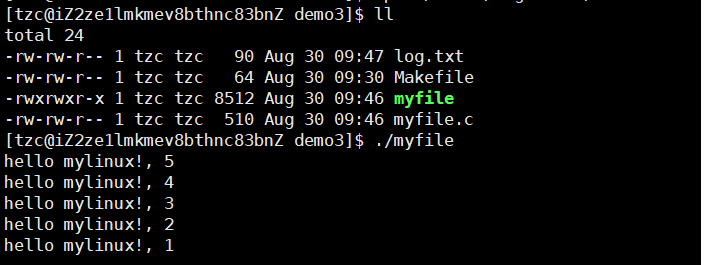
三、文件描述符
文件描述符就是调用系统接口open的返回值,打开成功返回该文件的文件描述符,打开失败返回-1。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<fcntl.h>int main()
{int fd1 = open("./log.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0644);int fd2 = open("./log.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0644);int fd3 = open("./log.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0644);int fd4 = open("./log.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0644);printf("fd1: %d\n",fd1);printf("fd2: %d\n",fd2);printf("fd3: %d\n",fd3);printf("fd4: %d\n",fd4);return 0;
}
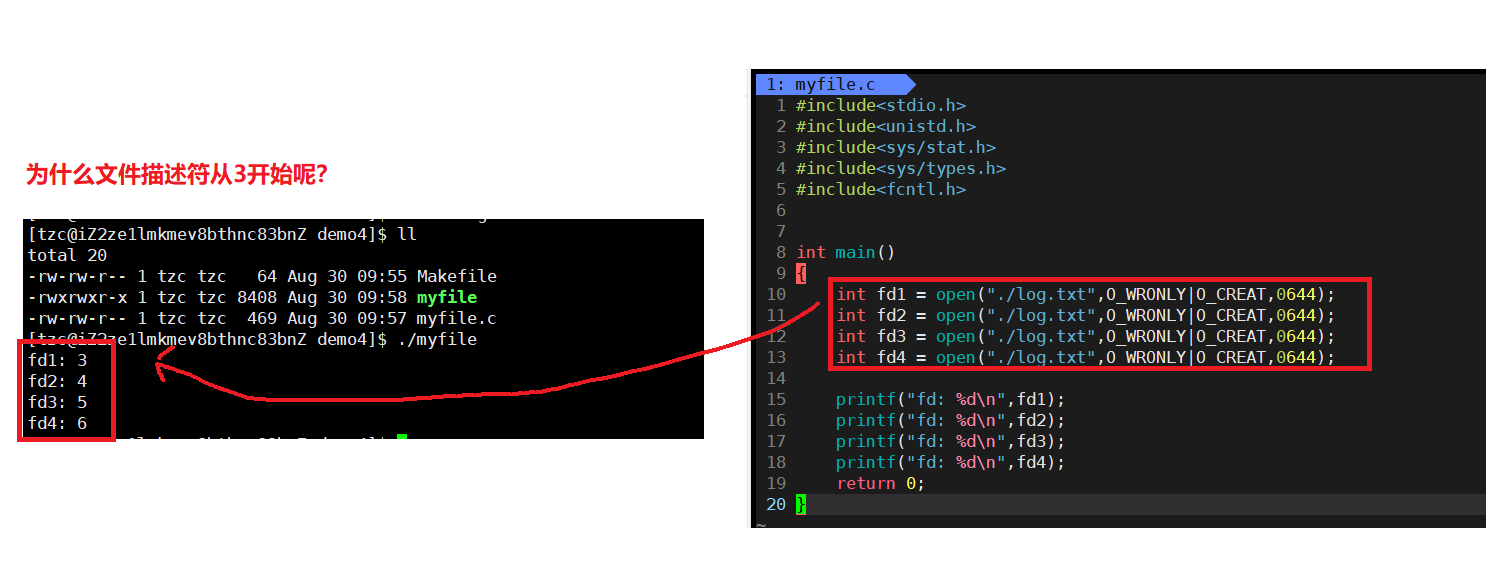
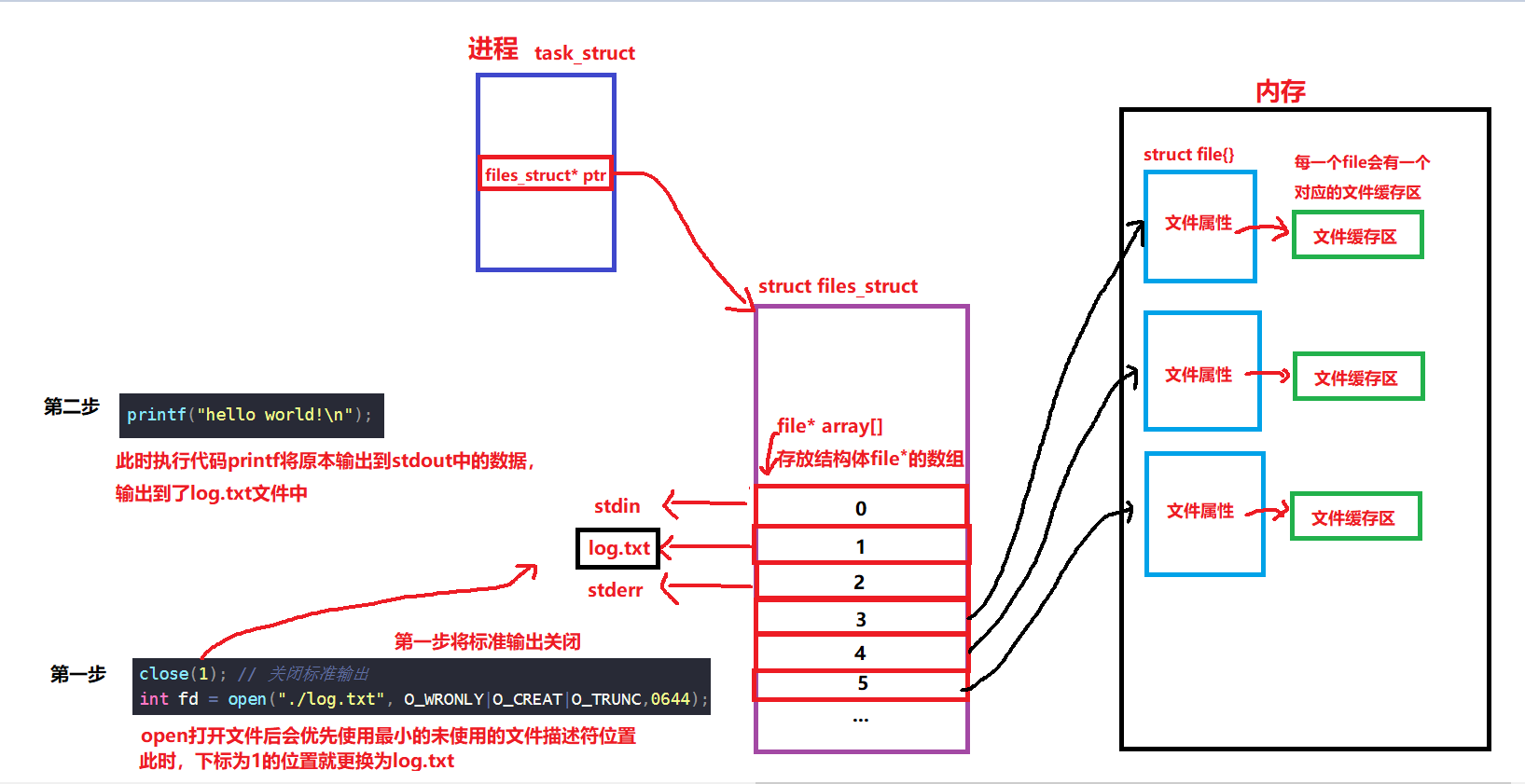
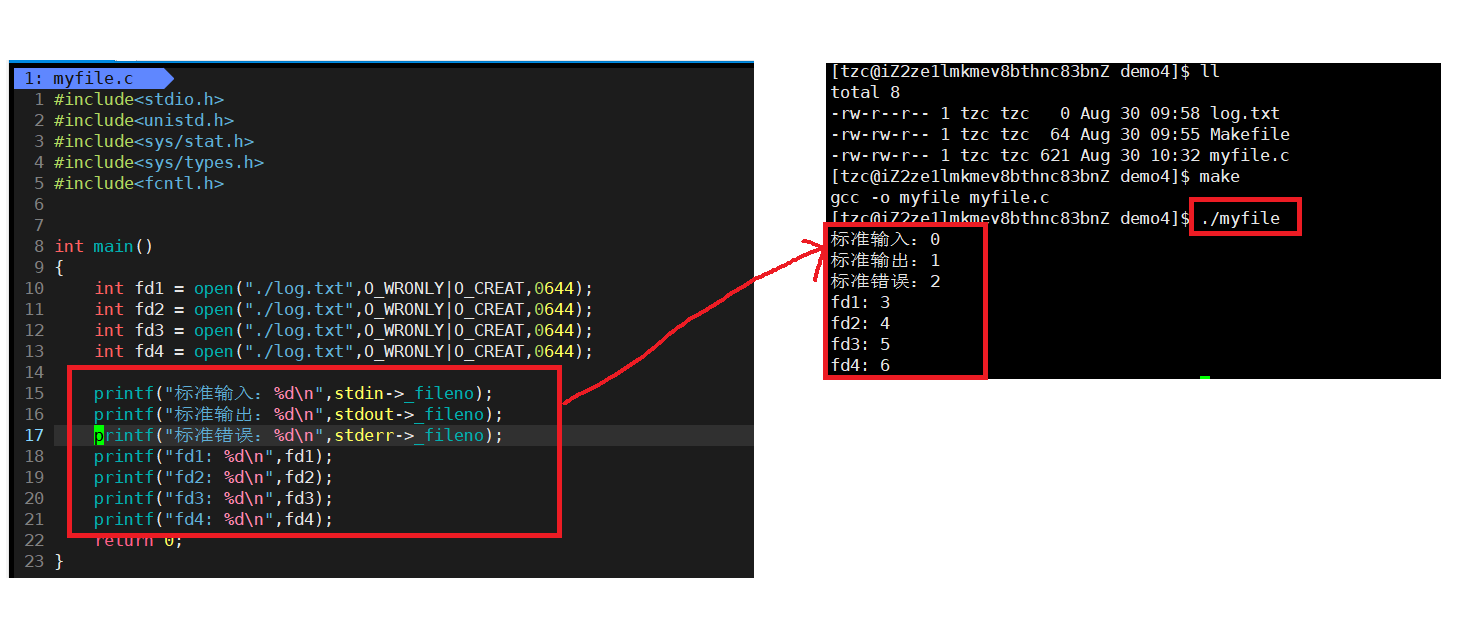
实际上文件描述符就是一个数组的下标,如何理解?
系统的标准输入,标准输出和标准错误占据了数组的前三个位置,所以我们进程在打开文件的时候,默认文件描述符就是从3开始。
如何验证?
四、重定向
1.输出重定向
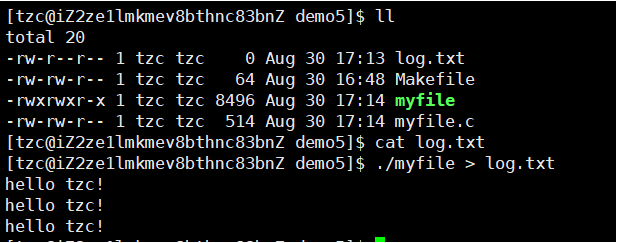
1 #include<stdio.h>2 #include<unistd.h>3 #include<sys/stat.h>4 #include<sys/types.h>5 #include<fcntl.h>6 #include<string.h>7 8 int main()9 {10 close(1); // 关闭标准输出11 int fd = open("./log.txt", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0644);12 // int fd = open("./log.txt", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0644); // 追加重定向 只是换成append 13 if(fd<0)14 { 15 perror("open"); 16 return 1; 17 } 18 19 int count = 5; 20 while(count--) 21 { 22 printf("hello world!\n"); 23 } 24 25 return 0; 26 }

原理:
2.输入重定向
1 #include<stdio.h>2 #include<unistd.h>3 #include<sys/stat.h>4 #include<sys/types.h>5 #include<fcntl.h>6 #include<string.h>7 8 int main()9 {10 close(0); // 关闭标准输入11 int fd = open("./log.txt", O_RDONLY);12 if(fd<0)13 {14 perror("open");15 return 1; 16 }17 18 int a,b;19 scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);20 printf("a=%d, b=%d\n",a,b);21 22 return 0;23 }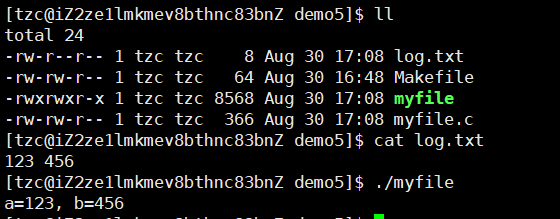
原理跟输出重定向相同,不过要关闭的是stdin
除了代码方式,我们可以通过指令方式进行重定向
1 #include<stdio.h>2 #include<unistd.h>3 #include<sys/stat.h>4 #include<sys/types.h>5 #include<fcntl.h>6 #include<string.h>7 8 int main()9 {10 printf("you can see me!\n");11 printf("you can see me!\n");12 printf("you can see me!\n");13 printf("you can see me!\n");14 15 fprintf(stdout,"hello linux!\n");16 fprintf(stdout,"hello linux!\n");17 fprintf(stdout,"hello linux!\n");18 19 fprintf(stderr,"hello tzc!\n");20 fprintf(stderr,"hello tzc!\n"); 21 fprintf(stderr,"hello tzc!\n");22 23 24 return 0;25 }
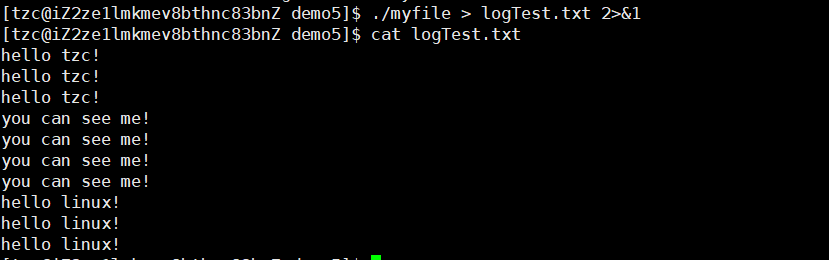
将原本输出到显示器文件中的数据重定向到log.txt中,重定向stdout的内容,所以stderr中的内容还是被打印到显示器文件中了
如果要对标准错误(stderr)的内容重定向到文件中可以另加修饰。
此时我们可以看到标准错误和标准输出都打印到同一个文件中。
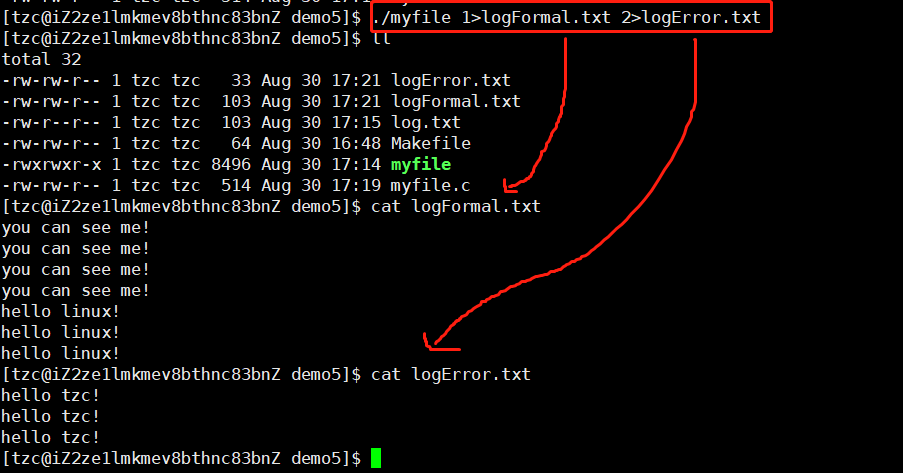
也可以进行分开重定向
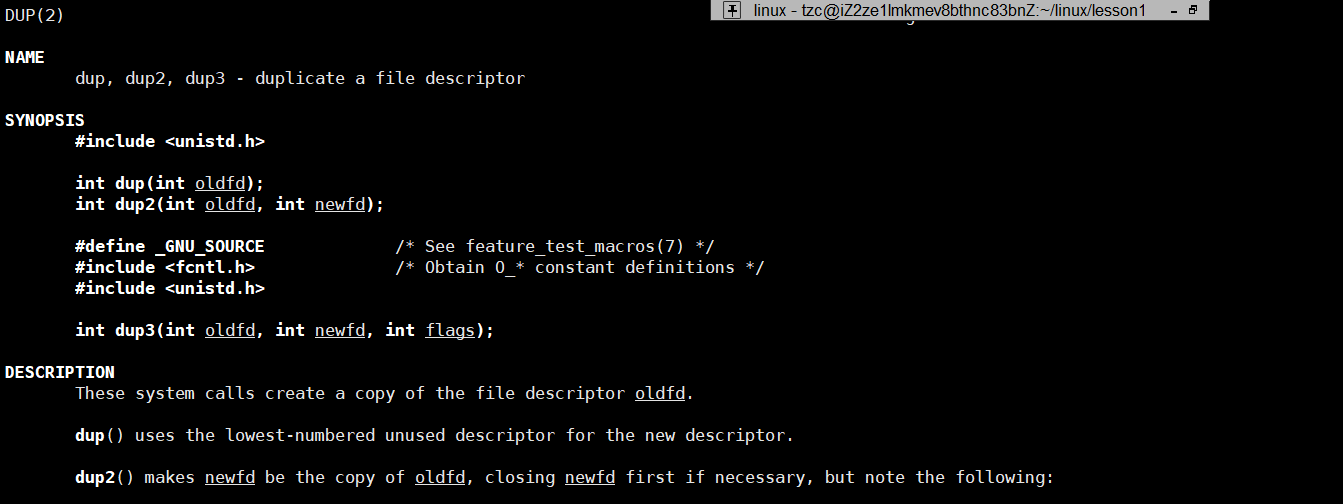
五、dup2
我们发现在对数据进行重定向的时候,操作比较复杂,系统提供了一个函数用来简化重定向操作
dup2有两个参数,oldfd和newfd,他的底层原理实际是将newfd的指针覆盖,换成指定oldfd位置的指针
使用:
1 #include<stdio.h>2 #include<unistd.h>3 #include<sys/stat.h>4 #include<sys/types.h>5 #include<fcntl.h>6 #include<string.h>7 8 #define LOG "log.txt"9 10 int main()11 {12 int fd=open(LOG,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666); //打开文件13 if(fd==-1)14 {15 perror("open");16 return -1;17 }18 19 dup2(fd,1); //将下标为1位置的内容覆盖为fd位置下标中内容20 21 printf("hello linux!\n");22 printf("hello linux!\n");23 printf("hello linux!\n"); 24 25 return 0;26 }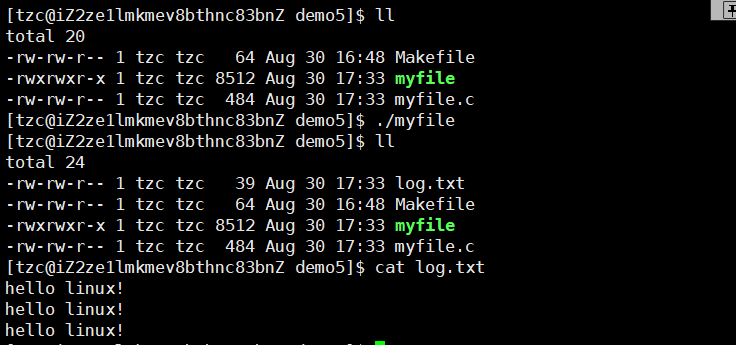



)




![[递归] 子集 全排列和组合问题](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[递归] 子集 全排列和组合问题)



)

)

)


