设计模式之保护性暂停
Guarded Suspension,这个设计模式,主要用在一个线程等待另一个线程的执行结果(发请求等待响应)
-
有一个结果需要从一个线程传递到另一个线程,传递只进行一次,用设计模式保护性暂停。
-
如果有结果不断从一个线程到另一个线程那么可以使用另一个设计模式消息队列(之后的知识)
-
JDK 中, join 的实现、 Future 的实现,采用的就是此模式
-
因为要等待另一方的结果,因此归类到同步模式
想要让一个线程等待另一个线程的执行结果,可以让这两个线程都关联上同一个 Guarded 0bject保护对象,让对象的管程的waitset来充当通知的桥梁,使用对象的wait()/notify()方法来进行通知。
结果如何从线程2传到线程1?其实保护对象由开发者创建,它的属性就是response。线程1对该对象加锁并执行wait()方法,线程1首先执行陷入阻塞。线程2也对保护对象加锁,当它执行完毕之后,将结果记录在保护对象的response之中然后执行notifyAll()方法唤醒线程1。线程1被唤醒,它就可以从保护对象的response属性中拿到线程2处理的结果。
改进:
如果要多个类之间进行通信,使用保护对象不是很方便。 因此设计一个用来解耦的中间类,这样不仅能够解耦【结果等待者】和【结果生产者】,还能够同时支持多个任务的管理。
注意:在这种情况下,结果等待者和结果生产者还是一一对应的。如果结果等待者和结果生产者是多对多的关系,要用到另一种设计模式——生产者/消费者。
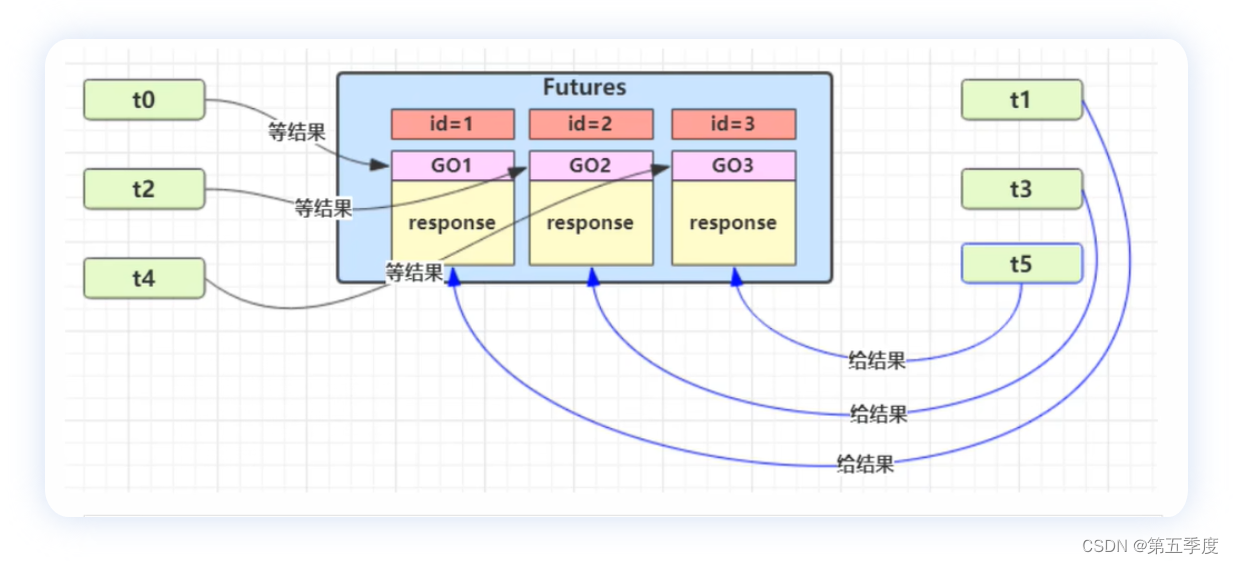
需要创建一个保护对象的管理器来管理多个保护对象。
package org.example;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;/*** @author xcy*/public class Main {static Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger("test");public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//结果等待者//这个for循环创建了5个保护对象,创建对象的方法确实是原子性的,但是这5个对象的保护对象不会和线程序号一致//因为5个线程并不是循环new出一个立刻就执行一个,线程的启动会有延迟//比如说线程1、2、3、4、5,并不是按照12345的顺序启动,会随机启动,所以最后线程名和创建出保护对象名称并不一致//如果想要让保护对象的序号与线程一致,要根据当前线程的序号来创建保护对象,而不是循环计数for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {int finalI=i;new Thread(() -> {GuardedObject guardedObject = GuardedObjectManager.createGuardedObject();logger.debug("开始等待结果,线程的保护对象为:"+guardedObject.getId());guardedObject.waitResult();logger.debug("等到结果:" + guardedObject.getResponse());},"t"+finalI).start();}Thread.sleep(1000);//结果生产者for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) {int finalI = i;new Thread(() -> {GuardedObject guardObject = GuardedObjectManager.getGuardObject(finalI - 5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"获得保护对象:"+guardObject);guardObject.complete(finalI);},"t"+finalI).start();}}
}/*** 保护对象,用于两个线程之间的通信*/
class GuardedObject {private Integer id;private Object response;public GuardedObject(Integer id) {this.id = id;}/*** 拥有该对象锁的线程释放对象锁,进入等待队列*/public synchronized Object waitResult() {while (response == null) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}return this.response;}/*** 唤醒该对象等待队列中的线程*/public synchronized void complete(Object response) {System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread()+"返回结果"+response);this.response = response;this.notifyAll();}public Integer getId() {return id;}public Object getResponse() {return response;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "GuardedObject{" +"id=" + id +'}';}
}/*** 用来管理GuardedObject*/
class GuardedObjectManager {private static int id;/*** 由于hashmap是线程不安全的,所以用hashtable保证put和get的原子性*/public static Map<Integer, GuardedObject> map = new Hashtable<>();public synchronized static GuardedObject createGuardedObject() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":"+id);GuardedObject guardedObject = new GuardedObject(id);map.put(id, guardedObject);id++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":"+id);return guardedObject;}public static GuardedObject getGuardObject(int id) {return map.get(id);}
}
结果:
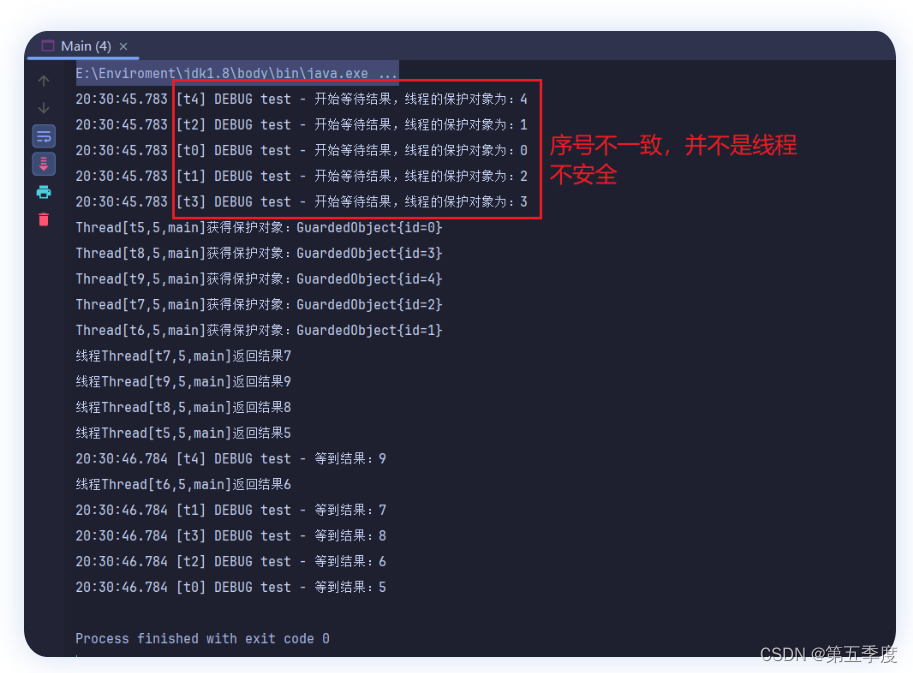

研究进展)


)


(dw、sublime Text、webstorm、HBuilder X))

)









