环境搭建
基本环境
选择的是Vmware+ubuntu的配置,注意ubuntu的版本一定要是20.04,作者试过16版本,不行,建议直接安装20.04版,不然环境配置都浪费不少时间有点得不偿失。(Vmware可以用Virtualbox代替)
qemu+xv6
参考官网教程
ps:刚装好的系统可以先更换镜像源(参考ubuntu 20.04 LTS 更换阿里云源)
这里将官网教程流程拷贝下来供大家拷贝:
第一步:
sudo apt-get install git build-essential gdb-multiarch qemu-system-misc gcc-riscv64-linux-gnu binutils-riscv64-linux-gnu
第二步:
sudo apt-get remove qemu-system-misc
sudo apt-get install qemu-system-misc=1:4.2-3ubuntu6
测试结果如下显示就是对的:
# in the xv6 directory
make qemu
# ... lots of output ...
init: starting sh
$
gitee配置
本处采用git来协调不同平台的代码,由于gitub比较慢于是将代码上传到gitee上(上传的时候可能会显示冲突,解决方法参考:代码冲突强制覆盖上传),至于gitee如何配置环境可以参考Windows环境安装及配置git并连接gitee远程仓库和ubuntu下Git的安装和使用(针对gitee)
。
实验部分
sleep (easy)
实现一个简单的休眠函数,容易,调api即可
//sleep.c
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {// int i;if (argc == 2) {sleep(atoi(argv[1]));} else {fprintf(2, "there is a need for an augument to determin the time to sleep");exit(1);}exit(0);
}
pingpong (easy)
考察到了pipe()函数的使用,使用管道一端写一端读即可。
//pingpong.c
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"char buf[96];char tmp[100];char* itoch(int input) {int i = 0;int l, r;while (input != 0) {tmp[i++] = (input % 10) + '0';input /= 10;}l = 0;r = i - 1;while (l < r) {char temp = tmp[l];tmp[l] = tmp[r];tmp[r] = temp;l++;r--;}tmp[i] = '\0';// fprintf(1, tmp);return tmp;
}int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {int pftos[2], pstof[2];pipe(pftos);pipe(pstof);// int pid = fork();// read// getpidif (fork() == 0) {//son pidclose(pftos[1]);close(pstof[0]);// fprintf(1, "son read\n");if (read(pftos[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) != 1) {fprintf(2, "ping read error");exit(1);}// fprintf(1, "son read success\n");char* tmp = itoch(getpid());fprintf(1, tmp);fprintf(1, ": ");fprintf(1, "received ping\n");if (write(pstof[1], "i", 1) != 1) {fprintf(2, "pong write error");exit(1);}close(pftos[0]);close(pstof[1]);exit(0);}//parent pidclose(pftos[0]);close(pstof[1]);// fprintf(1, "father write begin\n");if (write(pftos[1], "o", 1) != 1) {fprintf(2, "ping write error");exit(1);}// fprintf(1, "father write success\n");if (read(pstof[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) != 1) {fprintf(2, "pong read error");exit(1);}char* tmp = itoch(getpid());fprintf(1, tmp);fprintf(1, ": ");fprintf(1, "received pong\n");wait(0);close(pftos[1]);close(pstof[0]);exit(0);
}
primes (moderate)/(hard)
通过筛子来筛选,具体如下图所示:
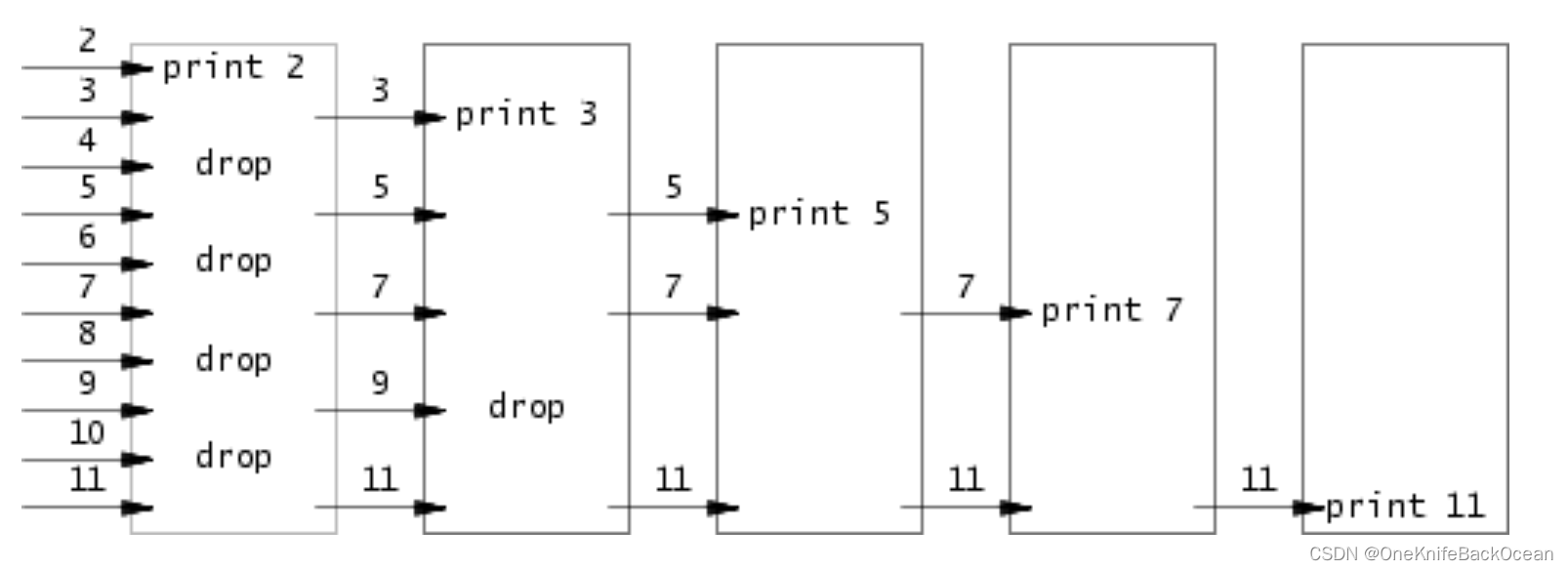
需要注意两点:
- 注意文件描述符的关闭,如果不及时关闭描述符可能会用尽文件描述符;
- 注意关闭管道的写端,当管道的写端的引用为0时read读端才会返回零,代表文件结束。
本处的代码并没有优化到最好,个人认为更好的实现可参考:6.S081-Lab1 总结笔记(0基础向)
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"
#include "kernel/spinlock.h"typedef enum {true = 1,false = 0
} bool;void buildProcess(int listenfd, int writefd) {int num;int self = -1;int status = fork();if (status == 0) {bool next = false;close(writefd);close(0);dup(listenfd);close(listenfd);//close(1);//dup(pfd[1]);//close(pfd[1]);int pfd[2];pipe(pfd);while (1) {int read_bytes = read(0, &num, 4);if (read_bytes == 0 || read_bytes == -1) {break;}if (self == -1) {self = num;printf("prime %d\n", num);continue;}if (num % self != 0) {if (!next) {next = true;buildProcess(pfd[0], pfd[1]);}write(pfd[1], &num, 4); }} close(pfd[0]);close(pfd[1]);close(0);wait(0);exit(0);} else if (status == -1) {fprintf(2, "fork error");exit(1);} }int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {int i;bool next = false;int pfd[2];pipe(pfd);for (i = 2; i <= 35; ++i) {if (i == 2) {printf("prime %d\n", i);}if (i % 2 == 1) {if (!next) {next = true;buildProcess(pfd[0], pfd[1]);close(pfd[0]);}write(pfd[1], &i, 4);} }close(pfd[1]);printf("end");wait(0);exit(0);
}
注释:有个待解决的问题,就是pipe后的两个文件描述符中,似乎不能将写端重定向到文件描述符1,具体原因待阅读源码后确认。
find (moderate)
这题算比较简单了,注意参考usr/find.c
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"
#include "kernel/fs.h"void find(const char* root, const char* target) {char buf[512], *p;int fd;struct dirent de;struct stat st;if((fd = open(root, 0)) < 0){fprintf(2, "find: cannot open %s\n", root);return;}if(fstat(fd, &st) < 0){fprintf(2, "find: cannot stat %s\n", root);close(fd);return;}if (st.type == T_FILE) {fprintf(2, "%s is no a directory!!!\n", root);close(fd);return;}if(strlen(root) + 1 + DIRSIZ + 1 > sizeof buf){printf("ls: path too long\n");}strcpy(buf, root);p = buf+strlen(buf);*p++ = '/';while(read(fd, &de, sizeof(de)) == sizeof(de)){if(de.inum == 0 || strcmp(de.name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(de.name, "..") == 0) continue;strcpy(p, de.name);int tmpfd;if((tmpfd = open(buf, 0)) < 0){fprintf(2, "open: cannot open %s\n", buf);return;}if(fstat(tmpfd, &st) < 0){fprintf(2, "fstat: cannot stat %s\n", buf);close(tmpfd);return;}if (st.type == T_FILE) {if (strcmp(de.name, target) == 0) {printf("%s/", root);printf("%s\n", de.name);}} else if (st.type == T_DIR) {find(buf, target);}close(tmpfd);}close(fd);
}int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {if (argc != 3) {fprintf(2, "too many or too few parameters\n");exit(1);}find(argv[1], argv[2]);exit(0);
}
xargs (moderate)
注意exec的参数,别的话就是些细节啦
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"char buf[1024];int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {int i;int line = 0;int size = read(0, buf, sizeof buf);char* input[argc];for (i = 1; i < argc; ++i) {input[i - 1] = argv[i];}if (size == -1) {fprintf(2, "read error");}for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {if (buf[i] == '\n') {line++;}}char arguments[line][32];int pos = 0, curr = 0;for (i = 0; i < size; ++i) {if (buf[i] == '\n') {arguments[curr][pos] = '\0';curr++;pos = 0;} else {arguments[curr][pos++] = buf[i];}}for (i = 0; i < line; ++i) {input[argc - 1] = arguments[i];if (fork() == 0) {exec(argv[1], input);exit(0);}wait(0);}exit(0);
}


)
)
![[2024] 十大免费电脑数据恢复软件——轻松恢复电脑上已删除文件](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[2024] 十大免费电脑数据恢复软件——轻松恢复电脑上已删除文件)



:数据类型、数值类型、字符串类型、布尔类型、undefined、类型转换、隐式转换、显式转换、Number)


)







