交叉验证
文章目录
- 交叉验证
- 外生变量
- 比较不同的模型
时间序列预测中的主要挑战之一是随着时间的推移固有的不确定性和变异性,因此验证所采用的模型的准确性和可靠性至关重要。交叉验证是一种强大的模型验证技术,特别适用于此任务,因为它提供了有关模型在未见数据上的预期性能的见解,确保在实际场景中部署之前,预测是可靠和有弹性的。
TimeGPT 理解时间序列预测的复杂需求,融合了 cross_validation 方法,旨在简化时间序列模型的验证过程。这个功能使从业者能够对历史数据严格测试他们的预测模型,评估它们的有效性,同时调整它们以获得最佳性能。本教程将指导您完成在 TimeGPT 类中进行交叉验证的微妙过程,确保您的时间序列预测模型不仅构建良好,而且经过验证是值得信赖和精确的。
# 导入colab_badge模块,用于生成Colab徽章
from nixtlats.utils import colab_badge
colab_badge('docs/tutorials/9_cross_validation')
# 导入必要的库
import numpy as np
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# 加载dotenv模块,用于从.env文件中加载环境变量
load_dotenv()
True
# 导入pandas库
import pandas as pd
# 导入TimeGPT类
from nixtlats import TimeGPT
# 创建TimeGPT对象,并传入token参数
# 如果没有传入token参数,则默认使用环境变量中的TIMEGPT_TOKEN
timegpt = TimeGPT(token='my_token_provided_by_nixtla'
)
# 创建一个TimeGPT对象,用于生成时间相关的文本。
timegpt = TimeGPT()
TimeGPT类中的cross_validation方法是一种高级功能,用于对时间序列预测模型进行系统验证。该方法需要一个包含按时间排序的数据的数据帧,并采用滚动窗口方案来精确评估模型在不同时间段的性能,从而确保模型的可靠性和稳定性。
关键参数包括freq,它表示数据的频率,如果未指定,则会自动推断。id_col、time_col和target_col参数分别指定每个系列的标识符、时间步长和目标值的列。该方法通过参数进行自定义,例如n_windows表示评估模型的独立时间窗口的数量,step_size确定这些窗口之间的间隔。如果未指定step_size,则默认为预测的时间范围h。
该过程还允许通过finetune_steps进行模型细化,指定在新数据上进行模型微调的迭代次数。通过clean_ex_first参数可以管理数据预处理,决定是否在预测之前清理外生信号。此外,该方法还支持通过date_features参数从时间数据进行增强特征工程,该参数可以自动生成关键的与日期相关的特征,也可以接受自定义函数进行定制特征创建。date_features_to_one_hot参数进一步支持将分类日期特征转换为适合机器学习模型的格式。
在执行过程中,cross_validation在每个窗口中评估模型的预测准确性,提供了模型性能随时间变化和过度拟合的稳健视图。这种详细评估确保生成的预测不仅准确,而且在不同的时间背景下保持一致。
# 读取数据集
pm_df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/peyton_manning.csv')# 使用timegpt库的cross_validation函数对数据进行交叉验证
# 参数说明:
# - pm_df: 待验证的数据集
# - h: 预测的时间步数
# - n_windows: 窗口数量,用于划分训练集和验证集
# - time_col: 时间列的列名
# - target_col: 目标列的列名
# - freq: 时间频率,这里设定为每天
timegpt_cv_df = timegpt.cross_validation(pm_df, h=7, n_windows=5, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value', freq='D',
)# 打印交叉验证结果的前几行
timegpt_cv_df.head()
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
| timestamp | cutoff | value | TimeGPT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2015-12-17 | 2015-12-16 | 7.591862 | 7.939553 |
| 1 | 2015-12-18 | 2015-12-16 | 7.528869 | 7.887512 |
| 2 | 2015-12-19 | 2015-12-16 | 7.171657 | 7.766617 |
| 3 | 2015-12-20 | 2015-12-16 | 7.891331 | 7.931502 |
| 4 | 2015-12-21 | 2015-12-16 | 8.360071 | 8.312632 |
# 导入IPython.display模块中的display函数from IPython.display import display
# 从timegpt_cv_df数据框中获取唯一的cutoff值,并赋值给变量cutoffs
cutoffs = timegpt_cv_df['cutoff'].unique()# 遍历cutoffs中的每个cutoff值
for cutoff in cutoffs:# 使用timegpt.plot函数绘制图形,并将结果赋值给变量fig# 绘图所需的数据为pm_df的最后100行和timegpt_cv_df中cutoff等于当前遍历值的行,删除列'cutoff'和'value'# 指定时间列为'timestamp',目标列为'value'fig = timegpt.plot(pm_df.tail(100), timegpt_cv_df.query('cutoff == @cutoff').drop(columns=['cutoff', 'value']),time_col='timestamp', target_col='value')# 显示图形display(fig)

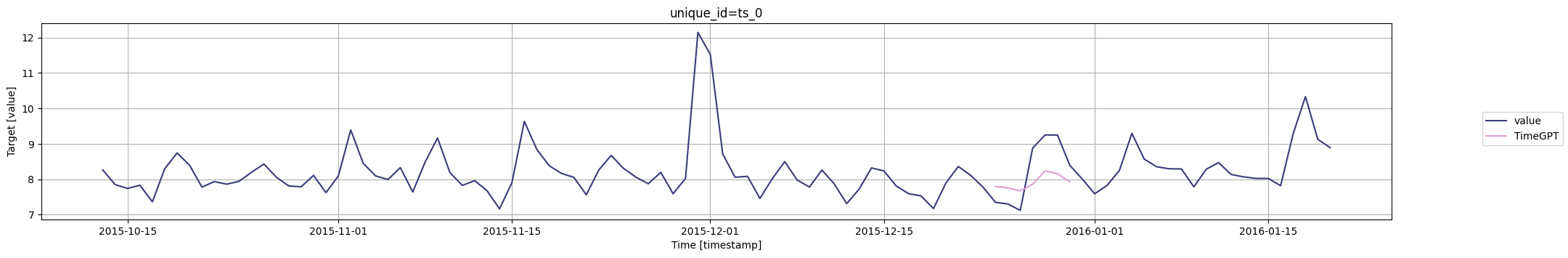
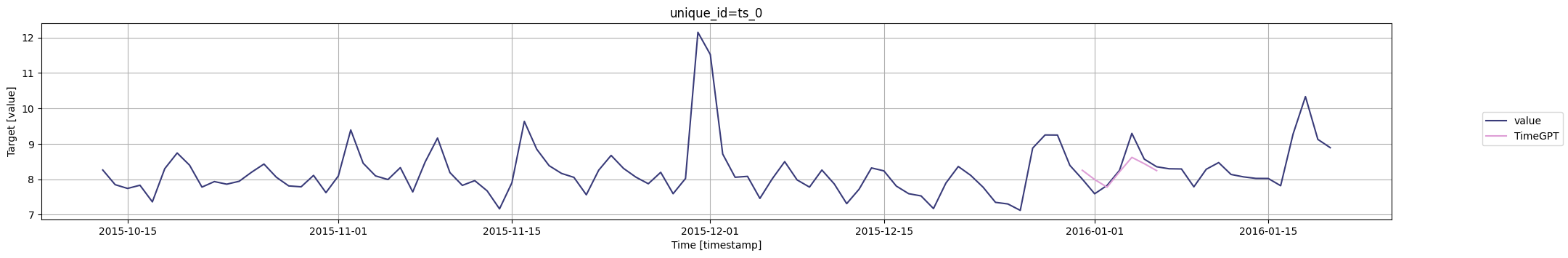
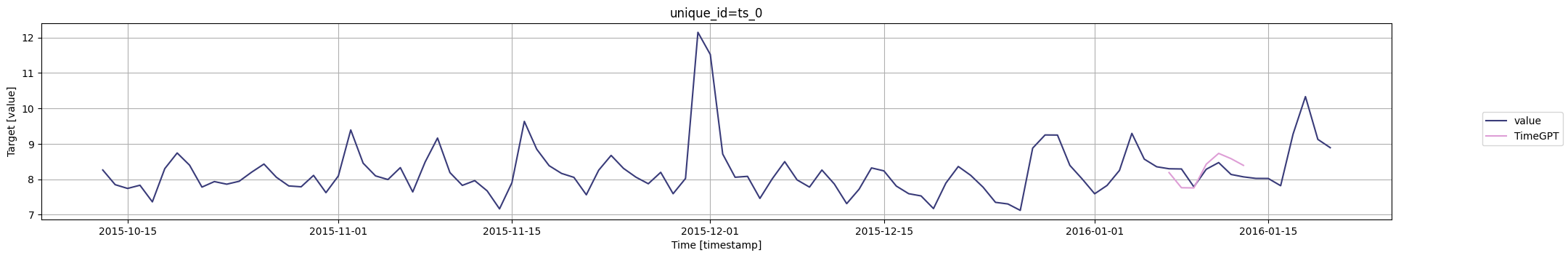

为了评估TimeGPT在分布预测方面的性能,您可以使用level参数生成预测区间。
# 导入所需模块和函数# 使用timegpt.cross_validation函数进行时间序列交叉验证
# 参数pm_df为待验证的时间序列数据
# 参数h为预测的时间步长,这里设置为7
# 参数n_windows为窗口数量,这里设置为5
# 参数time_col为时间列的列名,这里设置为'timestamp'
# 参数target_col为目标列的列名,这里设置为'value'
# 参数freq为时间序列的频率,这里设置为'D',表示按天
# 参数level为置信水平,这里设置为[80, 90],表示计算80%和90%的置信区间
# 返回值timegpt_cv_df为交叉验证结果的数据框
timegpt_cv_df = timegpt.cross_validation(pm_df, h=7, n_windows=5, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value', freq='D',level=[80, 90],
)
# 输出交叉验证结果的前几行数据
timegpt_cv_df.head()
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Restricting input...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
| timestamp | cutoff | value | TimeGPT | TimeGPT-lo-90 | TimeGPT-lo-80 | TimeGPT-hi-80 | TimeGPT-hi-90 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2015-12-17 | 2015-12-16 | 7.591862 | 7.939553 | 7.564151 | 7.675945 | 8.203161 | 8.314956 |
| 1 | 2015-12-18 | 2015-12-16 | 7.528869 | 7.887512 | 7.567342 | 7.598298 | 8.176726 | 8.207681 |
| 2 | 2015-12-19 | 2015-12-16 | 7.171657 | 7.766617 | 7.146560 | 7.266829 | 8.266404 | 8.386674 |
| 3 | 2015-12-20 | 2015-12-16 | 7.891331 | 7.931502 | 7.493021 | 7.657075 | 8.205929 | 8.369982 |
| 4 | 2015-12-21 | 2015-12-16 | 8.360071 | 8.312632 | 7.017335 | 7.446677 | 9.178586 | 9.607928 |
# 获取时间截断点的唯一值
cutoffs = timegpt_cv_df['cutoff'].unique()# 遍历每个截断点
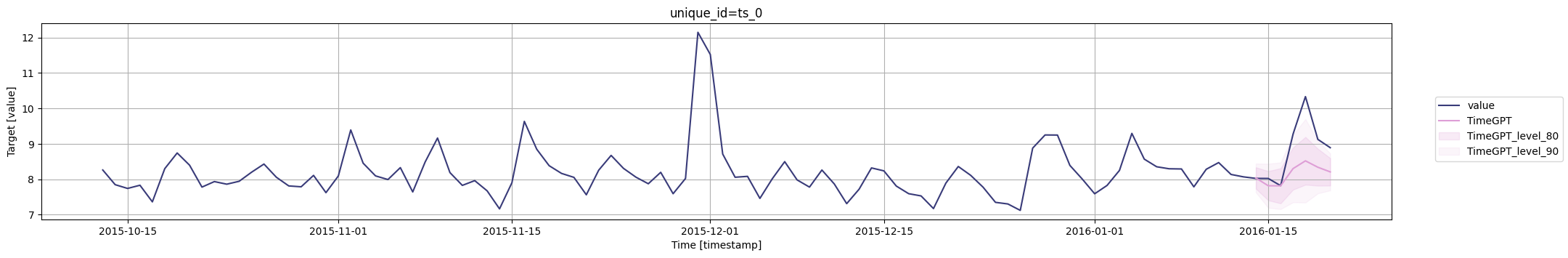
for cutoff in cutoffs:# 绘制图表fig = timegpt.plot(# 绘制最近100个数据点pm_df.tail(100), # 查询截断点等于当前截断点的数据,并删除'cutoff'和'value'列timegpt_cv_df.query('cutoff == @cutoff').drop(columns=['cutoff', 'value']),# 设置时间列为'timestamp'time_col='timestamp', # 设置目标列为'value'target_col='value',# 设置置信水平为[80, 90]level=[80, 90],# 设置模型为'TimeGPT'models=['TimeGPT'])# 显示图表display(fig)


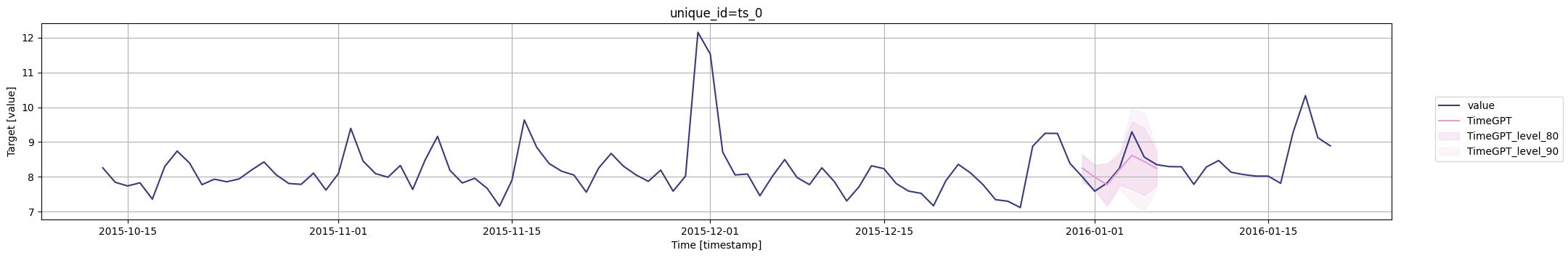
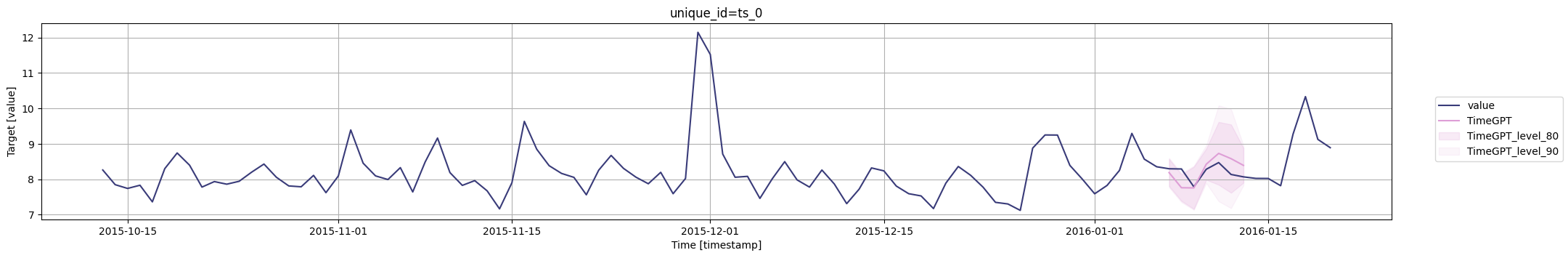

您还可以包括date_features以查看它们对预测准确性的影响。
# 对于给定的时间序列数据,进行时间序列交叉验证
# 使用timegpt.cross_validation函数进行交叉验证
# 参数说明:
# - pm_df: 待验证的时间序列数据
# - h: 预测的时间步长
# - n_windows: 窗口的数量,将时间序列数据划分为多个窗口进行交叉验证
# - time_col: 时间列的名称,用于指定时间序列数据中的时间信息
# - target_col: 目标列的名称,用于指定时间序列数据中的目标变量
# - freq: 时间序列数据的频率,以天为单位
# - level: 置信水平,用于计算预测区间
# - date_features: 日期特征,用于提取时间序列数据中的日期信息
# 返回值为交叉验证结果的数据框
timegpt_cv_df = timegpt.cross_validation(pm_df, h=7, n_windows=5, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value', freq='D',level=[80, 90],date_features=['month'],
)# 输出交叉验证结果的前几行数据
timegpt_cv_df.head()
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: month_1, month_2, month_3, month_4, month_5, month_6, month_7, month_8, month_9, month_10, month_11, month_12
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: month_1, month_2, month_3, month_4, month_5, month_6, month_7, month_8, month_9, month_10, month_11, month_12
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: month_1, month_2, month_3, month_4, month_5, month_6, month_7, month_8, month_9, month_10, month_11, month_12
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: month_1, month_2, month_3, month_4, month_5, month_6, month_7, month_8, month_9, month_10, month_11, month_12
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: month_1, month_2, month_3, month_4, month_5, month_6, month_7, month_8, month_9, month_10, month_11, month_12
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
| timestamp | cutoff | value | TimeGPT | TimeGPT-lo-90 | TimeGPT-lo-80 | TimeGPT-hi-80 | TimeGPT-hi-90 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2015-12-17 | 2015-12-16 | 7.591862 | 7.945311 | 7.542366 | 7.647852 | 8.242769 | 8.348255 |
| 1 | 2015-12-18 | 2015-12-16 | 7.528869 | 7.892559 | 7.271274 | 7.481059 | 8.304058 | 8.513843 |
| 2 | 2015-12-19 | 2015-12-16 | 7.171657 | 7.771581 | 7.113544 | 7.281711 | 8.261451 | 8.429619 |
| 3 | 2015-12-20 | 2015-12-16 | 7.891331 | 7.939502 | 6.988198 | 7.345371 | 8.533633 | 8.890807 |
| 4 | 2015-12-21 | 2015-12-16 | 8.360071 | 8.320170 | 7.140163 | 7.658314 | 8.982027 | 9.500178 |
# 获取时间戳的唯一值
cutoffs = timegpt_cv_df['cutoff'].unique()# 遍历每个唯一的时间戳
for cutoff in cutoffs:# 使用timegpt.plot函数绘制图形# 参数1:使用pm_df的最后100行数据作为输入数据# 参数2:使用timegpt_cv_df中cutoff等于当前遍历的时间戳的数据,删除cutoff和value列作为输入数据# 参数3:指定时间戳列为timestamp# 参数4:指定目标值列为value# 参数5:指定80和90为置信水平# 参数6:指定使用TimeGPT模型fig = timegpt.plot(pm_df.tail(100), timegpt_cv_df.query('cutoff == @cutoff').drop(columns=['cutoff', 'value']),time_col='timestamp', target_col='value',level=[80, 90],models=['TimeGPT'])# 显示图形display(fig)
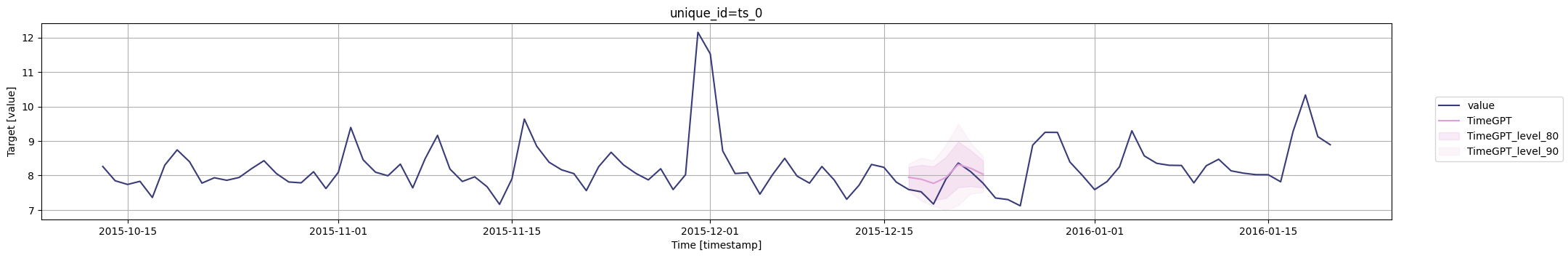

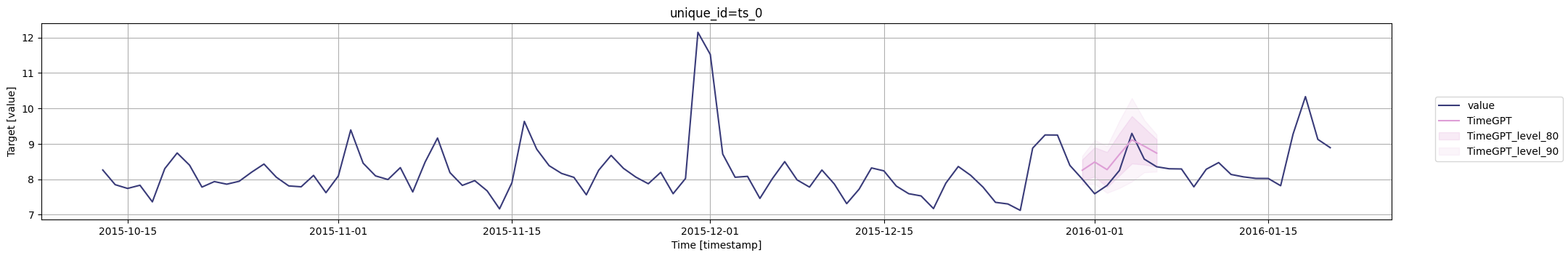
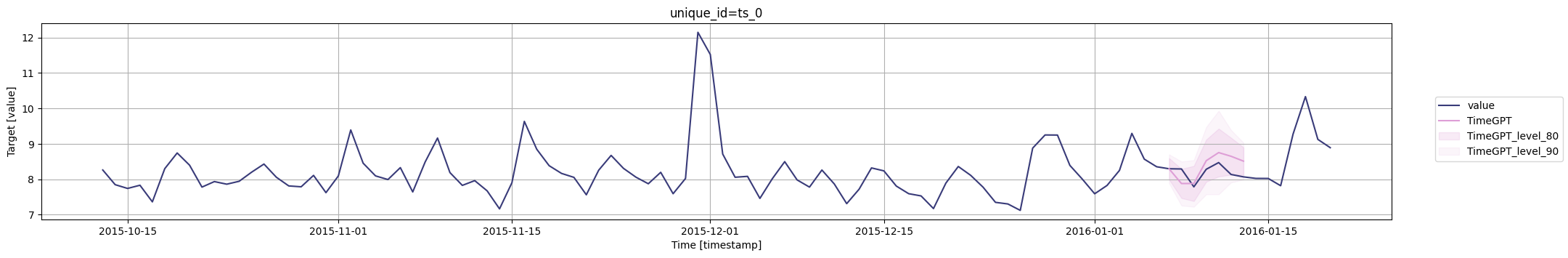
外生变量
此外,您可以传递外生变量以更好地向TimeGPT提供关于数据的信息。您只需在目标列之后简单地添加外生回归变量即可。
# 读取电力数据集Y_df,数据来自'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/electricity.csv'
Y_df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/electricity.csv')# 读取外部变量数据集X_df,数据来自'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/exogenous-vars-electricity.csv'
X_df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/exogenous-vars-electricity.csv')# 将Y_df和X_df数据集进行合并,合并后的数据集为df
df = Y_df.merge(X_df)
现在让我们使用这些信息对TimeGPT进行交叉验证。
# 导入TimeGPT模型
timegpt = TimeGPT(max_retries=2, retry_interval=5) # 创建TimeGPT对象,设置最大重试次数为2,重试间隔为5秒
# 导入的库已经存在,不需要添加import语句# 对数据进行交叉验证,将数据按照unique_id分组,每组取最后的100*48个数据进行交叉验证
# h=48表示预测未来48个时间点的值,n_windows=2表示将数据分为两个窗口进行交叉验证
# level=[80, 90]表示计算80%和90%置信区间
timegpt_cv_df_x = timegpt.cross_validation(df.groupby('unique_id').tail(100 * 48), h=48, n_windows=2,level=[80, 90]
)# 查询unique_id为"BE"的数据的cutoff值,并将其存储在cutoffs中
cutoffs = timegpt_cv_df_x.query('unique_id == "BE"')['cutoff'].unique()# 遍历cutoffs中的每个cutoff值,对unique_id为"BE"的数据进行预测并绘制图表
for cutoff in cutoffs:# 绘制unique_id为"BE"的数据的最后24*7个时间点的真实值和预测值,并将其存储在fig中# timegpt_cv_df_x.query('cutoff == @cutoff & unique_id == "BE"')表示查询cutoff值为当前遍历到的cutoff值,unique_id为"BE"的数据# drop(columns=['cutoff', 'y'])表示删除查询结果中的cutoff和y两列# models=['TimeGPT']表示使用TimeGPT模型进行预测# level=[80, 90]表示计算80%和90%置信区间fig = timegpt.plot(df.query('unique_id == "BE"').tail(24 * 7), timegpt_cv_df_x.query('cutoff == @cutoff & unique_id == "BE"').drop(columns=['cutoff', 'y']),models=['TimeGPT'],level=[80, 90],)# 显示图表display(fig)
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Inferred freq: H
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Inferred freq: H
WARNING:nixtlats.timegpt:The specified horizon "h" exceeds the model horizon. This may lead to less accurate forecasts. Please consider using a smaller horizon.
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: Exogenous1, Exogenous2, day_0, day_1, day_2, day_3, day_4, day_5, day_6
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Inferred freq: H
WARNING:nixtlats.timegpt:The specified horizon "h" exceeds the model horizon. This may lead to less accurate forecasts. Please consider using a smaller horizon.
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: Exogenous1, Exogenous2, day_0, day_1, day_2, day_3, day_4, day_5, day_6
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...


比较不同的模型
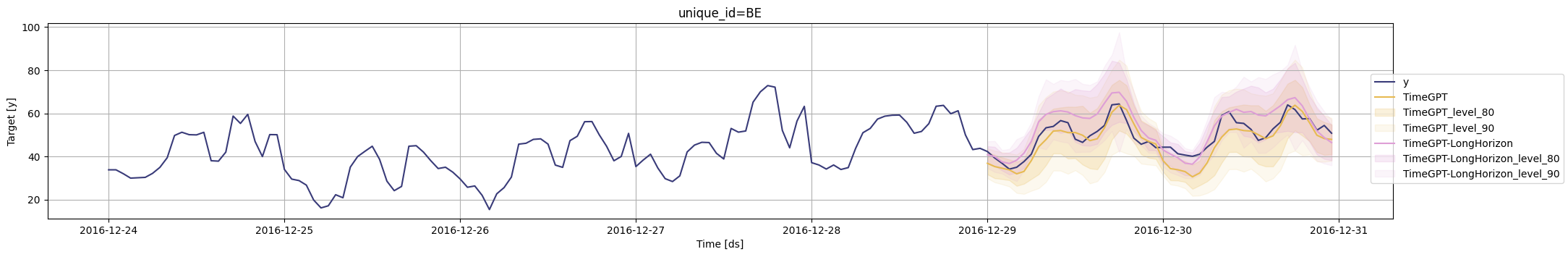
此外,您可以使用model参数为不同的TimeGPT实例生成交叉验证。
# 对数据进行交叉验证
timegpt_cv_df_x_long_horizon = timegpt.cross_validation(df.groupby('unique_id').tail(100 * 48), # 对数据进行分组,每个组取最后的100 * 48个数据h=48, # 预测的时间步长为48n_windows=2, # 使用2个窗口进行交叉验证level=[80, 90], # 设置置信水平为80%和90%model='timegpt-1-long-horizon', # 使用timegpt-1-long-horizon模型
)# 将列名中的'TimeGPT'替换为'TimeGPT-LongHorizon'
timegpt_cv_df_x_long_horizon.columns = timegpt_cv_df_x_long_horizon.columns.str.replace('TimeGPT', 'TimeGPT-LongHorizon')# 将timegpt_cv_df_x_long_horizon与timegpt_cv_df_x进行合并
timegpt_cv_df_x_models = timegpt_cv_df_x_long_horizon.merge(timegpt_cv_df_x)# 获取unique_id为"BE"的数据的cutoff值
cutoffs = timegpt_cv_df_x_models.query('unique_id == "BE"')['cutoff'].unique()# 对每个cutoff值进行循环
for cutoff in cutoffs:# 绘制图形fig = timegpt.plot(df.query('unique_id == "BE"').tail(24 * 7), # 获取unique_id为"BE"的最后24 * 7个数据timegpt_cv_df_x_models.query('cutoff == @cutoff & unique_id == "BE"').drop(columns=['cutoff', 'y']), # 获取cutoff和unique_id为"BE"的数据,并删除'cutoff'和'y'列models=['TimeGPT', 'TimeGPT-LongHorizon'], # 绘制'TimeGPT'和'TimeGPT-LongHorizon'模型的图形level=[80, 90], # 设置置信水平为80%和90%)# 显示图形display(fig)INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Inferred freq: H
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Inferred freq: H
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: Exogenous1, Exogenous2, day_0, day_1, day_2, day_3, day_4, day_5, day_6
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Preprocessing dataframes...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Inferred freq: H
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Using the following exogenous variables: Exogenous1, Exogenous2, day_0, day_1, day_2, day_3, day_4, day_5, day_6
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Calling Forecast Endpoint...
INFO:nixtlats.timegpt:Validating inputs...





)














