有粉丝叫我帮他做一下这道题。。。。

额。。。。。。这同学应该好好听课啦 哈哈
int[] a = {25, 24, 12, 76, 101, 96, 28};Arrays.sort(a);//排序System.out.println("排序后数组如下");for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {System.out.print(a[i] + " ,");}既然写到这里了就看下底层实现吧
断点跟踪调用的是DualPivotQuicksort.java类的java双基准快速排序方法sort实现
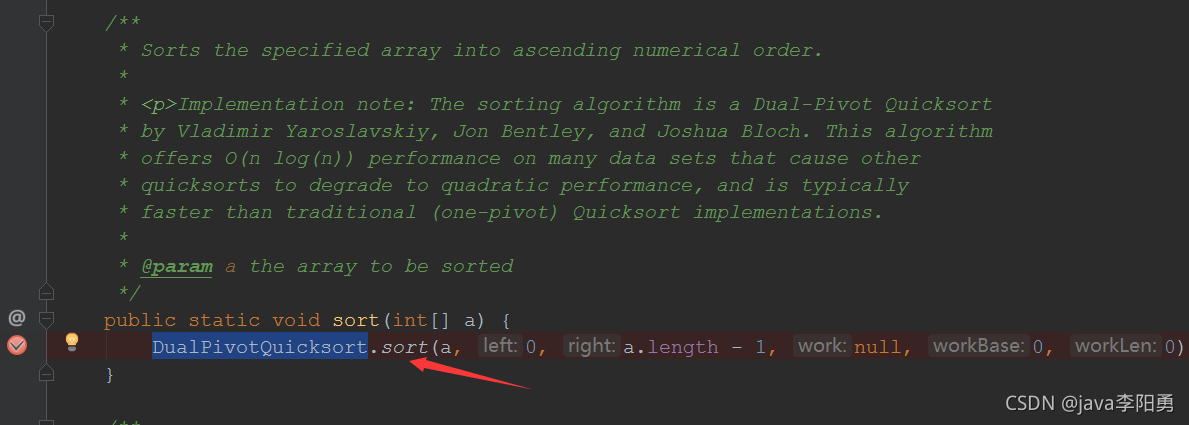
跟踪进去就是具体排序方法的实现、其中具体方法:参数 int[] a是需被排序的int数组, left和right是该数组中需要被排序的部分的左右界限. 而后面的work, workBase和workLen三个参数其实并不会参与双基准快速排序, 而是当系统认为本数组更适合使用归并排序(merge sort)的时候, 供归并排序使用。具体代码算法源码如下。
static void sort(int[] a, int left, int right,int[] work, int workBase, int workLen) {// Use Quicksort on small arraysif (right - left < QUICKSORT_THRESHOLD) {sort(a, left, right, true);return;}/** Index run[i] is the start of i-th run* (ascending or descending sequence).*/int[] run = new int[MAX_RUN_COUNT + 1];int count = 0; run[0] = left;// Check if the array is nearly sortedfor (int k = left; k < right; run[count] = k) {if (a[k] < a[k + 1]) { // ascendingwhile (++k <= right && a[k - 1] <= a[k]);} else if (a[k] > a[k + 1]) { // descendingwhile (++k <= right && a[k - 1] >= a[k]);for (int lo = run[count] - 1, hi = k; ++lo < --hi; ) {int t = a[lo]; a[lo] = a[hi]; a[hi] = t;}} else { // equalfor (int m = MAX_RUN_LENGTH; ++k <= right && a[k - 1] == a[k]; ) {if (--m == 0) {sort(a, left, right, true);return;}}}/** The array is not highly structured,* use Quicksort instead of merge sort.*/if (++count == MAX_RUN_COUNT) {sort(a, left, right, true);return;}}// Check special cases// Implementation note: variable "right" is increased by 1.if (run[count] == right++) { // The last run contains one elementrun[++count] = right;} else if (count == 1) { // The array is already sortedreturn;}// Determine alternation base for mergebyte odd = 0;for (int n = 1; (n <<= 1) < count; odd ^= 1);// Use or create temporary array b for mergingint[] b; // temp array; alternates with aint ao, bo; // array offsets from 'left'int blen = right - left; // space needed for bif (work == null || workLen < blen || workBase + blen > work.length) {work = new int[blen];workBase = 0;}if (odd == 0) {System.arraycopy(a, left, work, workBase, blen);b = a;bo = 0;a = work;ao = workBase - left;} else {b = work;ao = 0;bo = workBase - left;}// Mergingfor (int last; count > 1; count = last) {for (int k = (last = 0) + 2; k <= count; k += 2) {int hi = run[k], mi = run[k - 1];for (int i = run[k - 2], p = i, q = mi; i < hi; ++i) {if (q >= hi || p < mi && a[p + ao] <= a[q + ao]) {b[i + bo] = a[p++ + ao];} else {b[i + bo] = a[q++ + ao];}}run[++last] = hi;}if ((count & 1) != 0) {for (int i = right, lo = run[count - 1]; --i >= lo;b[i + bo] = a[i + ao]);run[++last] = right;}int[] t = a; a = b; b = t;int o = ao; ao = bo; bo = o;}}虽然看似简单的一行代码其实底层的实现也是很复杂的、对算法感兴趣的同学可以仔细看看底层实现。



实现)
...)






实现)
实现)

实现(二))




实现)