为什么选择插件,而不是组件?
- 调用简单 this.$toast("xxx") ,不必再模板中提前定义 , 动态插入移除
- 插件独立于业务
- 更新不影响代码逻辑,做到热更新
- 抽象,封装
- 适用于toast,Dialog,Alert,Message,picker,Actionsheet等组件
react-toast-alert demo地址
使用方法:
import $ from '@/component/Toast/index';
...
$.toast({
type:0,
content: "我是默认Toast",
time: 1000,
opacity: .5,
onSucc() {
console.log("我是Toast的回调!")
}
});
$.toast("我是默认Toast");
$.toast({
type:3,
content: "我是默认loading",
time: 1000,
});
setTimeout(() => { //3s后隐藏
$.hide();
}, 3000);
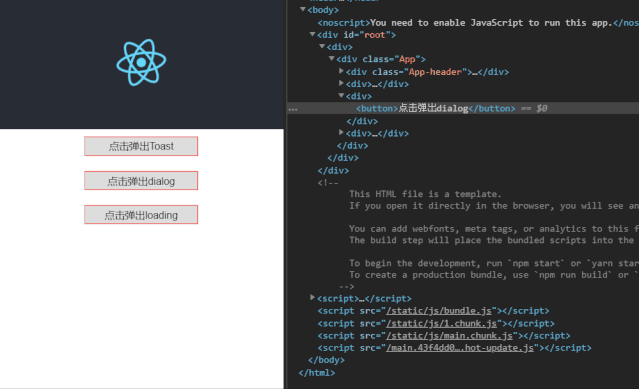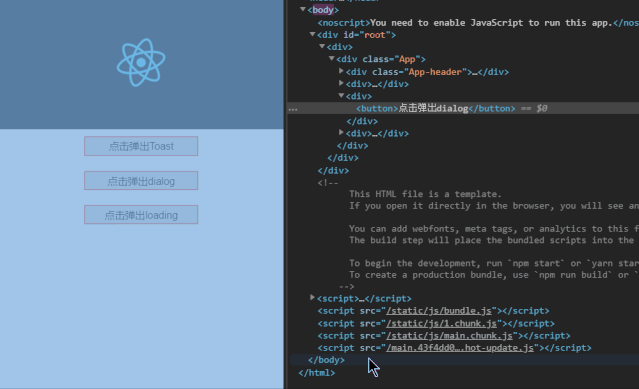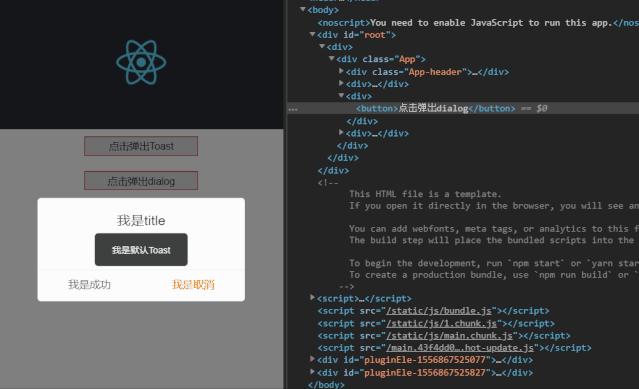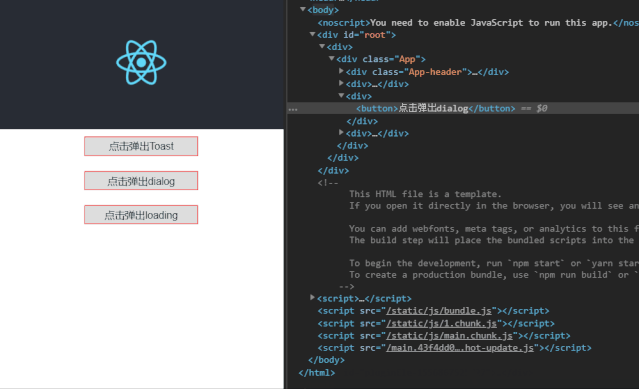
$.dialog({
type: 0,
opacity:0.5,
title: "我是title",
content: "我是content",
btnSucc: "我是成功",
btnFail: "我是取消",
onSucc(e) {
e.stopPropagation();
$.toast("我是默认Toast");
},
onFail(e) {
e.stopPropagation();
console.log("我是失败的回调!");
}
});
Vue 插件
在Vue里,一般将toast,alert等非业务相关的写成插件,挂载在Vue的原型链上,使用的时候直接this.$toast即可,非常方便!相关原理在这里就不说了,感兴趣的可以查阅官网. 先看看Vue的插件写法:
@/components/vue-toast/index.js
import ToastComponent from "./vue-toast.vue"; // 引入先前写好的vue
var Toast = {};
//避免重复install,设立flag
Toast.installed = false;
Toast.install = function(Vue, options = {
type: "success", //success fail warning loading toast
msg: "操作成功",
time: 1000,
callback() {
}
}) {
if(Toast.installed) return;
var obj;
Vue.prototype.$toast = (config = {}, type) => {
if(type == 'close') {
obj && obj.removeToast();
return false;
}
if(typeof config=="object"){
config = {
...options,
...config
}
}else{
config = {
...options,
...{
type: "toast",
msg: config
}
}
}
// 如果页面有toast则不继续执行
if(document.querySelector('.vue-toast')) return;
// 1、创建构造器,定义好提示信息的模板
const toastTip = Vue.extend(ToastComponent);
obj = new toastTip();
for(var property in config) {
obj[property] = config[property];
}
//删除弹框
obj.removeToast = function() {
document.body.removeChild(tpl);
}
//插入页面
let tpl = obj.$mount().$el;
document.body.appendChild(tpl);
Toast.installed = true;
if(['success', 'fail', 'warning','toast'].indexOf(config.type) > -1) {
setTimeout(() => {
obj.removeToast();
obj.callback();
}, config.time)
}
['close'].forEach(function(type) {
Vue.prototype.$toast[type] = function(msg) {
return Vue.prototype.$toast({}, type)
}
});
};
};
// 自动安装 ,有了ES6就不要写AMD,CMD了
if(typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
window.Vue.use(Toast)
};
export default Toast
@/components/vue-toast/vue-toast.vue
<template>
<div class="mask vue-toast">
<div>
<div class="toast" v-if="['success', 'fail', 'warning','loading'].indexOf(type) > -1">
<div class="icon" v-if="['success', 'fail', 'warning'].indexOf(type) > -1">
<div v-if="type=='success'" class="success-icon">div>
<div v-if="type=='fail'" class="fail-icon">div>
<div v-if="type=='warning'" class="warning-icon">div>
div>
<div class="loading-icon" v-else>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
div>
<div class="msg" v-html="msg">div>
div>
<div v-else class="toast-msg" v-html="msg">div>
div>
div>
template>
<script>export default {
data() {return {msg: " ",type: "success"
};
}
};script>
<style scoped="scoped " lang="less">
.mask {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
position: fixed;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
z-index: 10000;
.toast-msg {
font-size: 0.24rem;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
transform: translateX(-50%);
color: #fff;
left: 50%;
padding: 0.18rem 0.27rem;
overflow: hidden;
border-radius: 4px;
white-space: nowrap;
display: block;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
}
.toast {
font-size: 0rem;
padding: 0.27rem .090rem;
width: 2.26rem;
overflow: hidden;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
flex-direction: column;
color: #f2f2f2;
background: rgba(51, 51, 51, 0.94);
border-radius: 0.09rem;
text-align: center;
.icon {
width: 0.72rem;
height: 0.72rem;
border-radius: 50%;
border: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
position: relative;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
position: relative;
.success-icon {
border-right: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
transform: rotate(45deg);
width: 0.27rem;
height: 0.45rem;
margin-top: -0.18rem;
}
.fail-icon {
&:before {
content: " ";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) rotate(45deg);
border-top: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
width: 0.5rem;
height: 0px;
}
&:after {
content: " ";
content: " ";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) rotate(-45deg);
border-top: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
width: 0.5rem;
height: 0px;
}
}
.warning-icon {
&:before {
content: " ";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -500%) rotate(90deg);
border-top: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
width: 0.27rem;
height: 0px;
}
&:after {
content: " ";
content: " ";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, 250%) rotate(-45deg);
background: #f2f2f2;
width: 3px;
border-radius: 50%;
height: 3px;
}
}
}
.msg {
margin-top: 0.18rem;
font-size: 0.24rem;
}
}
}
.loading-icon {
font-size: 0px;
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 0.72rem;
height: 0.72rem;
position: relative;
span {
position: absolute;
height: 1px;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
width: 0.18rem;
animation: loading-fade-light 1.1s infinite linear;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3);
transform-origin: -0.18rem 50%;
margin-left: 0.18rem;
&:nth-child(1) {
animation-delay: 0s;
transform: rotate(0deg);
}
&:nth-child(2) {
animation-delay: 0.1s;
transform: rotate(30deg);
}
&:nth-child(3) {
animation-delay: 0.2s;
transform: rotate(60deg);
}
&:nth-child(4) {
animation-delay: 0.3s;
transform: rotate(90deg);
}
&:nth-child(5) {
animation-delay: 0.4s;
transform: rotate(120deg);
}
&:nth-child(6) {
animation-delay: 0.5s;
transform: rotate(150deg);
}
&:nth-child(7) {
animation-delay: 0.6s;
transform: rotate(180deg);
}
&:nth-child(8) {
animation-delay: 0.7s;
transform: rotate(210deg);
}
&:nth-child(9) {
animation-delay: 0.8s;
transform: rotate(240deg);
}
&:nth-child(10) {
animation-delay: 0.9s;
transform: rotate(270deg);
}
&:nth-child(11) {
animation-delay: 1s;
transform: rotate(300deg);
}
&:nth-child(12) {
animation-delay: 1.1s;
transform: rotate(330deg);
}
}
}
@-webkit-keyframes loading-fade-light {
0% {
background-color: #fff;
}
100% {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0);
}
}
@keyframes loading-fade-light {
0% {
background-color: #fff;
}
100% {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0);
}
}
style>
入口文件注册:
import vueToast from '@/components/vue-toast'
Vue.use(vueToast);
React 插件toast的封装
Toast/index.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import Toast from './toast';
export default class Global {
static toastEle='';
static toast(option) {
var setting={
type:0,
content:"默认信息",
time:2000,
opacity:0,
onSucc:()=>{}
};
if(typeof option =="string"){
setting={...setting,content:option,type:4}
}else{
setting={...setting,...option}
}
this.show(0,setting);
if(setting.type!==3){ //loading需要手动关闭
setTimeout(() => {
this.hide();
setting.onSucc();
}, setting.time);
}
}
static dialog(option) {
var setting={
type:0,
title:"我是默认title",
content:"我是默认content",
btnSucc:"我是默认btn",
CloseShow:false,
onClose(){
console.log("蒙层回调");
},
onSucc(){
console.log("成功回调");
},
onFail(){
console.log("失败回调");
}
};
setting={...setting,...option};
this.show(1,setting);
}
static show(n,setting) {
var div = document.createElement('div');
var id = document.createAttribute("id");
this.toastEle='pluginEle-'+new Date().getTime();
id.value = this.toastEle;
div.setAttributeNode(id);
document.body.appendChild(div);
ReactDOM.render(<Toast setting={setting} />, div);
}
static hide() {
var toastEle = document.querySelector("#"+this.toastEle);
if(toastEle){
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(toastEle);
document.body.removeChild(toastEle);
}
}
}Toast/toast.js
import React from "react";
import './toast.less'
export default class Toast extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
checkToast(n) {
switch(n) {
case 0:
return (<div className="icon"><div className="success-icon">div>div>)
break;
case 1:
return (<div className="icon"><div className="fail-icon">div>div>)
break;
case 2:
return (<div className="icon"><div className="warning-icon">div>div>)
break;
case 3:
return (
<div className="loading-icon"><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span><span>span>div>
)
break;
default:
return null
}
}
render() {
let {
type,content,opacity = 0
} = this.props.setting;
let style = {
"background": `rgba(0,0,0,${opacity})`
}
return(
<div className="mask" style={style}><div className="toast">
{this.checkToast(type)}<div className="msg">{content}div>div>div>
);
}
}
Toast/toast.less
.mask {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
position: fixed;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
z-index: 10000;
.toast-msg {
font-size: 24px;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
transform: translateX(-50%);
color: #fff;
left: 50%;
padding:18px 27px;
overflow: hidden;
border-radius: 4px;
white-space: nowrap;
display: block;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
}
.toast {
font-size: 0px;
padding: 27px 9px;
width: 226px;
overflow: hidden;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
flex-direction: column;
color: #f2f2f2;
background: rgba(51, 51, 51, 0.94);
border-radius: 9px;
text-align: center;
.icon {
width:72px;
height:72px;
border-radius: 50%;
border: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
position: relative;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
position: relative;
margin-bottom: 18px;
.success-icon {
border-right: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
transform: rotate(45deg);
width:27px;
height: 45px;
margin-top: -18px;
}
.fail-icon {
&:before {
content: " ";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) rotate(45deg);
border-top: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
width: 50px;
height: 0px;
}
&:after {
content: " ";
content: " ";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%) rotate(-45deg);
border-top: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
width: 50px;
height: 0px;
}
}
.warning-icon {
&:before {
content: "";
display: block;
position: absolute;
top: 15px;
left: 50%;
background:#f2f2f2;
width:1px;
height: 30px;
}
&:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
bottom: 14px;
left: 50%;
background:#f2f2f2;
width: 6px;
margin-left: -2px;
border-radius: 50%;
height: 6px;
}
}
}
.msg {
font-size:24px;
}
}
}
.loading-icon {
font-size: 0px;
margin-bottom: 18px;
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 72px;
height: 72px;
position: relative;
span {
position: absolute;
height: 1px;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
width: 18px;
animation: loading-fade-light 1.1s infinite linear;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3);
transform-origin: -18px 50%;
margin-left: 18px;
&:nth-child(1) {
animation-delay: 0s;
transform: rotate(0deg);
}
&:nth-child(2) {
animation-delay: 0.1s;
transform: rotate(30deg);
}
&:nth-child(3) {
animation-delay: 0.2s;
transform: rotate(60deg);
}
&:nth-child(4) {
animation-delay: 0.3s;
transform: rotate(90deg);
}
&:nth-child(5) {
animation-delay: 0.4s;
transform: rotate(120deg);
}
&:nth-child(6) {
animation-delay: 0.5s;
transform: rotate(150deg);
}
&:nth-child(7) {
animation-delay: 0.6s;
transform: rotate(180deg);
}
&:nth-child(8) {
animation-delay: 0.7s;
transform: rotate(210deg);
}
&:nth-child(9) {
animation-delay: 0.8s;
transform: rotate(240deg);
}
&:nth-child(10) {
animation-delay: 0.9s;
transform: rotate(270deg);
}
&:nth-child(11) {
animation-delay: 1s;
transform: rotate(300deg);
}
&:nth-child(12) {
animation-delay: 1.1s;
transform: rotate(330deg);
}
}
}
@-webkit-keyframes loading-fade-light {
0% {
background-color: #fff;
}
100% {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0);
}
}
@keyframes loading-fade-light {
0% {
background-color: #fff;
}
100% {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0);
}
}
使用
import $ from '@/component/Toast/index';
...
$.toast({
type:0,
content: "我是默认Toast",
time: 1000,
opacity: .5,
onSucc() {
console.log("我是Toast的回调!")
}
});
$.toast("我是默认Toast");
为什么不挂载在React原型链上?
有坑!主要原因还是React组件的this神出鬼没!
ES6 toast插件
var body = document.body
var tip
var timeout
var time = 3000
var setStyleTime = 50
function Tip (str, time) {
if (tip) {
clearTimeout(timeout)
// tip.find('p').html(str);
} else {
tip = document.createElement('div')
tip.className = '__toast'
tip.innerHTML = str
// tip.style.cssText = 'z-index: 999;position: fixed;webkit-transition: opacity .3s ease;transition: opacity .3s ease;opacity: 0;color: #fff;border-radius: 8px;left: 50%;width: 80%;margin-left: -40%; /*px*/text-align: center;line-height: 1.5;background: rgba(0,0,0,.6);padding: 1% 1%;top: 45%;box-sizing: border-box;font-size: 1.5em;';
body.appendChild(tip)
setTimeout(function () {
tip.style.opacity = 1
}, setStyleTime)
}
timeout = clear(time)
}
function clear (time) {
return setTimeout(remove, time)
}
function remove () {
if (tip) {
body.removeChild(tip)
tip = null
}
}
function entry (msg, expire) {
msg = msg || ''
if (!expire || expire <= setStyleTime) {
expire = time
}
Tip(msg, expire)
};
export default entry
附:React开发技巧
自动注册全局组件或函数 require.context
我的业务场景大部分是中后台,虽然封装和使用了很多第三方组件,但还是免不了需要自己封装和使用很多业务组件。但每次用的时候还需要手动引入,真的是有些麻烦的。
/**
* @desc webpack打包入口文件
* @example 自动引入子目录下所有js文件
*/
let moduleExports = {};
const r = require.context('./', true, /^\.\/.+\/.+\.js$/);
r.keys().forEach(key => {
let attr = key.substring(key.lastIndexOf('/') + 1, key.lastIndexOf('.'));
moduleExports[attr] = r(key);
});
module.exports = moduleExports;
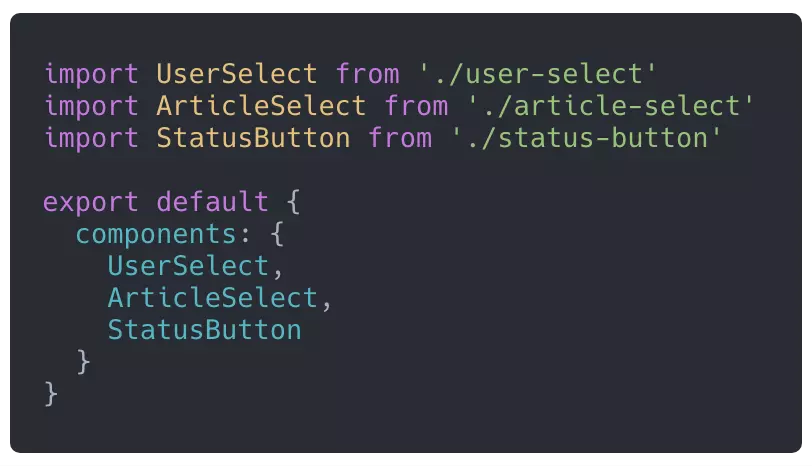
我们其实可以基于 webpack 的require.context来实现自动加载组件并注册的全局的功能。相关原理在之前的文章中已经阐述过了。具体代码如下
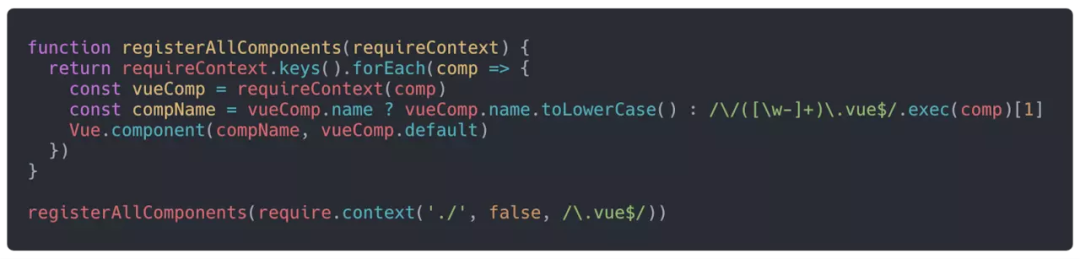 我们可以创建一个GlobalComponents文件夹,将你想要注册到全局的组件都放在这个文件夹里,在index.js里面放上如上代码。之后只要在入口文件main.js中引入即可。
我们可以创建一个GlobalComponents文件夹,将你想要注册到全局的组件都放在这个文件夹里,在index.js里面放上如上代码。之后只要在入口文件main.js中引入即可。
//main.js
import './components/Table/index' // 自动注册全局业务组件
这样我们可以在模板中直接使用这些全局组建了。不需要再繁琐的手动引入了。
一把梭改变state值
this.setState({
[name]: value
});
const { data } = this.state;
this.setState({ data: {...data, key: 1 } });
另外一种可以通过callback的方式改变state的值
this.setState(({ data }) => ({ data: {...data, key: 1 } }));
还可以:
this.setState((state, props) => {
return { counter: state.counter + props.step };
});
还可以一把梭:
this.state.a=1;
this.state.b="张三";
this.state.c=true;
this.state.xxx=...
...
this.setState(this.state); //一把梭
this.setState支持异步async await
this.setState((prevState) => ({
isFiltered: !prevState.isFiltered
}), () => {
this.filterData();
});
clickMe=(e)=>{
this.setState((prevState)=>{
return {num:prevState.num+1}
});
}
async clickMe1(){
await this.setState((prevState)=>{
return {num:prevState.num+1}
});
await this.setState((prevState)=>{
return {num:prevState.num+1}
});
await this.setState((prevState)=>{
return {num:prevState.num+1}
});
}
唯一key
react数组循环,基本都会设置一个唯一的key,表格的对象数组循环一般没什么问题,数据基本都会有一个id。那有种情况就比较坑了,出现在表单形式的页面结构中,对某个数组进行增删改操作,一般对于非对象数组而言,没有id,可能很多人会偷懒,循环的时候,直接设置数组的下标index作为key,当出现增删改时候,就会出现数据对不上或者重新渲染组件的问题等。解决方案有很多种,例如把字符串数组等重组对象数组,每个元素设置一个唯一id等。另外有个方式:推荐使用shortid生成唯一key的数组,和数据数组一起使用,省去提交数据时再重组数组。
import React from 'react';
import shortid from 'shortid';
class Demo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
data: ['a', 'b', 'c']
}
this.dataKeys = this.state.data.map(v => shortid.generate());
}
deleteOne = index => { // 删除操作
const { data } = this.state;
this.setState({ data: data.filter((v, i) => i !== index) });
this.dataKyes.splice(index, 1);
}
render() {
return (
<ul>
{
data.map((v, i) => <li onClick={i => this.deleteOne(i)}
key={this.dataKeys[i]}
>
{v}li>
)
} ul>
)
}
}
// 稍微抽取,可以封装一个通用的组件
三目运算
通过判断值是否存在来控制元素是否显示,一般三目运算可以达到此效果,最简单的还是用短路的写法:
// 不错
const flag = 'something';
flag && <div>div>
// 很好
// 注意一般可能上面写法多一些,但当flag为0 的时页面上会显示0,用!!将其转为boolean避免坑,
// 代码也更规范
const flag = 'something';
!!flag && <div>div>
使用组件,传递props
const { data, type, something } = this.state;
<Demo data={data}type={type}something={something}
/>也许另外一种传递方式更简洁:
const { data, type, something } = this.state;
<Demo
{...{ data, id, something }}
/>简化props
组件的props有时候会定义很多,但是调用组件传递props的时候又想一个个传,不想一次性传递一个option对象,通过扩展运算符和解构赋值可以简化此操作:
const Demo = ({ prop1, prop2, prop3, ...restProps }) => (
<div>
xxxx
{ restProps.something }div>
)
// 父组件使用Demo
prop1={xxx}
prop2={xxx}
something={xxx}
/>
优化React 性能
React 性能优化有很多种方式,那常见的一种就是在生命周期函数shouldComponentUpdate里面判断某些值或属性来控制组件是否重新再次渲染。
判断一般的字符串,数字或者基础的对象,数组都还是比较好处理,那嵌套的对象或者数组就比较麻烦了,对于这种,可以转成字符串处理,但属性值的位置不同时,那就无效了。
推荐使用lodash(或者其他的类似库)的isEqual对嵌套数组或对象进行判断(相比其他方式更简单些)
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (_.isEqual(nextState.columns, this.state.columns)) return false;
return true;
}
创建弹层
创建弹层的三种方式:
1.普通组件通过state和样式控制,在当前组件中显示弹层-每次引入组件并且render里面控制显示,挂载节点在某组件里面
// 弹层
const Dialog = () => <div>弹层div>
// 某组件
render() {
return (
this.state.showDialog && <Dialog />
)
}2.通过Portals创建通道,在根节点外部挂载组件-但还是需要每次引入并且在render里面调用
// 弹层
class Dialog extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.el = document.createElement('div');
}
componentDidMount() {
modalRoot.appendChild(this.el);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
modalRoot.removeChild(this.el);
}
render() {
return ReactDOM.createPortal(
this.props.children || <div>xxxxdiv>,
this.el,
);
}
}
// 某组件
render() {
return (
this.state.showDialog && <Dialog />
)
}3.推荐使用ReactDom.render创建弹层-挂载根节点外层,使用也更方便
// demo
let dialog;
class Dialog {
show(children) { // 显示
this.div = document.createElement('div');
document.body.appendChild(this.div);
ReactDom.render(children || <div>xxxxdiv>, this.div);
}
destroy() { // 销毁
ReactDom.unmountComponentAtNode(this.div);
this.div.parentNode.removeChild(this.div);
}
}
export default {
show: function(children) {
dialog = new Dialog();
dialog.show(children);
},
hide: xxxxx
};
// 某组件
import Dialog from 'xxx';
alert = () => {
Dialog.show(xxxx);
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.alert}>点击弹层button>
)
}
插槽:children
render props是现在很流行的一种渲染方式,通过回调函数,渲染子组件,参数可为父组件的任意属性值(官网也有相应的介绍)新版的contextApi也采用了这个模式。
很多种场景使用此方式的做法:
// 权限控制组件,只需要封装一次connect,
// 通过render props向子组件传递权限
class AuthWidget extends Component {
render() {
return this.props.children(this.props.auth);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
const { auth } = state;
return { auth: state.auth };
};
export default connect(mapStateToProps)(AuthWidget);
// 其他组件使用
children={auth => auth.edit && 编辑}
/>
// 使用antd的form时
const Test = ({ form, children }) => {
return children(form);
};
const FormTest = Form.create()(Test);
class Demo extends Component {
render() {
return (
xxxxx
{ form => {
this.form = form;
return (
{getFieldDecorator('field', xxx)(
)}
)
}}
)
}
}
子组件改变父组件的state
子组件改变父组件的state方式有很多种,可以在父组件设置一个通用函数,类似:setParentState,通过子组件回调处理时,就可以更方便的统一处理:
// 父组件
state = {
data: {}
}
setParentState = obj => {
this.setState(obj);
}
// 子组件
onClick = () => {
this.props.setParentState({ data: xxx });
}
永远不要直接设置state的值
永远不要直接设置state的值:this.state.data = { a: 1 }。这个会导致几个问题: 1:组件不会重新渲染
2:shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) 函数里面 this.state的值是已经改变了,和nextState的值相同。
举个栗子:
// wrong
const { data } = this.state;
data.a = 1; // 等价于this.state.data.a = 1;
this.setState({ data });
// shouldComponentUpdate里面观察到 this.state 和nextState的值是相同的
// 此时函数里面性能相关的优化是无效的
// correct 需要用到当前state值的写法
this.setState(state => ({ data: {...state.data, a: 1} }))

周期性边界条件.)






)







![altium导出钻孔文件_[Altium Designer 学习]怎样输出Gerber文件和钻孔文件](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/altium导出钻孔文件_[Altium Designer 学习]怎样输出Gerber文件和钻孔文件)


