Spring深入理解之ComponentScan
一、概述
ComponentScan顾名思义包扫描,底层其实就可以通过递归算法+反射将其装载成bean来实现的,实在开发过程中,Spring已经帮我们实现好了,我们其实就可以直接使用XML或者注解的形式来进行业务处理。
二、@ComponentScan的作用
@ComponentScan注解有两个作用
作用一:扫描含有@Component,@Controller,@Service和@Repository的类,并将其注入到spring容器中。
作用二:扫描含有@Configuration的类,并使其生效。
分析:作用一相信大家都明白其含义,再次不在赘述。作用二举例说明,例如Config2可以扫描到config2_test目录,该目录下不仅含有@Component,@Controller,@Service和@Repository注解标注的四个类,还包含Config1配置类。Config1配置类,可以扫描到config1_test目录,并且里面还包含一个@Bean注解。
三、同一个配置类上多个@ComponentScan可能会报错
下面的配置类在我公司电脑的idea版本里是可以将config3_test目录下的所有类都注册到spring容器中,但是在我家里的电脑上以及另一个同事的电脑上会报编译期错误,代码运行也会出错。
四、@ComponentScans的使用
由于同一个类上直接写多个@ComponentScan可能会报错,因此建议使用@ComponentScans,它可以解决直接在一个配置类上写多个@ComponentScan在有些电脑或idea版本上报错的问题。
@ComponentScan 详解
@ComponentScan 的作用就是根据定义的扫描路径,把符合扫描规则的类装配到spring容器中,注解定义如下。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
public @interface ComponentScan {@AliasFor("basePackages")String[] value() default {};@AliasFor("value")String[] basePackages() default {};Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> scopeResolver() default AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class;ScopedProxyMode scopedProxy() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT;String resourcePattern() default "**/*.class";boolean useDefaultFilters() default true;ComponentScan.Filter[] includeFilters() default {};ComponentScan.Filter[] excludeFilters() default {};boolean lazyInit() default false;@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target({})public @interface Filter {FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION;@AliasFor("classes")Class<?>[] value() default {};@AliasFor("value")Class<?>[] classes() default {};String[] pattern() default {};}
}
basePackages与value: 用于指定包的路径,进行扫描
basePackageClasses: 用于指定某个类的包的路径进行扫描
nameGenerator: bean的名称的生成器
useDefaultFilters: 是否开启对@Component,@Repository,@Service,@Controller的类进行检测
includeFilters: 包含的过滤条件
- FilterType.ANNOTATION:按照注解过滤
- FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE:按照给定的类型
- FilterType.ASPECTJ:使用ASPECTJ表达式
- FilterType.REGEX:正则
- FilterType.CUSTOM:自定义规则
excludeFilters: 排除的过滤条件,用法和includeFilters一样
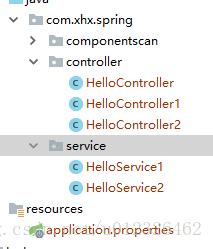
我的工程结构如下,测试对controller和service的扫描,其中HelloController没有加@Controller等任何注解,就是一个普通类。
修改配置类如下:应用默认的过滤器,扫描service包:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring.service",useDefaultFilters = true
)
public class MyConfig {
}
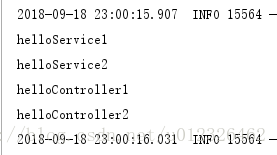
系统注入了两个service进去

改成如下所示:HelloController所在的包的类也被扫描了进去
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring.service",useDefaultFilters = true,basePackageClasses = HelloController.class
)
public class MyConfig {
}
系统中会注入下面就给类
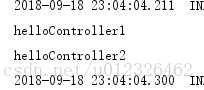
把默认的过滤器关掉,扫描带Controller注解的。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring",useDefaultFilters = false,includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})}
)
public class MyConfig {
}
按照类的类型扫描,虽然HelloController没有加注解,但是被注入到了spring容器中
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring",useDefaultFilters = false,includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes = {HelloController.class})}
)
public class MyConfig {
}
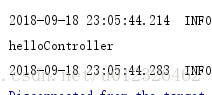
自定义扫描过滤器
package com.xhx.spring.componentscan.config;import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;import java.io.IOException;public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter {@Overridepublic boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {String className = metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName();if(className.contains("Controller")){return true;}return false;}
}
修改配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring",useDefaultFilters = false,includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {MyTypeFilter.class})}
)
public class MyConfig {
}
输出结果:
输出spring容器中的bean的测试类:只过滤输出了名字中含有hello的类。
package com.xhx.spring.componentscan;import com.xhx.spring.componentscan.config.MyConfig;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ComponentScanApplicationTests {@Testpublic void testLoads() {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);List<String> hello = Arrays.stream(context.getBeanDefinitionNames()).collect(Collectors.toList());hello.stream().filter(name->name.contains("hello")).peek(System.out::println).count();}}



















