R相关小教程链接:
用R构建气泡图案例小教程
【小教程】散点图、饼图怎么在我的文章中完美展示小教程
热图在论文发表中完美呈现小教程
R与密度、函数、变量的微妙关系
北京市计算中心医用数据库建设解决方案
更多内容,请关注“生信会议”公众号
Different types of 2d density chart. Source
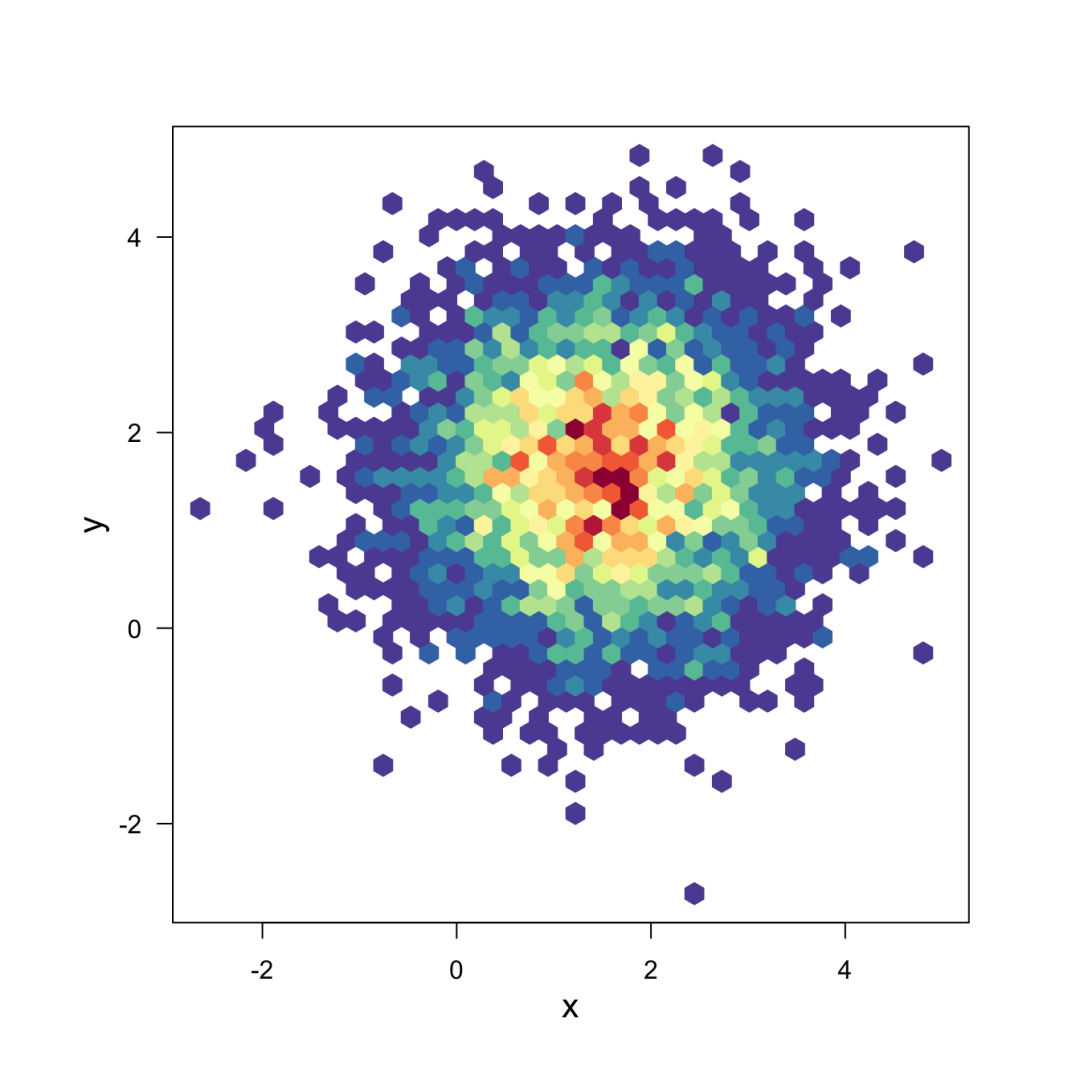
Density 2d
2d密度图显示了两个数值变量之间的关系。一个在X轴上,另一个在Y轴上,就像散点图一样。然后,在二维空间的特定区域内观察到的数量被计数并由颜色梯度表示。二维密度图有几种类型:
01
Definition
Definition
此页面专门用于一组图形,允许研究两个定量变量的组合分布。这些图形基本上是众所周知的密度图和直方图的扩展。
对于每个变化,全局概念是相同的。一个变量在X轴上表示,另一个变量在Y轴上表示,就像散射图(1)一样)。然后,计算二维空间特定区域内的观测数,并用颜色梯度表示。形状可以变化:
· 六边形经常被使用,导致一个六边形图表(2)
· 正方形制作2d直方图(3)
· 计算核密度估计也可以得到2d密度图(5)或等高线图(6)
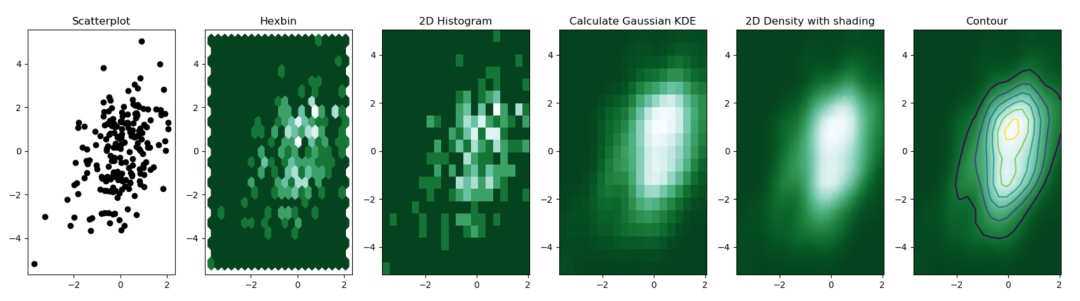
以下是这些不同可能性的概述
# Librariesimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom scipy.stats import kde
# Create data: 200 points
data = np.random.multivariate_normal([0, 0], [[1, 0.5], [0.5, 3]], 200)
x, y = data.T
# Create a figure with 6 plot areas
fig, axes = plt.subplots(ncols=6, nrows=1, figsize=(21, 5))
# Everything starts with a Scatterplot
axes[0].set_title('Scatterplot')
axes[0].plot(x, y, 'ko')# Thus we can cut the plotting window in several hexbins
nbins = 20
axes[1].set_title('Hexbin')
axes[1].hexbin(x, y, gridsize=nbins, cmap=plt.cm.BuGn_r)
# 2D Histogram
axes[2].set_title('2D Histogram')
axes[2].hist2d(x, y, bins=nbins, cmap=plt.cm.BuGn_r)
# Evaluate a gaussian kde on a regular grid of nbins x nbins over data extents
k = kde.gaussian_kde(data.T)
xi, yi = np.mgrid[x.min():x.max():nbins*1j, y.min():y.max():nbins*1j]
zi = k(np.vstack([xi.flatten(), yi.flatten()]))
# plot a density
axes[3].set_title('Calculate Gaussian KDE')
axes[3].pcolormesh(xi, yi, zi.reshape(xi.shape), cmap=plt.cm.BuGn_r)
# add shading
axes[4].set_title('2D Density with shading')
axes[4].pcolormesh(xi, yi, zi.reshape(xi.shape), shading='gouraud', cmap=plt.cm.BuGn_r)
# contour
axes[5].set_title('Contour')
axes[5].pcolormesh(xi, yi, zi.reshape(xi.shape), shading='gouraud', cmap=plt.cm.BuGn_r)
axes[5].contour(xi, yi, zi.reshape(xi.shape) )# save
plt.savefig("IMG/density2d.png")
02
What for
What for
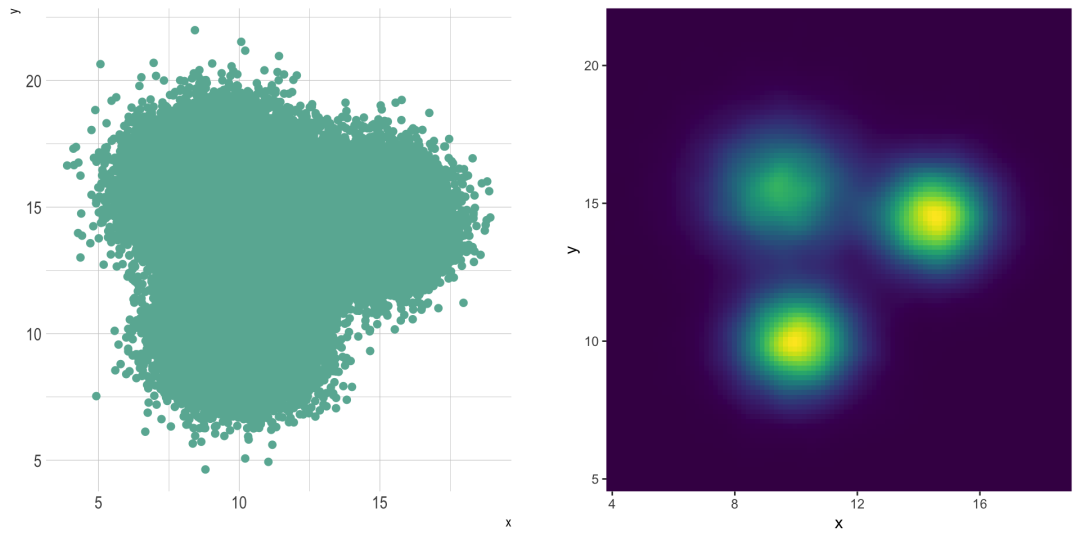
二维分布是非常有用的,以避免过度绘制在一个散射图。这里有一个例子,显示了超图散点图和2d密度图之间的区别。在第二种情况下,出现了一个非常明显的隐藏模式:
# Librarieslibrary(tidyverse)library(hrbrthemes)library(viridis)library(patchwork)
# Dataset:
a
b
c
data
p1 % ggplot( aes(x=x, y=y)) + geom_point(color="#69b3a2", size=2) + theme_ipsum() + theme(
legend.position="none"
)
p2
legend.position='none'
)
p1 + p2
03
Variation
Variation
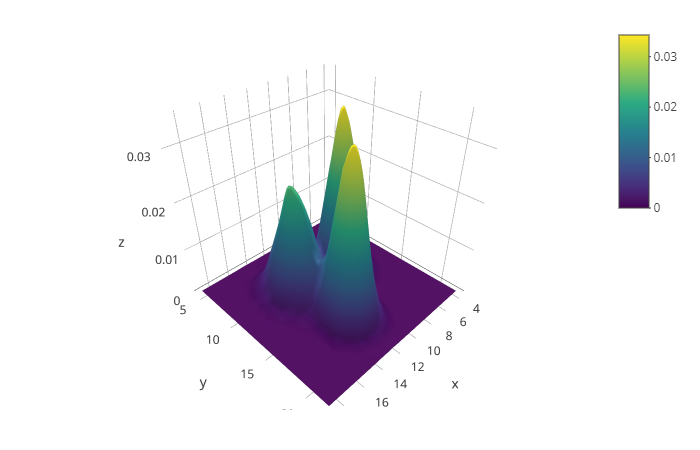
2d发行是一种罕见的值得使用3d的情况。
可以在网格中转换散点图信息,并计算网格每个位置上的数据点的数量。然后,不是用渐变颜色来表示这个数字,表面图使用3d来表示密度比其他的要高。
在这种情况下,3组的位置变得明显:
library(plotly)library(MASS)
# Compute kde2d
kd
# Plot with plotlyplot_ly(x = kd$x, y = kd$y, z = kd$z) %>% add_surface()
03
Variation
Variation

2d发行是一种罕见的值得使用3d的情况。
可以在网格中转换散点图信息,并计算网格每个位置上的数据点的数量。然后,不是用渐变颜色来表示这个数字,表面图使用3d来表示密度比其他的要高。
在这种情况下,3组的位置变得明显:
library(plotly)library(MASS)
# Compute kde2d
kd
# Plot with plotlyplot_ly(x = kd$x, y = kd$y, z = kd$z) %>% add_surface()
一、
2D HISTOGRAM WITH GEOM_BIN2D()
这是经典直方图的二维版本。地块区域被分割成许多小正方形,每个正方形中的点数由其颜色表示。
2d density plot with ggplot2
这篇文章介绍了2d密度图的概念,并解释了如何使用R和ggplot2来构建它。考虑了二维直方图、hexbin图、二维分布等。
The issue with geom_point()
如果你有大量的点,一个2d密度图对于研究两个数值变量之间的关系是有用的。
为了避免重叠(就像旁边的散点图一样),它将地块区域划分为大量的小片段,并表示该片段中的点数。
二维密度图有几种类型。每个都有自己的ggplot2功能。这篇文章描述了所有这些。
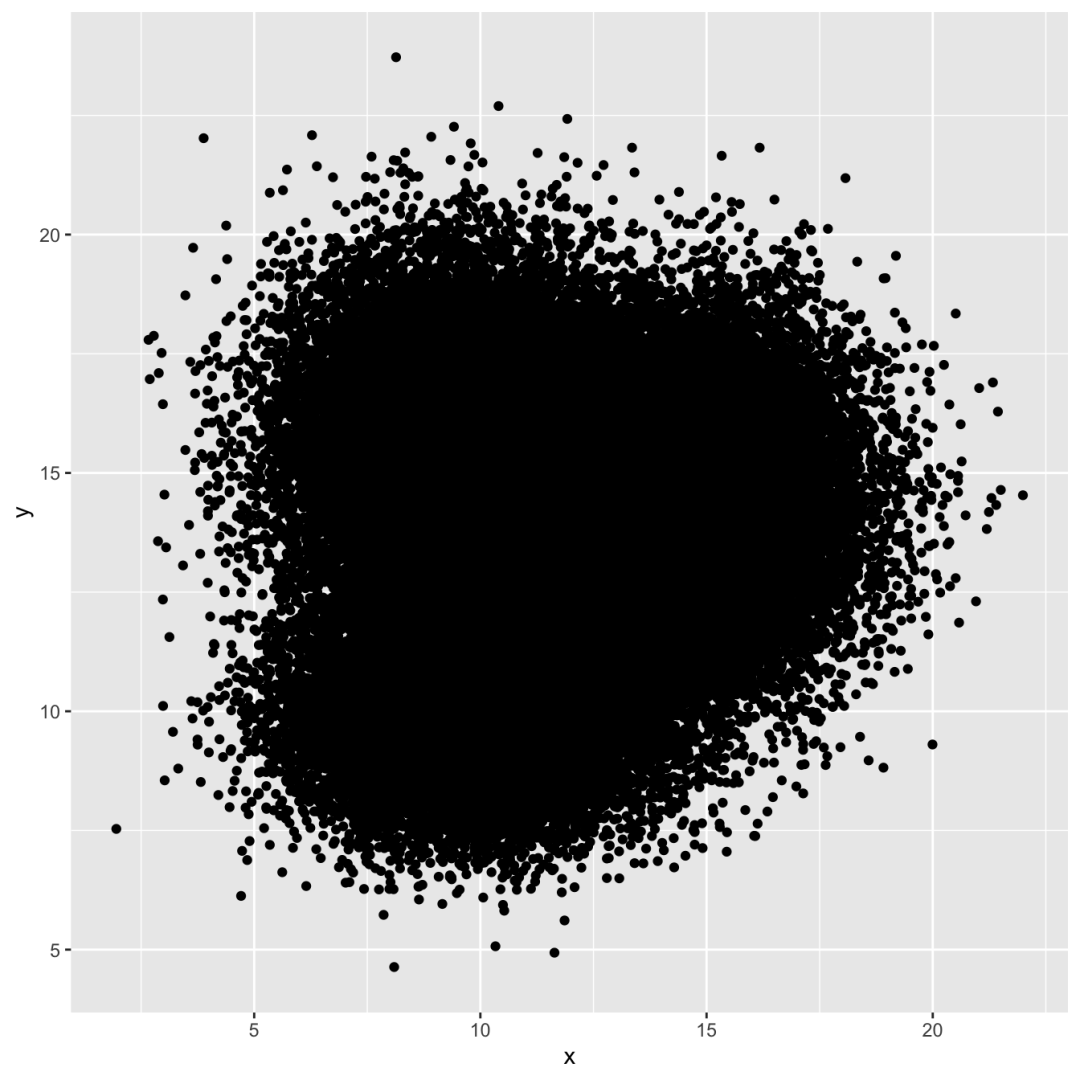
# Librarylibrary(tidyverse) # Dataa
2d Histogramwith geom_bin2d()
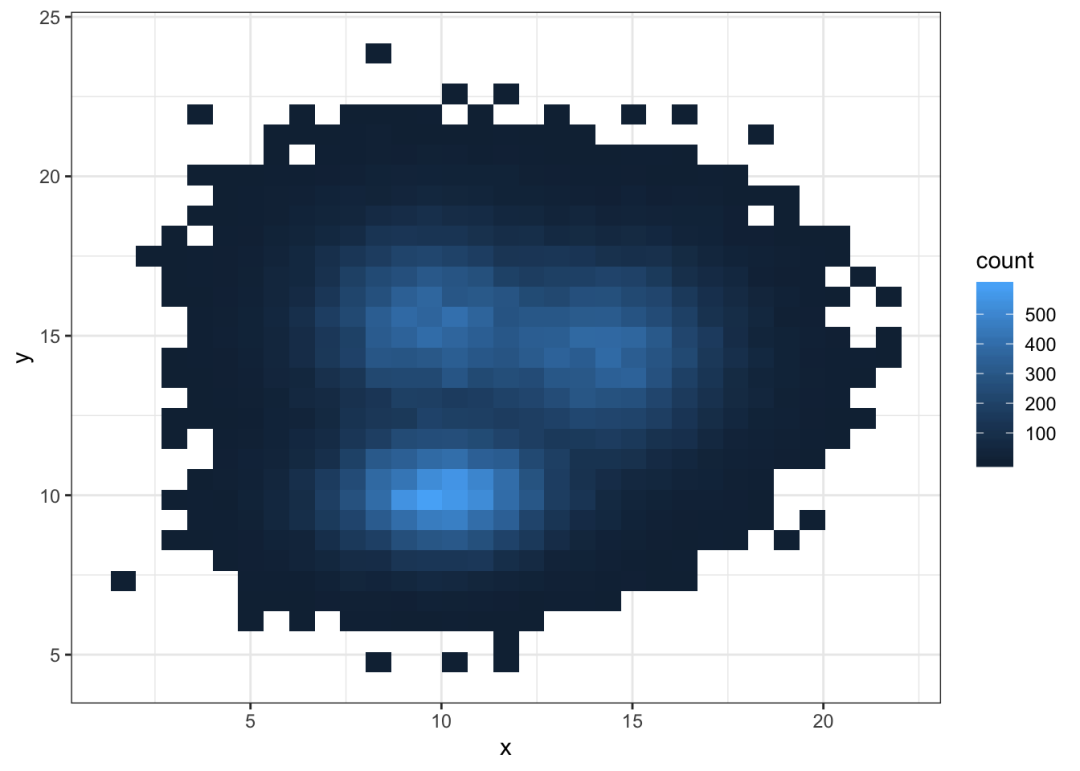
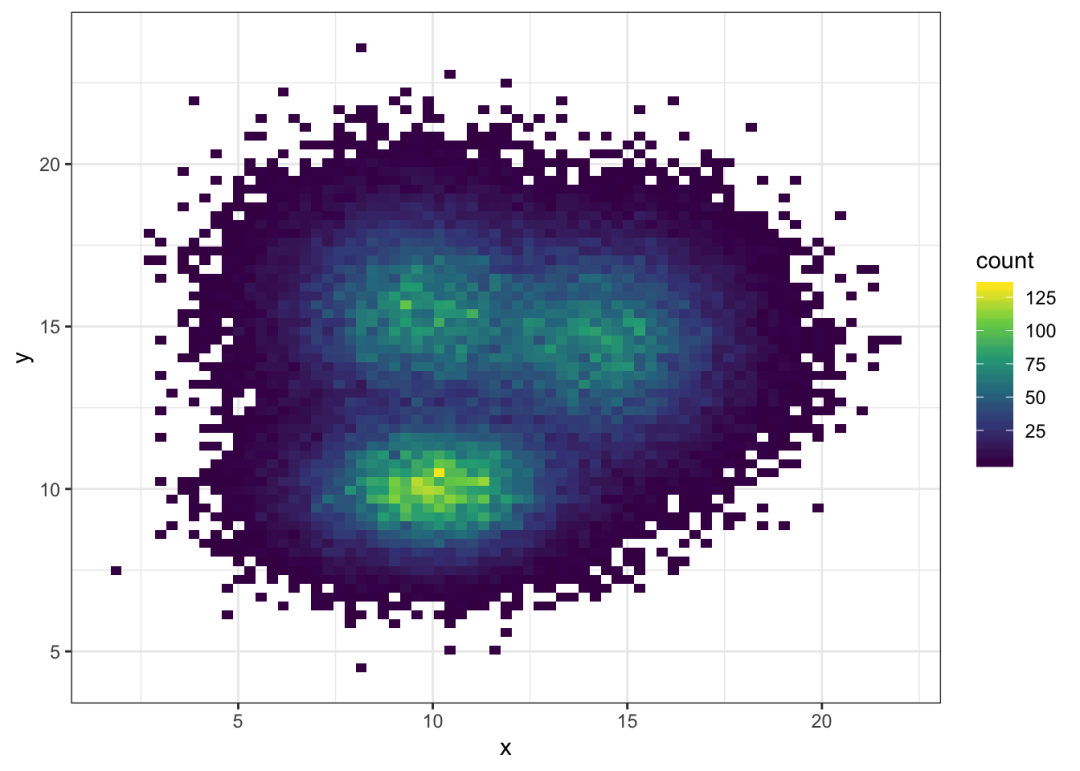
对于2d直方图,plot area被划分为多个正方形。(这是一个经典的直方图的2d版本)。使用geom_bin_2d()函数调用它。此函数提供了一个bin参数,用于控制要显示的bin的数量。
注意:如果您不相信垃圾箱选项的重要性,请阅读本文。
# 2d histogram with default optionggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + geom_bin2d() + theme_bw() # Bin size control + color paletteggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + geom_bin2d(bins = 70) + scale_fill_continuous(type = "viridis") + theme_bw()
Hexbin chart with geom_hex()
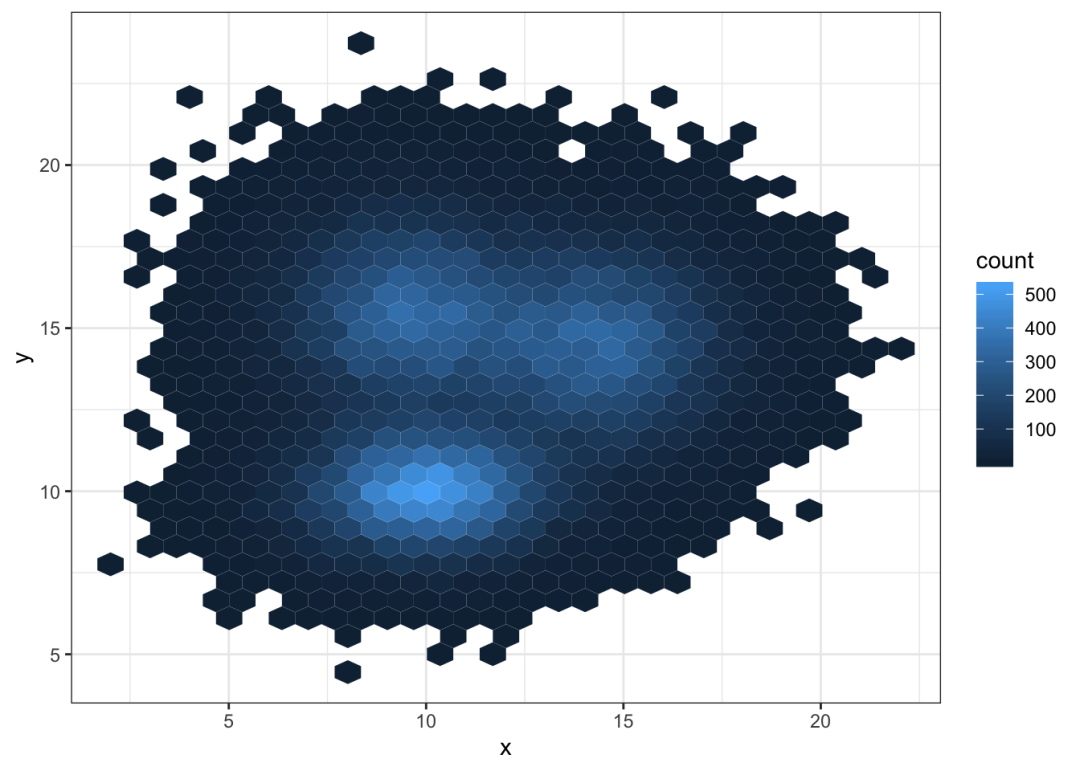
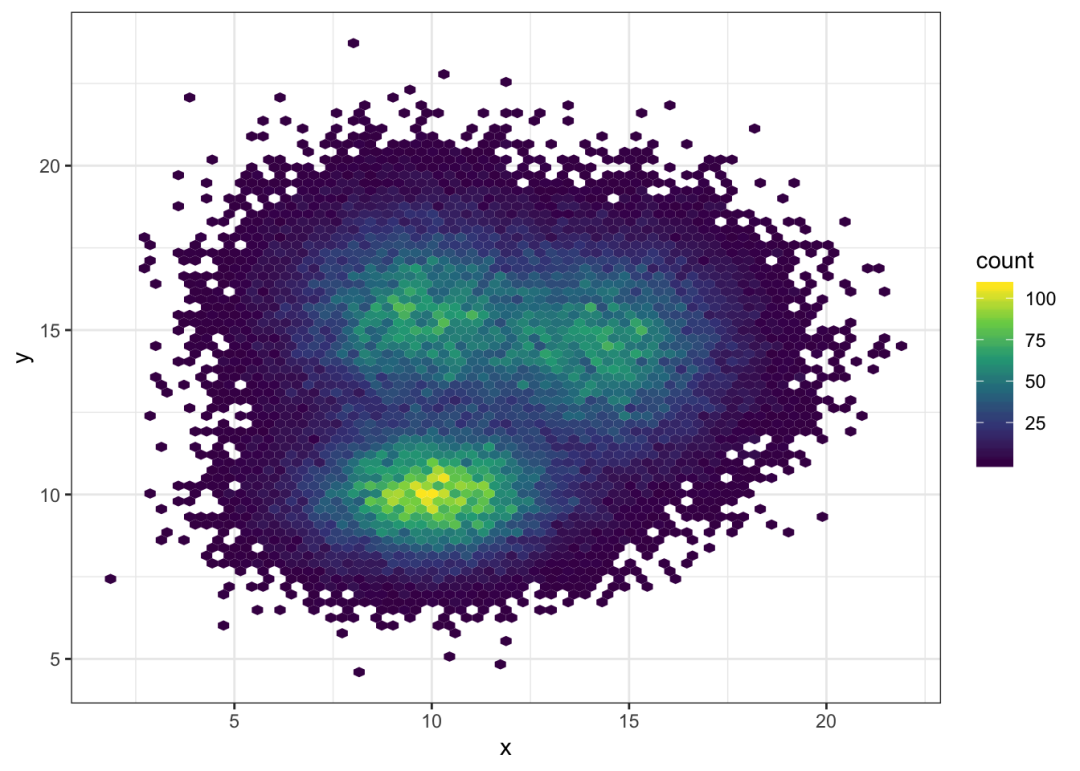
另一种方法是将地块划分为多个六边形:因此称为hexbin图,使用geom_hex()函数制作。
这个函数还提供了bin参数,用于控制每个轴的除数。
# Hexbin chart with default optionggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + geom_hex() + theme_bw() # Bin size control + color paletteggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + geom_hex(bins = 70) + scale_fill_continuous(type = "viridis") + theme_bw()
2d distribution with geom_density_2d or stat_density_2d
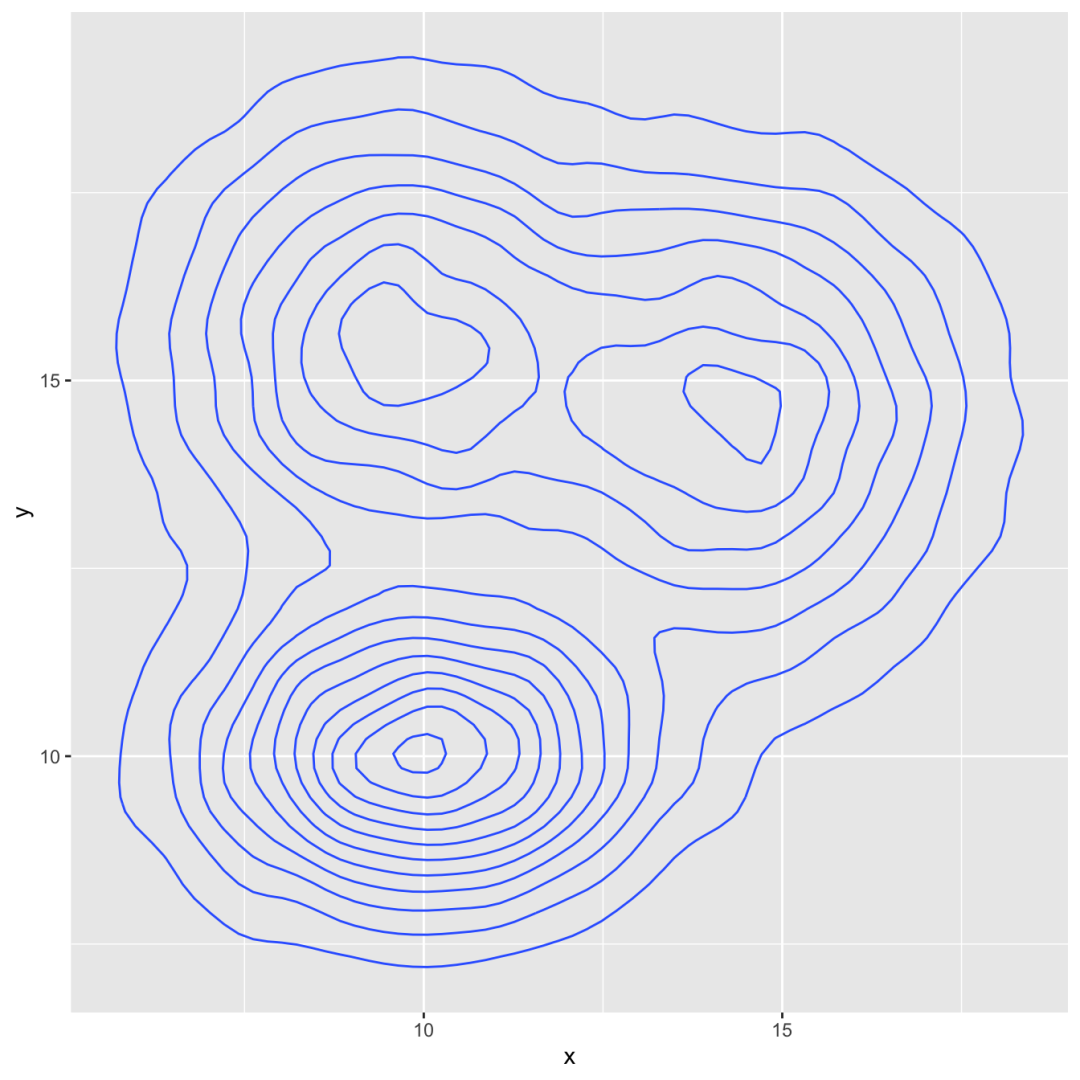
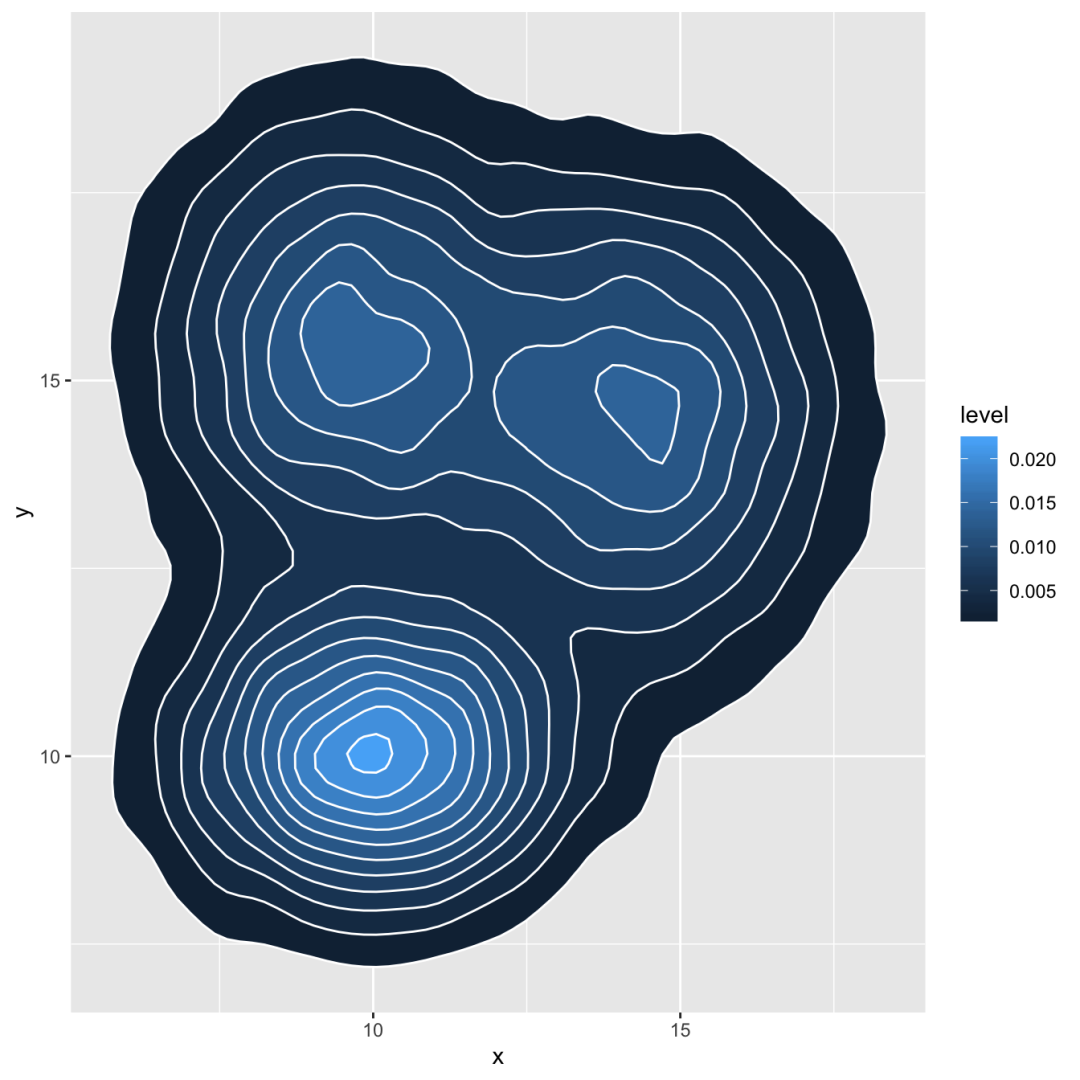
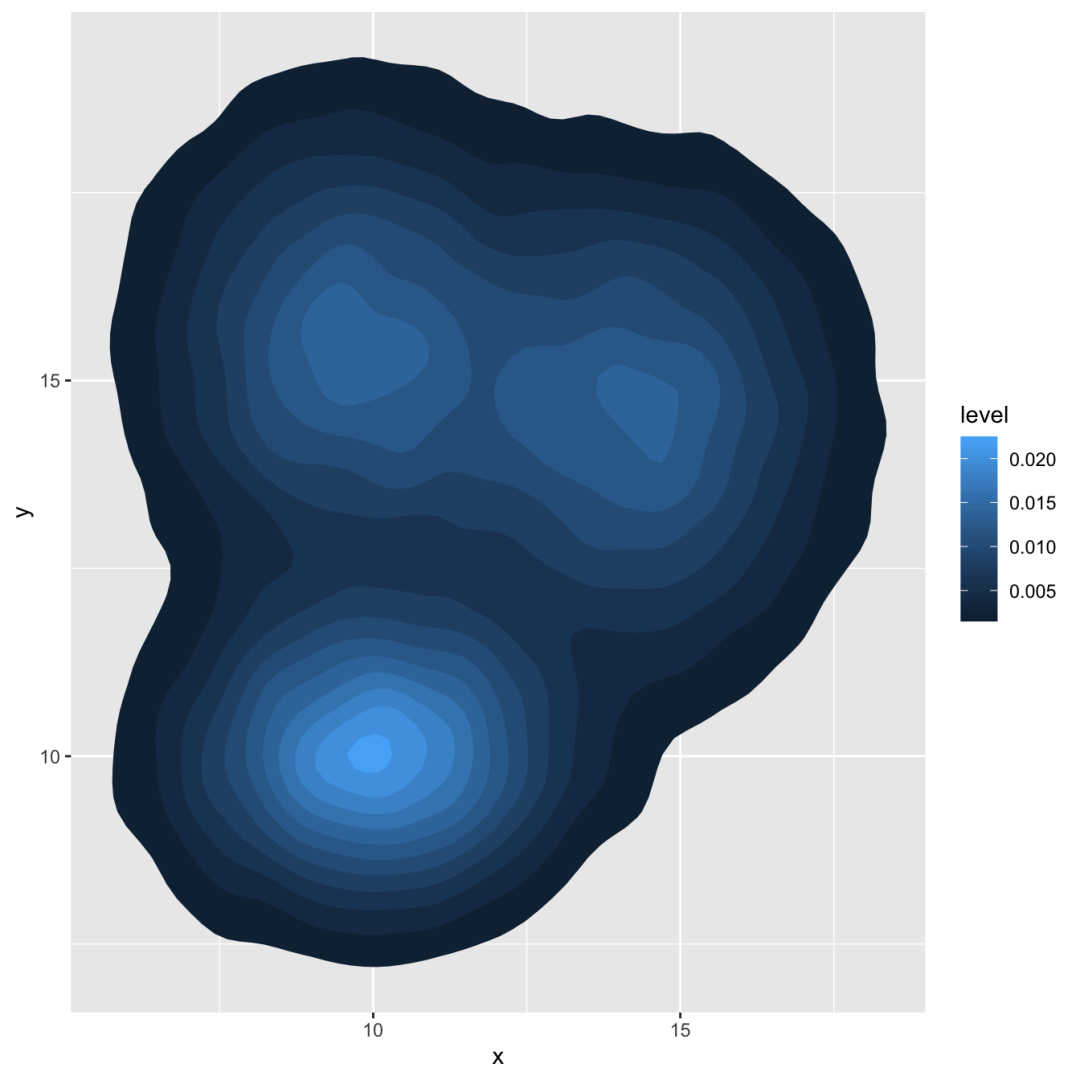
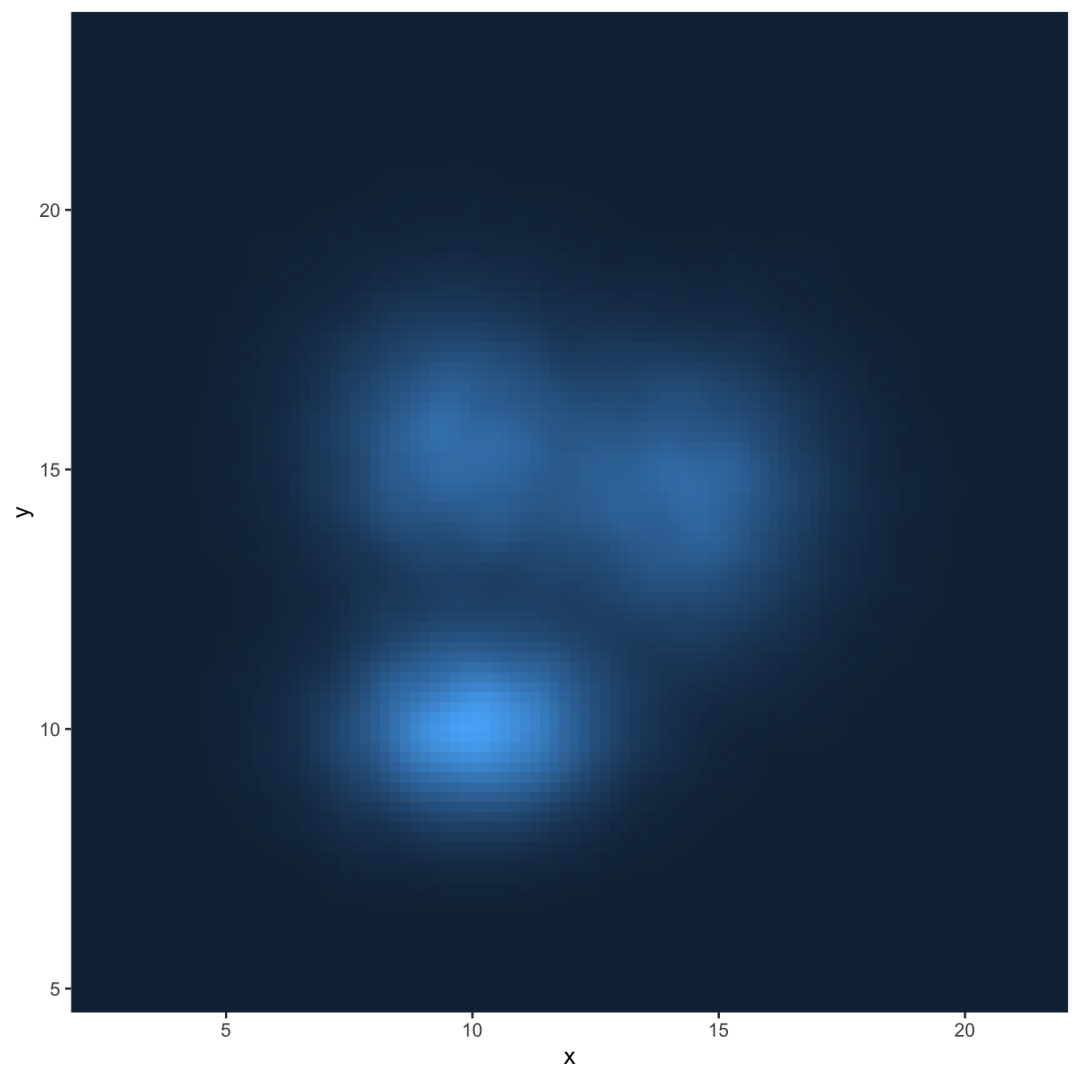
由于可以绘制密度图而不是柱状图,因此可以计算2d密度并表示它。ggplot2提供了几种可能性:您可以显示分布或区域的轮廓线,或使用光栅函数:
# Show the contour onlyggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + geom_density_2d() # Show the area onlyggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..level..), geom = "polygon") # Area + contourggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..level..), geom = "polygon", colour="white") # Using rasterggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..density..), geom = "raster", contour = FALSE) + scale_x_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + theme( legend.position='none' )
Customize the color palette
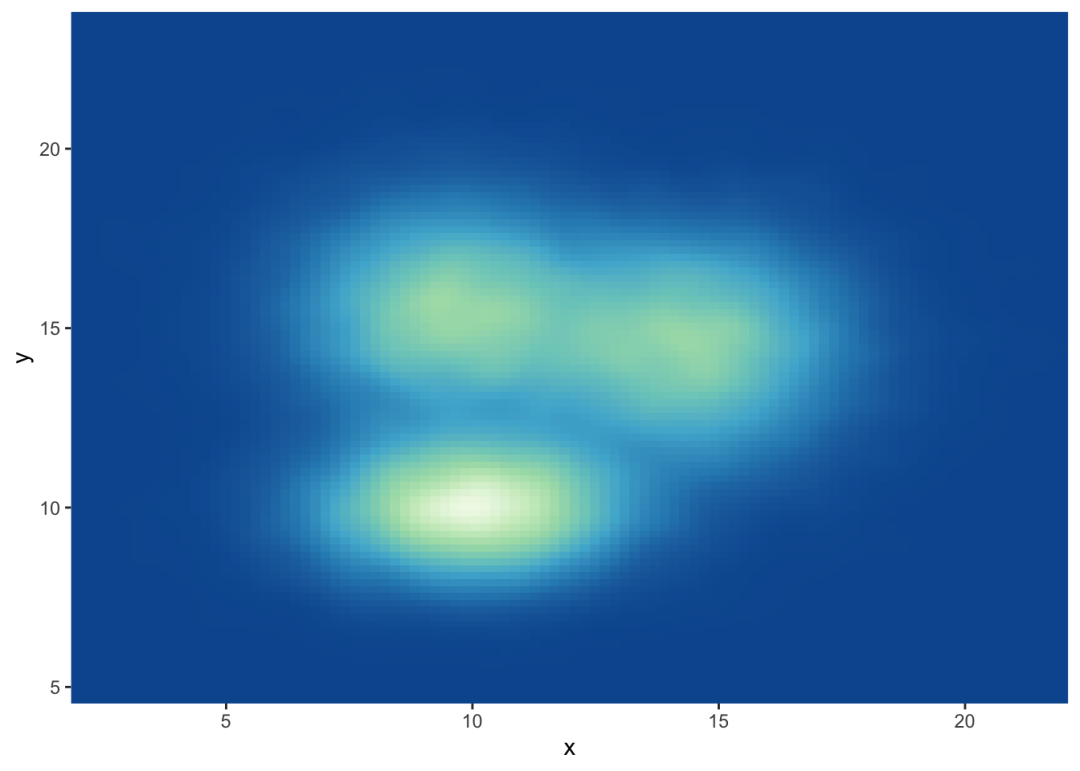
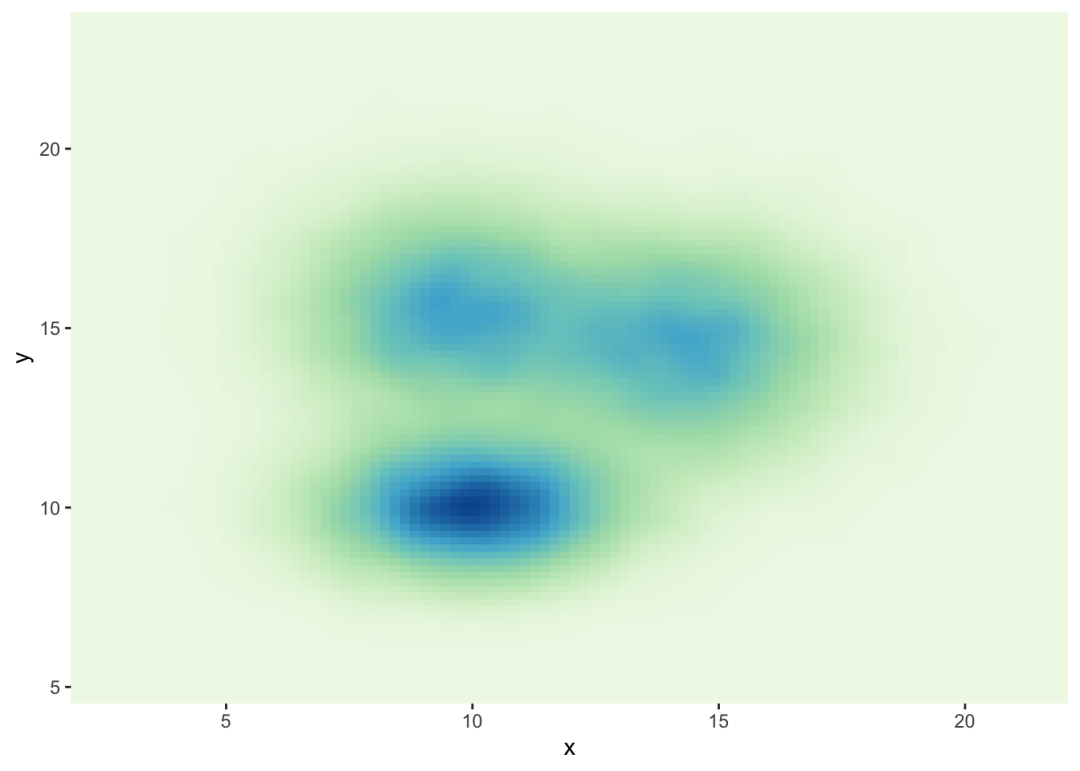
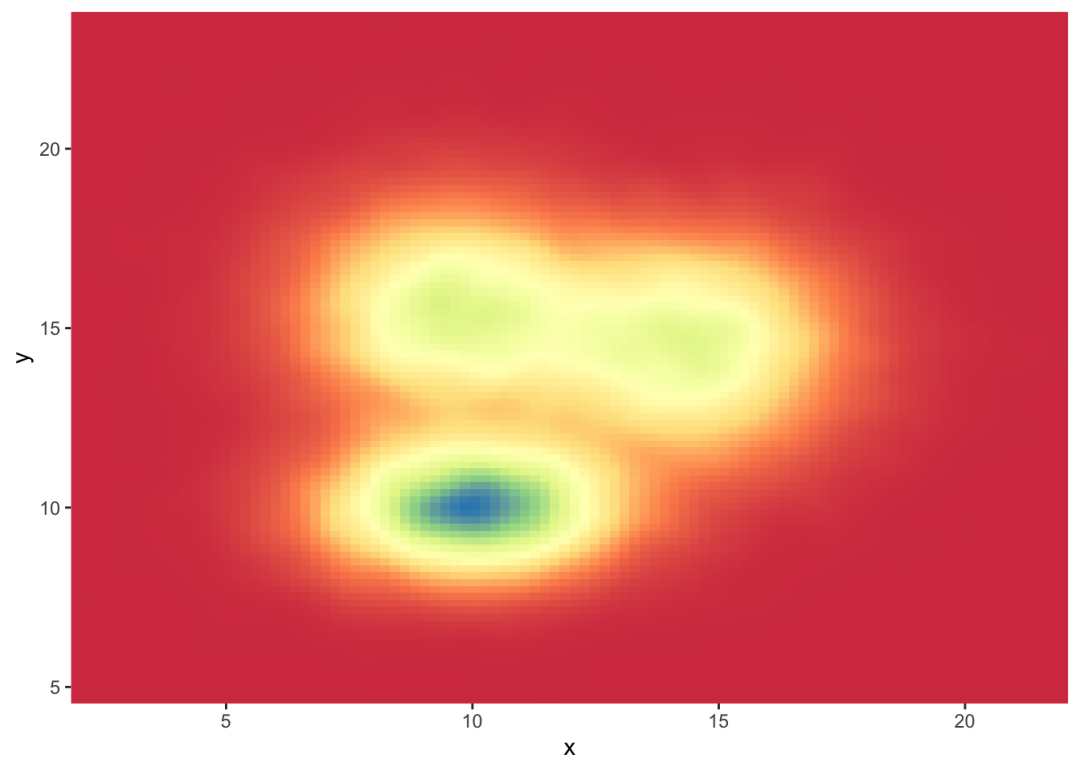
无论你使用的是2d柱状图、hexbin图还是2d分布,你都可以并且应该自定义图表的颜色。这里有一个使用scale_fill_distiller()函数的建议。您可以在图库的ggplot2部分中看到其他方法。
# Call the palette with a numberggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..density..), geom = "raster", contour = FALSE) + scale_fill_distiller(palette=4, direction=-1) + scale_x_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + theme( legend.position='none' ) # The direction argument allows to reverse the paletteggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..density..), geom = "raster", contour = FALSE) + scale_fill_distiller(palette=4, direction=1) + scale_x_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + theme( legend.position='none' ) # You can also call the palette using a name.ggplot(data, aes(x=x, y=y) ) + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..density..), geom = "raster", contour = FALSE) + scale_fill_distiller(palette= "Spectral", direction=1) + scale_x_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) + theme( legend.position='none' )
二、
OTHER EXAMPLES
Hexbin chart with the hexbin package
这篇文章解释了如何使用hexbin包用R构建hexbin图。Hexbin图是一个2d密度图,允许可视化两个数值变量之间的关系。
在显示大型数据集时,散点图很难解释,因为点不可避免地会覆盖图,而且可以??不能单独区分。
bin可以被看作是一个二维的直方图,其中容器的阴影代替了条形的高度。这种技术是在hexbin包中计算的。
这个例子已经由Myles Harrison发表在r -blogger上。

# Packageslibrary(hexbin)library(RColorBrewer) # Create datax
Hexbin chart and scatterplot with ggplot2
这篇文章解释了如何使用R和ggplot2构建一个顶部带有散点图的hexbin图。它是对使用ggplot2的2d密度图页面的一个补充。
此图扩展了使用ggplot2文档的2d密度图中描述的概念。它简单地说明了可以在二维密度图的顶部添加散点图。
# librarylibrary(ggplot2) # datasample_data
培训最新安排:
2020.10.19-23实用生物信息学研讨班
2020.10.27-30生物医学公共数据深度挖掘及应用培训班
2020.11.03-06转录组学专题实操班
2020.11.11-13生物分子互作常用软件实操班
2020.11.18-20微生物组学数据分析与挖掘专题培训班
2020.11.24-27生物信息学Python语言实操班
2020.11.25-27 10X Genomics单细胞转录组测序及多组学数据挖掘技术培训班
2020.12.02-04基因组关联分析技术应用培训班
2020.12-09-11生命科学的数据可视化与科研作图—实用工具与技巧实操班
2020.12.16-18多组学数据分析及挖掘培训班
2020.12.21-23计算机辅助设计—分子模拟与蛋白互作研讨班
2020.12.28-31数据分析与R语言制图实操班
【咨询请联系】
QQ号:2814500767
邮箱:bcc-sxpx@bcc.ac.cn
徐老师 010-59341786,15801436028(微信同号)
员老师 010-59341773,18701529461(微信同号)
技术服务
数据库构建
可提10X空间转录组
10X单细胞转录组
有参(无参)转录组
16S
基因关联分析
蛋白分子对接
同源建模
分子动力学
网络药理学
虚拟筛选等等相关技术服务、以及对应的培训学习
相关业务咨询
王老师:15001065280
邮箱:wangxf@bcc.ac.cn

?)








)

)


使用TCP传输对象)
![python量化策略源码_[Python源码] 十大经典日内策略之空中花园(附源码分享)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/python量化策略源码_[Python源码] 十大经典日内策略之空中花园(附源码分享))



