什么是bcd码数据传输通讯
传输障碍 (Transmission Impairment)
In the data communication system, analog and digital signals go through the transmission medium. Transmission media are not ideal. There are some imperfections in transmission mediums. So, the signals sent through the transmission medium are also not perfect. This imperfection cause signal impairment.
在数据通信系统中,模拟和数字信号通过传输介质。 传输媒体并不理想。 传输介质存在一些缺陷。 因此,通过传输介质发送的信号也不完美。 这种缺陷会导致信号损伤 。
It means that signals that are transmitted at the beginning of the medium are not the same as the signals that are received at the end of the medium that is what is sent is not what is received. These impairments tend to deteriorate the quality of analog and digital signals.
这意味着在媒体开始处发送的信号与在媒体结束处接收的信号不同,即发送的内容与接收的内容不同。 这些损害往往会降低模拟和数字信号的质量。
后果 (Consequences)
For a digital signal, there may occur bit errors.
对于数字信号,可能会发生误码。
For analog signals, these impairments degrade the quality of the signals.
对于模拟信号,这些损害会降低信号质量。
损害原因 (Causes of impairment)
There are three main causes of impairment are,
造成损害的三个主要原因是:
Attenuation
衰减
Distortion
失真
Noise
噪声
1)衰减 (1) Attenuation)
Here attenuation Means loss of energy that is the weaker signal. Whenever a signal transmitted through a medium it loses its energy, so that it can overcome by the resistance of the medium.
此处的衰减表示能量损失,即较弱的信号。 每当通过介质传输的信号都会损失其能量,因此可以通过介质的阻力克服。
That is why a wire carrying electrical signals gets warm, if not hot, after a while. Some of the electrical energy is converted to heat in the signal.
这就是为什么载有电信号的电线会在一段时间后变热,甚至变热的原因。 某些电能在信号中转换为热量。
Amplifiers are used to amplify the signals to compensate for this loss.
放大器用于放大信号以补偿这种损耗。
This figure shows the effect of attenuation and amplification:
该图显示了衰减和放大的效果 :
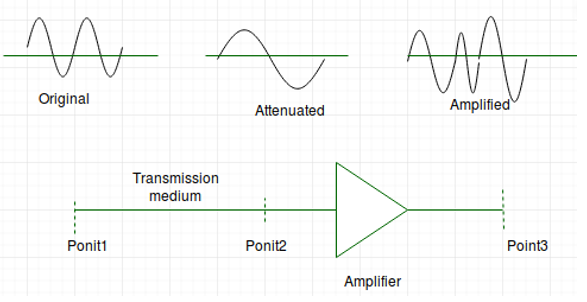
A signal has lost or gained its strength, for this purpose engineers use the concept of decibel(dB).
信号丢失或增强了强度,为此,工程师使用分贝(dB)的概念。
Decibel is used to measure the relative strengths of two signals or a signal at two different points.
分贝用于测量两个信号或两个不同点的信号的相对强度。
If a signal is attenuated then dB is negative and if a signal is amplified so the db is positive.
如果信号衰减,则dB为负;如果信号放大,则db为正。
Attenuation(dB) = 10log10(P2/P1)
衰减(dB)= 10log10(P2 / P1)
where P2 and P1 are the power of a signal at points1 and 2.
其中P2和P1是点1和2处的信号功率。
2)失真 (2) Distortion)
If a signal changes its form or shape, it is referred to as distortion. Signals made up of different frequencies are composite signals. Distortion occurs in these composite signals.
如果信号改变其形式或形状,则称为失真。 由不同频率组成的信号是复合信号。 这些复合信号中会发生失真。
Each component of frequency has its propagation speed traveling through a medium and therefore, different components have different delay in arriving at the final destination.
频率的每个分量都具有通过介质传播的传播速度,因此,不同的分量在到达最终目的地时会有不同的延迟。
It means that signals have different phases at the receiver than they did at the source.
这意味着信号在接收器处的相位与在信号源处的相位不同。
This figure shows the effect of distortion on a composite signal:
该图显示了失真对复合信号的影响:
3)噪音 (3) Noise)
Noise is another problem. There are some random or unwanted signals mix up with the original signal is called noise. Noises can corrupt the signals in many ways along with the distortion introduced by the transmission media.
噪音是另一个问题。 有一些随机或不想要的信号与原始信号混合在一起称为噪声。 噪声会以多种方式破坏信号,并破坏传输介质带来的失真。
Different types of noises are:
不同类型的噪音是:
Thermal noise
热噪声
Intermodulation noise
互调噪声
Crosstalk
相声
Impulse noise
脉冲噪声
a)热噪声 (a) Thermal noise)
The thermal noise is random motion of electrons in a conductor that creates an extra signal not originally sent by the transmitter.
热噪声是导体中电子的随机运动,会产生额外的信号,该信号最初不是由发射器发送的。
It is also known as white noise because it is distributed across the entire spectrum (as the frequency encompass over a broad range of frequencies).
也被称为白噪声,因为它分布在整个频谱中(因为频率涵盖了很宽的频率范围)。
b)互调噪声 (b) Intermodulation noise)
More than one signal share a single transmission channel, intermodulation noise is generated.
多个信号共享一个传输通道,会产生互调噪声。
For instance, two signals S1 and S2 will generate signals of frequencies (S1 + S2) and (s1 - S2), which may interfere with the signals of the same frequencies sent by the sender. due to If nonlinearity present in any part of the communication system, intermodulation noise is introduced.
例如,两个信号S1和S2将生成频率为(S1 + S2)和(s1-S2)的信号,这可能会干扰发送方发送的相同频率的信号。 由于如果通信系统的任何部分都存在非线性,则会引入互调噪声。
c)相声 (c) Cross talk)
Cross talk is an effect a wire on the another. One wire acts as a sending antenna and the transmission medium acts as the receiving antenna.
串扰是一种相互影响的作用。 一根导线充当发送天线,传输介质充当接收天线。
Just like in telephone system, it is a common experience to hear conversation of other people in the background. This is known as cross talk.
就像在电话系统中一样,在后台听到其他人的交谈是一种常见的体验。 这就是所谓的串扰。
d)脉冲噪声 (d) Impulse noise)
Impulse noise is irregular pulses or spikes( a signal with high energy in a very short period) generated by phenomena like that comes from power lines, lightning, spark due to loose contact in electric circuits and so on.
脉冲噪声是不规则的脉冲或尖峰(在很短的时间内具有高能量的信号),是由电源线,雷电,电路接触不良引起的火花等现象产生的。
It is a primary source of bit-errors in digital data communication that kind of noise introduces burst errors.
噪声引入突发错误是数字数据通信中比特错误的主要来源。
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/computer-networks/transmission-impairment.aspx
什么是bcd码数据传输通讯
之timeline的推拉两种模式)


函数)
之Python学习基础篇)









)

方法与示例)


