linux 文件浏览器
你为什么要学习? (Why would you want to learn?)
Linux is probably the most used operating system when it comes to development. For a developer, Linux provides all the required tools. Learning how to navigate the Linux file system can really benefit if you plan on using Linux as your primary operating system or for development purpose. The Linux command line is a very powerful tool that makes it easy and fast to access files on the system.
在开发方面,Linux可能是最常用的操作系统。 对于开发人员,Linux提供了所有必需的工具。 如果计划将Linux用作主要操作系统或用于开发目的,那么学习如何导航Linux文件系统将真正受益。 Linux命令行是一个非常强大的工具,可以轻松快速地访问系统上的文件。
Linux文件系统 (The Linux File System)
Linux organizes its files in a hierarchical directory structure. The files are organized in a tree-like manner. The directories may contain files and other directories. The first directory in the Linux file system is the root directory (named as a /). The root directory is the parent of all other directories in the file system. It contains files and sub-directories, which contain more files and sub-directories and so on.
Linux以分层目录结构组织其文件。 这些文件以树状方式组织。 这些目录可能包含文件和其他目录。 Linux文件系统中的第一个目录是根目录 (名为/ )。 根目录是文件系统中所有其他目录的父目录。 它包含文件和子目录,其中包含更多文件和子目录,依此类推。
Fig. 1: The contents of Root Directory.
图1:根目录的内容。
基本命令 (Basic Commands)
1) pwd: print the name of the current working directory on the terminal
1)pwd:在终端上打印当前工作目录的名称
To check which directory we are currently working in, we can use the "pwd" command. This command prints the absolute path of the current/working directory.
要检查我们当前在哪个目录中,可以使用“ pwd”命令 。 此命令显示当前/工作目录的绝对路径。
When we log in to the system, our current working directory is set to our home directory. Each user is assigned its own home directory where he writes his files.
当我们登录到系统时,我们当前的工作目录被设置为我们的主目录 。 每个用户都被分配有自己的主目录,他在其中写入文件。
2) ls: list the contents of the current working directory
2)ls:列出当前工作目录的内容
To see what files we have in the current working directory we can use the "ls" command.
要查看当前工作目录中有哪些文件,可以使用“ ls”命令 。
3) cd: change directory
3)cd:更改目录
To change our current working directory we use "cd" command. To change the current working directory type "cd" followed by the pathname of the new directory to which you want to go. A pathname is a route that we take to reach a particular directory. Pathnames can be specified in two ways:
要更改当前的工作目录,请使用“ cd”命令 。 要更改当前的工作目录,请键入“ cd”,后跟要转到的新目录的路径名。 路径名是我们到达特定目录所采用的路由。 可以通过两种方式指定路径名 :
Absolute Pathnames
绝对路径名
An absolute pathname begins with the root directory and follows the tree structure until the path to the desired directory is reached. For example, if I want to reach the directory bin in the usr directory which is a part of the root directory, the absolute pathname would be "/usr/bin".
绝对路径名从根目录开始,并遵循树结构,直到到达所需目录的路径为止。 例如,如果我想到达usr目录(它是根目录的一部分)中的目录bin ,则绝对路径名为“ / usr / bin” 。
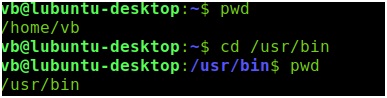
Relative Pathnames
相对路径名
Unlike absolute pathnames which start from the root directory, Relative pathnames start from the working directory. Linux uses two particular symbols to represent the current directory and its parent directory in the file system. These are the "." and ".." symbols.
与绝对路径名从根目录开始不同,相对路径名从工作目录开始。 Linux使用两个特殊的符号表示文件系统中的当前目录及其父目录。 这些是“。” 和“ ..”符号。
The "." symbol refers to the working directory and the ".." symbol refers to the parent directory of the working directory. Let's see this.
“。” 符号是工作目录, “ ..”符号是工作目录的父目录。 让我们看看这个。
pwd : /usr/bin
密码:/ usr / bin
Let's change our working directory i.e., /usr/bin to its parent directory which is /usr. We can do this as:
让我们将工作目录(即/ usr / bin)更改为其父目录/ usr 。 我们可以这样做:
(a) Using absolute pathname
(a)使用绝对路径名
(b) Using relative pathname
(b)使用相对路径名

主目录的快捷方式 (A shortcut to home directory)
The "~" symbol represents the home directory of the user. So we can use this symbol to directly go to the home directory or list its contents with ls.
“〜”符号代表用户的主目录。 因此,我们可以使用该符号直接转到主目录或使用ls列出其内容。
Summing Up
加起来
In this article we saw how shell treats the Linux File System. We also learned about absolute and relative pathnames and the basic commands that are used move about the file system.
在本文中,我们了解了shell如何处理Linux文件系统 。 我们还了解了绝对路径名和相对路径名以及在文件系统中使用的基本命令 。
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/linux/navigating-linux-file-system.aspx
linux 文件浏览器




方法及示例)














