瞎搞题啊。找出1 1 0 0这样的序列,然后存起来,这样的情况下最好的选择是1的个数除以这段的总和。
然后从前向后扫一遍。变扫边进行合并。每次合并。合并的是他的前驱。这样到最后从t-1找出的那条链就是最后满足条件的数的大小。
Room and Moor
Time Limit: 12000/6000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 307 Accepted Submission(s): 90
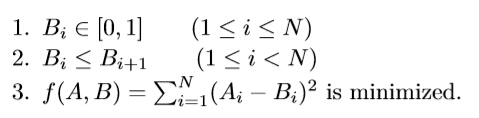
For each test case:
The first line contains a single integer N (1<=N<=100000), which denotes the length of A and B.
The second line consists of N integers, where the ith denotes Ai.
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define eps 1e-9
///#define M 1000100
#define LL __int64
///#define LL long long
///#define INF 0x7ffffff
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PI 3.1415926535898
#define zero(x) ((fabs(x)<eps)?0:x) using namespace std; const int maxn = 1000010; int num[maxn]; int sum[maxn][2]; int pre[maxn]; double x[maxn]; int main() { int T; cin >>T; while(T--) { int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d",&num[i]); int t = 0; int cnt1 = 0; int cnt2 = 0; if(!num[0]) cnt1 = 1; if(num[0]) cnt2 = 1; for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { if(num[i] > num[i-1]) { sum[t][0] = cnt1; sum[t++][1] = cnt2; cnt1 = cnt2 = 0; if(!num[i]) cnt1++; if(num[i]) cnt2++; continue; } if(!num[i]) cnt1++; if(num[i]) cnt2++; } sum[t][0] = cnt1; sum[t][1] = cnt2; t++; for(int i = 0 ; i < t; i++) x[i] = (1.0*sum[i][1]/((sum[i][0]+sum[i][1])*1.0)); pre[0] = -1; for(int i = 1; i < t; i++) { if(x[i] < x[i-1]) { sum[i][0] += sum[i-1][0]; sum[i][1] += sum[i-1][1]; x[i] = 1.0*sum[i][1]/(sum[i][1]+sum[i][0])*1.0; pre[i] = pre[i-1]; int p = pre[i]; while(p != -1) { if(x[i] < x[p]) { sum[i][0] += sum[p][0]; sum[i][1] += sum[p][1]; x[i] = 1.0*sum[i][1]/(sum[i][0]+sum[i][1])*1.0; pre[i] = pre[p]; p = pre[p]; continue; } break; } continue; } pre[i] = i-1; } int p = pre[t-1]; double ans =0; ans += sum[t-1][0]*pow(x[t-1], 2)+sum[t-1][1]*pow(x[t-1]-1, 2); while(p != -1) { ans += sum[p][0]*pow(x[p], 2)+sum[p][1]*pow(x[p]-1, 2); p = pre[p]; } printf("%.6lf\n",ans); } return 0; }
方法与示例)


方法与示例)
下的目录介绍)

方法与示例)


方法与示例)
:调试,及给 LXD 做贡献)

方法与示例)

方法)


方法)

)