总结完这个Mybatis的整体主要功能基本上就差不多完,还有一些细节的部分,后续都会记录补充。
插件这个东西一般用的比较少,就算用的多的插件也算是PageHelper分页插件;
PageHelper官网:https://github.com/pagehelper/Mybatis-PageHelper/blob/master/README_zh.md
官网上这个也有谈到Mybatis的插件流程分析。
使用示例
插件类
记录SQL执行的时间,
1、在JDK8之前必须实现Interceptor接口中的三个方法,在JDK8之后只需要实现intercept方法即可;
2、加上@Intercepts注解,并且附加上需拦截的类型以及方法@Signature:
type:插入的类,即指定的四个类型;
method:拦截插入类的方法;
args:拦截插入类方法的参数类型,按顺序。
3、实现的plugin方法,必须执行Plugin.wrap(target, this);JDK8之后在接口中写了默认方法。
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "query", args = { Statement.class, ResultHandler.class })
})
public class ThresHolderPlugin implements Interceptor {int threshold = 0;public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();Object proceed = invocation.proceed();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("select time: " + (end-start) + "ms");return proceed;}public Object plugin(Object target) {return Plugin.wrap(target, this);}public void setProperties(Properties properties) {this.threshold = Integer.valueOf(properties.getProperty("value"));System.out.println("threshold :" + threshold);}}
配置文件
<plugins><plugin interceptor="com.test.mybatis.MybatisTest.official.plugin.ThresHolderPlugin">//数据会传输到插件类的Properties<property name="value" value="10"></property></plugin></plugins>设计模式
责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern)
为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链。这种模式给予请求的类型,对请求的发送者和接收者进行解耦。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
在这种模式中,通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。如果一个对象不能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下一个接收者,依此类推。
责任链模式优点:
降低耦合度。它将请求的发送者和接收者解耦。
简化了对象。使得对象不需要知道链的结构。
增强给对象指派职责的灵活性。通过改变链内 的成员或者调动它们的次序,允许动态地新增 或者删除责任。
增加新的请求处理类很方便。
UML:
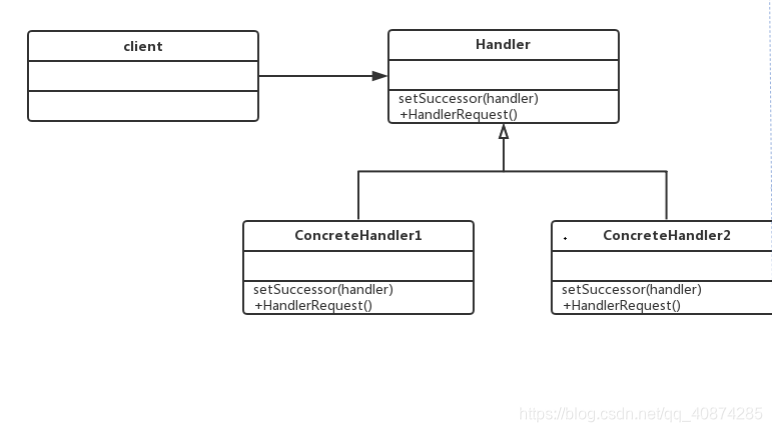
Handler:定义了一个处理请求的标准接口;
ConcreteHandler:具体的处理者,处理它负 责的部分,根据业务可以结束处理流程,也可 以将请求转发给它的后继者;
client :发送者,发起请求的客户端;
源码分析
在之前谈到Mybatis的核心流程分析中在加载Mybatis的配置文件的时候会把所有的插件加载带Configuration对象中的InterceptorChain变量当中,
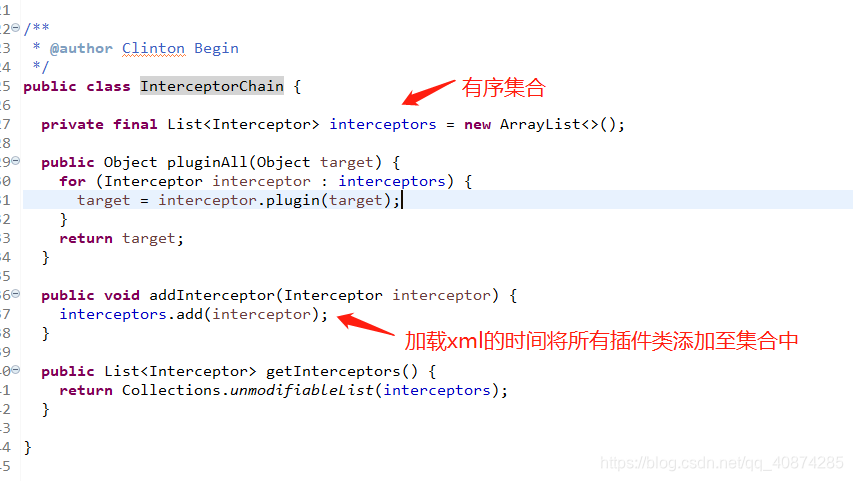
如果有多个插件类的话,因为InterceptorChain类储存插件类是有序集合,所以执行插件的顺序就是在xml配置插件的顺序;
在Configuration类中:
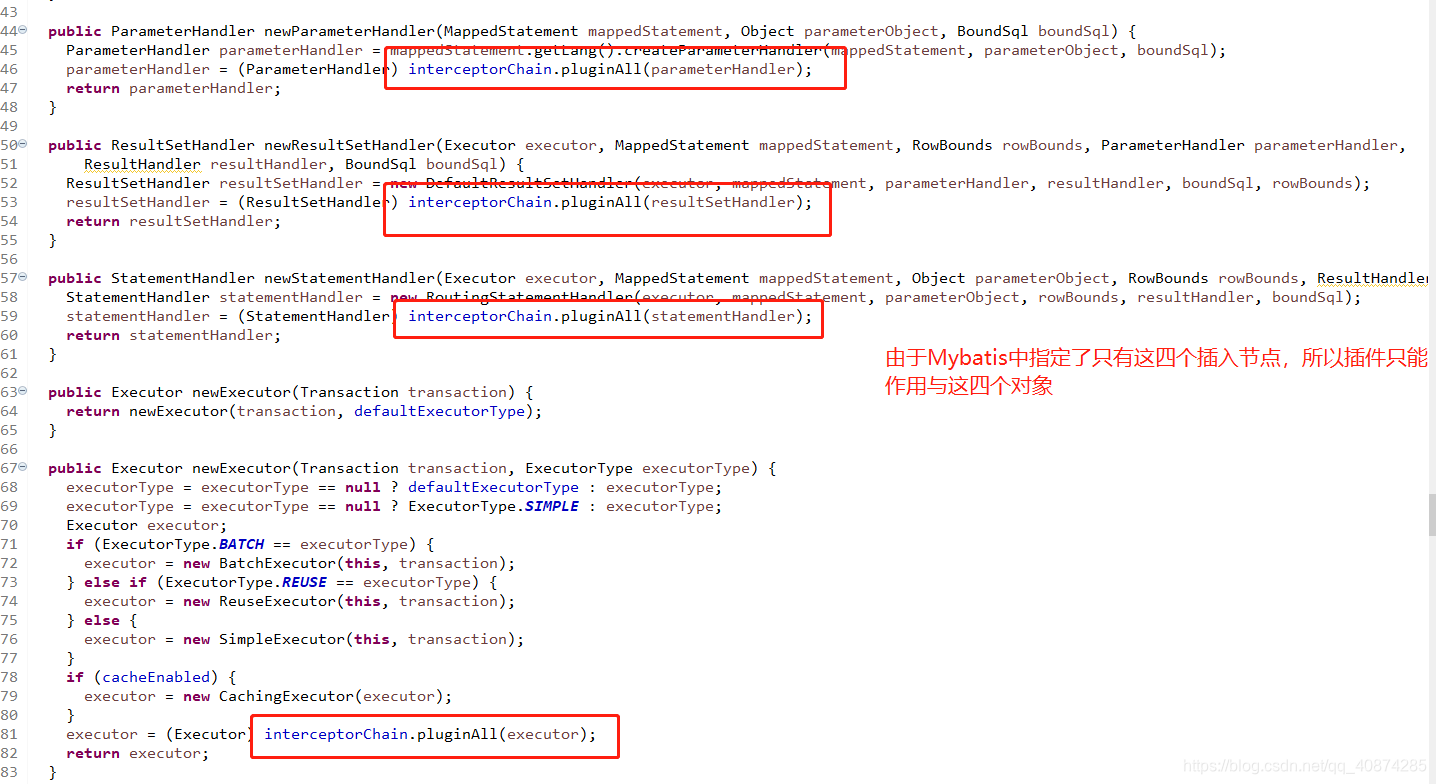
这里有个CacheExecutor执行器,当开启了二级缓存的时候,就是选用缓存执行器,使用是装饰器模式将真正的执行器包装了一层。
我们现在看一下这个pluginAll方法:
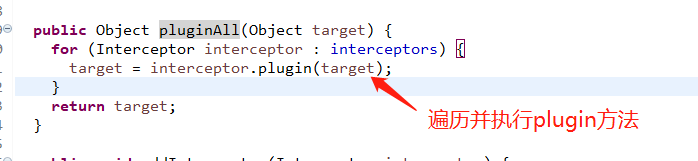
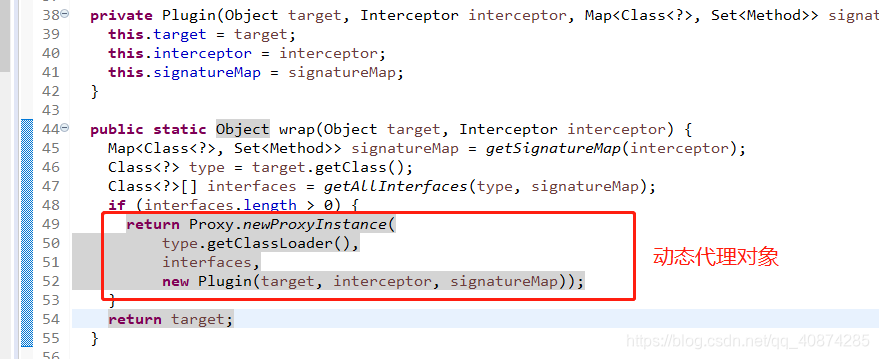
使用动态代理将真正的对象进行增强;
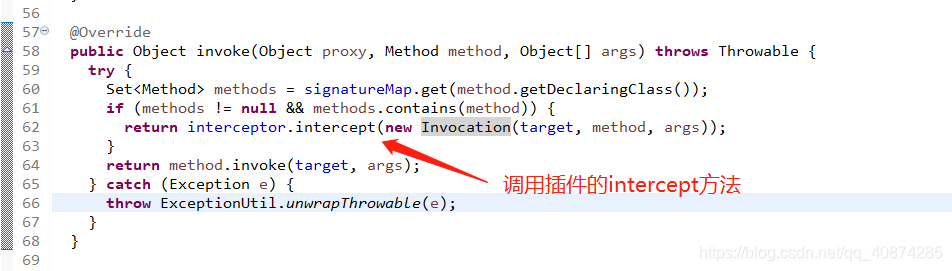
在之前那个方法中,必须执行Invocation的proceed()方法,这个方法就是执行method.invoke()方法;
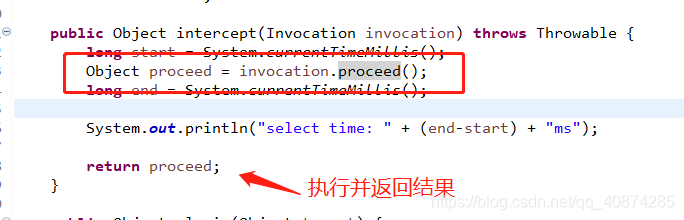
如果有多个插件的话,那么就会出现重复代理对象,那么重复代理对象的执行的话,执行过程如下:
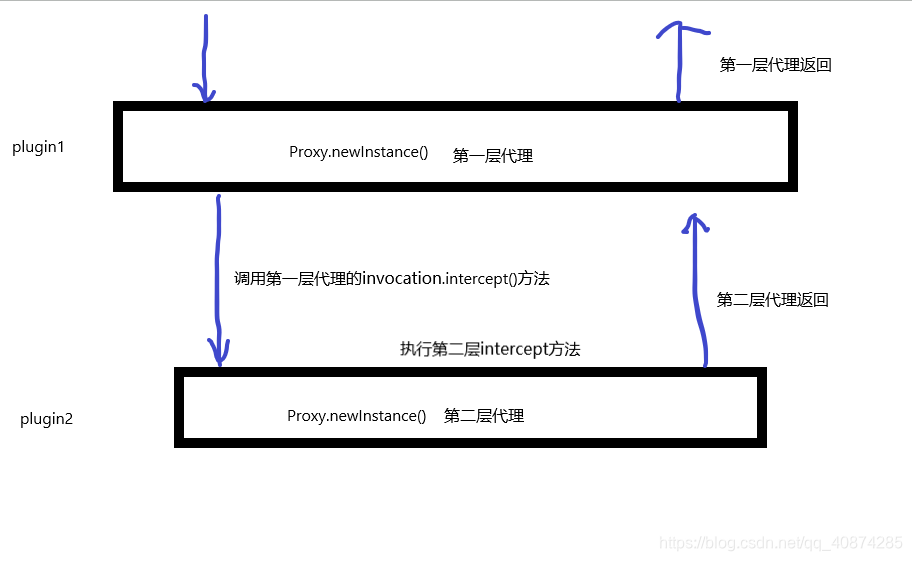
这就是责任链模式,一层嵌套着一层。
在配置XML文件中配置:
<plugins><plugin interceptor="com.test.mybatis.MybatisTest.official.plugin.ThresHolderPlugin"><property name="value" value="10"></property></plugin><plugin interceptor="com.test.mybatis.MybatisTest.official.plugin.ThresHolderPlugin2"><property name="value" value="20"></property></plugin>
</plugins>那么执行的过程就是:
ThresHolderPlugin2{
ThresHolderPlugin{
interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args))
}
}
插件的执行流程差不多了。大家可以在评论区多交流交流。







怎么用)

![[中医经络学习一]足阳明胃经](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[中医经络学习一]足阳明胃经)



)



...)

