
作者 | 七十一
来源 | 程序员巴士
前言
什么是快速失败:fail-fast 机制是java集合(Collection)中的一种错误机制。它只能被用来检测错误,因为JDK并不保证fail-fast机制一定会发生。当多个线程对同一个集合的内容进行操作时,就可能会产生fail-fast事件。
运行如下代码,即可出现异常:
// 关于fail-fast的一些思考
public class FailFastTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 构建ArrayListList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);for (int i : list) {list.remove(1);}}
}控制台会输出如下异常:
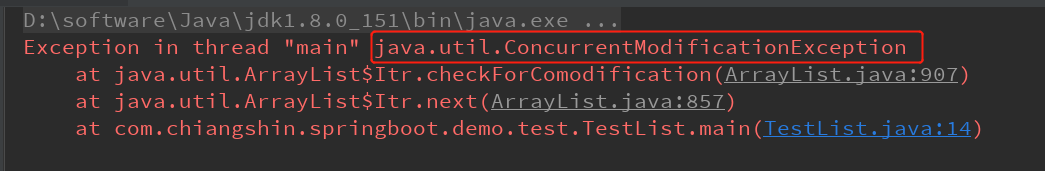
为什么要报这个错?途中出错的地方是ArrayList中的代码,定位到该处代码:
final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}modCount是这个集合修改的次数,这个属性来自AbstractList,而我们的ArrayList是继承了该抽象类的。
protected transient int modCount = 0;expectedModCount又是啥呢?当我们进行遍历时候debug一下发现进行forEach循环的时候其实走了下面这个方法iterator,而且遍历这个底层还是走的hasNext方法
public Iterator<E> iterator() {return new Itr();}判断是否有下一个元素
public boolean hasNext() {return cursor != size;}next()方法用于获取元素
public E next() {checkForComodification(); // 留意这个方法int i = cursor;if (i >= size)throw new NoSuchElementException();Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();cursor = i + 1;return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}点进这个new Itr(),惊喜的发现原来这个expectedModCount是在这里被赋值的而且和modCount一样
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {int cursor; // index of next element to returnint lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no suchint expectedModCount = modCount; // 注意:此处进行赋值............接下来看下ArrayList的remove()方法,其对modCount进行了增加,这是导致报错的原因
public E remove(int index) {rangeCheck(index);modCount++; // 对modCount进行了++的操作E oldValue = elementData(index);int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its workreturn oldValue;}上面的next()方法这有调用一个checkForComodification()方法,下面贴一下这方法的代码
final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}ArrayList里面remove()方法进行了modCount++操作,原来是我们对集合进行操作后改变了modCount导致上面代码成立,从而抛出异常
但是当我们使用Itr类的remove,也就是如下代码进行对元素改动时,不会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
public void remove() {if (lastRet < 0)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();try {ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);cursor = lastRet;lastRet = -1;// 将ArrayList的modCount赋值给Itr类的expectedModCount //这样再次调用next方法时就不会出现这俩个值不一致 从而避免报错expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}与ArrayList的remove()方法不同的是,该remove()方法调用ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);后显然modCount++了,但是马上又让expectedModCount = modCount就是这样才不会抛出异常。
梳理整个流程:
1、for循环遍历实质上调用的是Itr类的方法进行遍历(Itr类实现了Iterator)
2、Itr类在构造的时候会将ArrayList的modCount(实际上modCount是AbstractList的属性,但是ArrayList继承了AbstractList)赋值给Itr类的expectedModCount
3、for循环中调用的remove()方法时ArrayList的,这个方法会对modCount进行++操作
4、remove方法调用后,继续遍历会调用Itr的next()方法,而这个next()方法中的checkForComodification()方法会对modCount和expectedModCount进行对比,由于remove方法已经操作过modCount因此这俩个值不会相等,故报错。
如何改进?
1、可以使用Itr中的remove方法进行改进,改进代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {// 构建ArrayListList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();while(iterator.hasNext()) {iterator.next();iterator.remove();}System.out.println(list.size()); // 0}2、使用CopyOnWriterArrayList来代替Arraylist,它对ArrayList的操作时会先复制一份数据出来操作完了再将其更新回去替换掉旧的,所以CopyOnWrite容器只能保证数据的最终一致性,不能保证数据的实时一致性。这是采用了CopyOnWriterArrayList的fail-safe机制,当集合的结构被改变的时候,fail-safe机制会在复制原集合的一份数据出来,然后在复制的那份数据遍历,fail-safe机制,在JUC包的集合都是有这种机制实现的。
虽然fail-safe不会抛出异常,但存在以下缺点
1、复制时需要额外的空间和时间上的开销。
2、不能保证遍历的是最新内容。
总结
对于fail-fast机制,我们要操作List集合时可以使用Iterator的remove()方法在遍历过程中删除元素,或者使用fail-safe机制的CopyOnWriterArrayList,当然使用的时候需要权衡下利弊,结合相关业务场景。


往期推荐
低代码发展专访系列之八:低代码平台能够打破企业「应用孤岛」现象吗?
Medusa又一个开源的替代品
用了HTTPS,没想到还是被监控了
快速搭建实验环境:使用 Terraform 部署 Proxmox 虚拟机
点分享

点收藏

点点赞

点在看


















 基础知识 服务器搭建 系统管理 性能调优 虚拟化与集群应用免费全文_百度阅读...)
