【极简Python 自动化办公】Python写入Excel表格
【极简Python 自动化办公】专栏是介绍如何利用python办公,减少工作负荷。篇幅精炼,内容易懂,无论是否有编程基础,都非常适合。
在上次文章中,我们学习了【用python读取excel】,这次我们继续学习Python写excel吧!

0.摘要
本文大约需要15分钟,建议在电脑上打开,边阅读边操作。
- 安装Python读excel模块——xlwt
- 准备写入表格内容
- 编写python代码并运行
4.使用for循环语句读取并写入excel表格
1.安装xlwt
与上篇文章类似,需要在cmd窗口输入pip install xlwt。
2.准备写入表格内容
这步很简单,只要想好输入内容即可,这里设计了一个简单的表格内容作为写入内容(目前这个内容还不存在)。
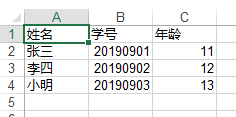
序号学号年龄张三2019090111李四2019090212小明2019090313
3.编写python代码并运行
新建一个writeexcel.py文件,用记事本或其他文本编辑工具打开。
本次写入excel的思路是,新建文件->指定行列->写入内容。
在文本编辑工具中输入如下代码,保存并关闭。
import xlwtf = xlwt.Workbook()
sheet1 = f.add_sheet('sheet1',cell_overwrite_ok=True)
column = ["姓名","学号","年龄"]
name = ["张三","李四","小明"]school_code = [20190901,20190902,20190903]age = [11,12,13]sheet1.write(0,0,column[0])#第1行第1列
sheet1.write(0,1,column[1])#第3行第3列
sheet1.write(0,2,column[2])#第2行第2列sheet1.write(1,0,name[0])#第2行第1列
sheet1.write(1,1,school_code[0])#第2行第1列
sheet1.write(1,2,age[0])#第3行第1列sheet1.write(2,0,name[1])
sheet1.write(2,1,school_code[1])
sheet1.write(2,2,age[1])sheet1.write(3,0,name[2])
sheet1.write(3,1,school_code[2])
sheet1.write(3,2,age[2])f.save('test1.xls')还是一样,注意每句的开头不可以有空格,因为python用缩进来表示编程的层次,缩进不同就会报错了。
在保存writeexcel.py的位置上打开cmd,运行 python writeexcel.py
可以看到结果:
4.使用for循环语句读取并写入excel表格
非常好!您已经学会了如何读取和写入excel表格。
但是,我们只能一个一个单元格读取和写入数据,这比手工操作excel表格快不了多少。
接下来,我们需要学习使用for循环,来批量读取一个excel表格,并循环写入另一个excel表格中。
不要删除test1.xls,在test1.xls文件的位置,新建一个rwexcel.py文件,将下面代码输入到文件中:
import xlrd
import xlwtwb = xlrd.open_workbook("test1.xls")#打开文件
sheet1 = wb.sheet_by_index(0)#获取第一个表格column = []#列名data=[]#获取列名
column.append(sheet1.cell(0,0).value)#姓名
column.append(sheet1.cell(0,1).value)#学号
column.append(sheet1.cell(0,2).value)#年龄for i in range(1,sheet1.nrows):#sheet1.nrows 行数coldata=[]coldata.append(sheet1.cell(i, 0).value)#姓名coldata.append(int(sheet1.cell_value(i, 1)))#学号coldata.append(sheet1.cell(i, 2).value)#年龄data.append(coldata)f = xlwt.Workbook()
sheetw = f.add_sheet('sheet1',cell_overwrite_ok=True)sheetw.write(0,0,column[0])#姓名
sheetw.write(0,2,column[2])#学号
sheetw.write(0,1,column[1])#年龄for i in range(len(data)):d=data[i]sheetw.write(i+1, 0, d[0]) # 第2行第1列sheetw.write(i+1, 1, d[1]) # 第2行第1列sheetw.write(i+1, 2, d[2]) # 第3行第1列f.save('test2.xls')运行后,会生成一个test2.xls,与test1.xls一模一样。
人生苦短,我用python早下班。如果觉得不错,对你工作中有帮助,请加我微信公众号flypython,我们一起探讨python相关问题













:程序的表示、转换与链接(第八周小测验)...)
![c# getresponsestream返回byte[]_C++模版和C#范型求同存异录(一)sizeof(T)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/c# getresponsestream返回byte[]_C++模版和C#范型求同存异录(一)sizeof(T))





