Android一键式清理,内存清理功能的实山清理大师等均提供一键式清理和一键加速等功能。实际上,它们杀死了一些后台进程以达到释放内存的目的。
基本思想是列出所有正在运行的进程,检查它们的重要值(RunningAppProcessInfo.importance,该值越大,进程的重要性越低),可以设置一个阈值,如果过程大于阈值,则可以终止该过程。
该过程的重要性具有以下级别:

/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this is a persistent process.
* Only used when reporting to process observers.
* @hide
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_PERSISTENT = 50;
/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this process is running the
* foreground UI.
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_FOREGROUND = 100;
/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this process is running something
* that is actively visible to the user, though not in the immediate
* foreground.
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_VISIBLE = 200;
/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this process is running something
* that is considered to be actively perceptible to the user. An
* example would be an application performing background music playback.
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_PERCEPTIBLE = 130;
/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this process is running an
* application that can not save its state, and thus can't be killed
* while in the background.
* @hide
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_CANT_SAVE_STATE = 170;
/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this process is contains services
* that should remain running.
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_SERVICE = 300;
/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this process process contains
* background code that is expendable.
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_BACKGROUND = 400;
/**
* Constant for {@link #importance}: this process is empty of any
* actively running code.
*/
public static final int IMPORTANCE_EMPTY = 500;
需要权限:
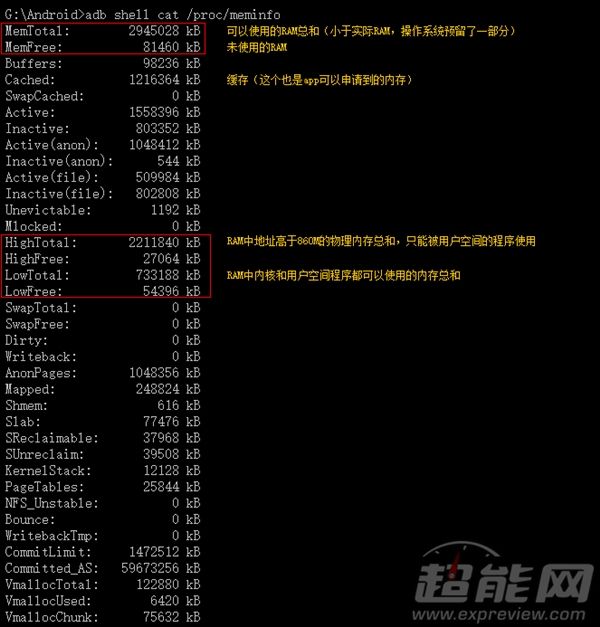
具体操作代码如下:
package com.example.demo;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ActivityManager;
import android.app.ActivityManager.MemoryInfo;
import android.app.ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager.NameNotFoundException;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class CleanProcessActivity extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "Clean";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_clean_process);
}
public void clean(View v){
//To change body of implemented methods use File | Settings | File Templates.
ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager) getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
ListinfoList = am.getRunningAppProcesses();
ListserviceInfos = am.getRunningServices(100);
long beforeMem = getAvailMemory(this);
Log.d(TAG, "-----------before memory info : " + beforeMem);
int count = 0;
PackageManager pm = getPackageManager();
if (infoList != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < infoList.size(); ++i) {
RunningAppProcessInfo appProcessInfo = infoList.get(i);
Log.d(TAG, "process name : " + appProcessInfo.processName);
//importance 该进程的重要程度 分为几个级别,数值越低就越重要。
Log.d(TAG, "importance : " + appProcessInfo.importance);
// 一般数值大于RunningAppProcessInfo.IMPORTANCE_SERVICE的进程都长时间没用或者空进程了
// 一般数值大于RunningAppProcessInfo.IMPORTANCE_VISIBLE的进程都是非可见进程,也就是在后台运行着
if (appProcessInfo.importance > RunningAppProcessInfo.IMPORTANCE_VISIBLE) {
String[] pkgList = appProcessInfo.pkgList;
for (int j = 0; j < pkgList.length; ++j) {//pkgList 得到该进程下运行的包名
String appName = null;
try {
appName = (String) pm.getApplicationLabel(pm.getApplicationInfo(pkgList[j], 0));
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
Log.d(TAG, "It will be killed, package name : " + pkgList[j]+" -- "+appName );
am.killBackgroundProcesses(pkgList[j]);
count++;
}
}
}
}
long afterMem = getAvailMemory(this);
Log.d(TAG, "----------- after memory info : " + afterMem);
Toast.makeText(this, "clear " + count + " process, "
+ (afterMem - beforeMem) + "M", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
private long getAvailMemory(CleanProcessActivity cleanProcessActivity) {
// 获取android当前可用内存大小
ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager) getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
MemoryInfo mi = new MemoryInfo();
am.getMemoryInfo(mi);
//mi.availMem; 当前系统的可用内存
//return Formatter.formatFileSize(context, mi.availMem);// 将获取的内存大小规格化
Log.d(TAG, "可用内存---->>>" + mi.availMem / (1024 * 1024));
return mi.availMem / (1024 * 1024);
}
}
注意:
我在此处选择的阈值为IMPORTANCE_VISIBLE级别,这意味着不可见的后台进程和服务将被杀死(某些系统进程除外)。
清洁效果类似于Kingsoft Cleaner和360 Desktop的一键式清洁效果。
如果您不想太猛烈地杀死进程,则可以选择IMPORTANCE_SERVICE级别来杀死那些长时间没有用或空的进程。此级别的清理功能不足以实山清理大师的效果。
以上是本文的全部内容。希望对每个人的学习都有帮助,也希望您能为脚本库提供更多支持。
本文来自电脑杂谈,转载请注明本文网址:
http://www.pc-fly.com/a/shoujiruanjian/article-326460-1.html



















