聚类(Clustering): K-means算法
1.归类:
聚类(clustering)属于非监督学习(unsupervised learning)
无类别标记( class label)
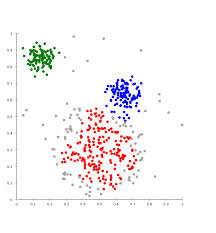
3. K-means 算法:
3.1 Clustering 中的经典算法,数据挖掘十大经典算法之一
3.2 算法接受参数 k ;然后将事先输入的n个数据对象划分为 k个聚类以便使得所获得的聚类满足:同一聚类中的对象相似度较高;而不同聚类中的对象相似度较小。(k表示数据要分的类别的数量,比如上图分为三种类型,则k=3)
3.3 算法思想:以空间中k个点为中心进行聚类,对最靠近他们的对象归类。通过迭代的方法,逐次更新各聚类中心的值,直至得到最好的聚类结果3.4 算法描述:(1)适当选择c个类的初始中心;(2)在第k次迭代中,对任意一个样本,求其到c各中心的距离,将该样本归到距离最短的中心所在的类;(3)利用均值等方法更新该类的中心值;(4)对于所有的c个聚类中心,如果利用(2)(3)的迭代法更新后,值保持不变(停止时机)/或达到预定的次数/分类变化小于预定值,则迭代结束,否则继续迭代。
3.5 算法流程:
输入:k, data[n];( k:分的类别数,data[n]:样本数据)(1) 选择k个初始中心点,例如c[0]=data[0],…c[k-1]=data[k-1];(通常用random随机挑选初始中心点)(2) 对于data[0]….data[n], 分别与c[0]…c[k-1]比较,假定与c[i]差值最少,就标记为i;(3) 对于所有标记为i点,重新计算c[i]={ 所有标记为i的data[j]之和}/标记为i的个数;(4) 重复(2)(3),直到所有c[i]值的变化小于给定阈值。
Euclidean Distance欧几里得距离即求向量之间的距离
概括:1.(随机)定义三个中心点.2.找最近的点3.用均值定义新的中心点.4.继续23步直到中心点保持不变/达到预定的次数/分类变化小于预定值
4.流程图:

示例:
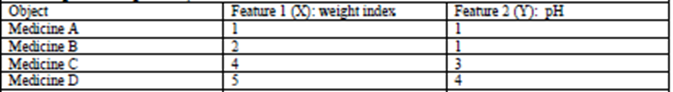
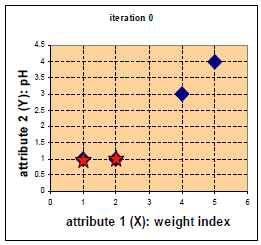
用矩阵计算距离:(不用Euclidean Distance方式计算)
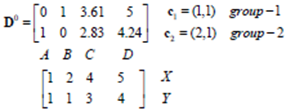
上标0表示第0次迭代,上面一行4个值分别表示与(1,1)的距离值
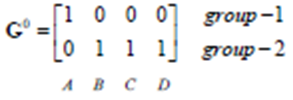
上下两排中,1表示对应位置的该点归为当前相同类,0则表示归为不同类
Group1的中心点不变(因为只有A一个点)
Group2的中心点为:(求均值)
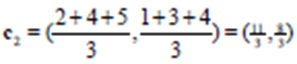
重新划分类别:

此时B点被分类为group1:
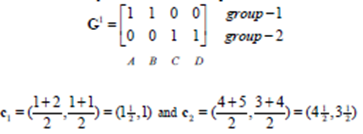
再分类:

此时,分类相比上次已经没有变化了:
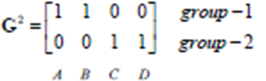
所以迭代停止
聚类算法优缺点:
优点:速度快,简单
缺点:最终结果跟初始点选择相关度很大,容易陷入局部最优,需直到k值
聚类(Clustering): K-means算法应用
Python中code实例应用:
import numpy as np# Function: K Means
# -------------
# K-Means is an algorithm that takes in a dataset and a constant
# k and returns k centroids (which define clusters of data in the
# dataset which are similar to one another).def kmeans(X,k,maxIt): '''X:数据集;k:分类个数;maxIt:设置的循环次数'''numPoints,numDim = X.shape #X(类型为numpy array),行数(也可以叫做点数)和列数(维度)dataSet = np.zeros((numPoints,numDim+1)) #注意这里有两组括号dataSet[:, :-1] = X #dataset中除了最后一列的值都用X的值替代'''array中直接使用等号这种赋值方法(“=”),必须两者维度相同,所以这里把最后一列除开在外,使两者维度相同'''# Initialize centroids randomly#随机生成初始中心点centroids = dataSet[np.random.randint(numPoints,size=k),:] #需要从所有行中选取k组作为中心点# centroids =dataSet[0:2,:] ##表示自行选取前两个axis中两组点作为中心点,用来核算算法是否准确#Randomly assign labels to initial centoridcentroids[:,-1] = range(1,k+1) #将中心点分类为1,2,k~等若干类# Initialize book keeping vars. 记账:迭代次数iterations = 0oldCentroids = None #每一次迭代完新的中心点就要变成旧的中心点,后面用
# Run the main k-means algorithm
# 停止函数中的参数:
# oldCentroids: 旧的中心点
# centroids:新的中心点,可以设置新旧相等时停止
# iterations: 记录循环多少次,可以用来设置到指定循环次数停止
# maxIt:循序循环的最大次数while not shouldStop(oldCentroids,centroids,iterations,maxIt):print('iterations:\n',iterations)print('dataSet:\n',dataSet)print('centroids:\n',centroids)# Save old centroids for convergence test. Book keepingoldCentroids = np.copy(centroids) #将新中心点变为就中心点,并且保留旧中心点的值,**使用np.copy**iterations += 1# Assign labels to each datapoint based on centroidsupdateLabels(dataSet,centroids) #调用更新label的函数centroids = getCentroids(dataSet,k) #获取中心点用于判断是否结束# We can also get the labels by calling getLabels(dataSet, centroids)return dataSet# Function: Should Stop
# -------------
# Returns True or False if k-means is done. K-means terminates either
# because it has run a maximum number of iterations OR the centroids stop changing.
# 终止条件:迭代次数到达指定次数;或中心点不再变化
def shouldStop(oldCentroids,centroids,iterations,maxIt):if iterations>maxIt:return Truereturn np.array_equal(oldCentroids,centroids) #**使用np.array_equal判断两数组值是否相等**判断类型相同则用?def updateLabels(dataSet,centroids): #距离中心点最短则与中心点归为一类,归类的具体方法后面单独封包了函数numPoints,numDim = dataSet.shapefor i in range(numPoints):dataSet[i,-1] = getLabelFromClosestCentroids(dataSet[i,:-1],centroids)#需要参数:中心点和每一行的特征值#归类方法比较复杂,单独封包一个函数def getLabelFromClosestCentroids(dataRow,centroids): # dataSetRow:一行一个实例。中心点(K行,列数相同的矩阵) label = centroids[0,-1] #第0个[]中的的倒数第一个值赋值给labelminDist = np.linalg.norm(dataRow - centroids[0,:-1]) #第一个距离就是最小值,dataRow?'''np.linalg.norm(X-Y):sqrt((x1-y1)^2+(x2-y2)^2),X=np.array([x1,x2]),Y=np.array([y1,y2]);可以理解为欧几里得distance求向量的距离'''#linalg=linear(线性)+algebra(代数),norm则表示范数for i in range(1,centroids.shape[0]+1): #+1?dist = np.linalg.norm(dataRow-centroids[i,:-1])if dist < minDist:minDist = distlabel = centroids[i,-1]print('minDist:',minDist)return label
# Function: Get Centroids
# -------------
# Returns k random centroids, each of dimension n.
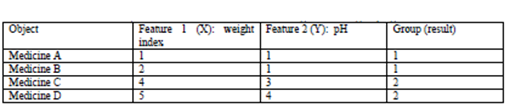
def getCentroids(dataSet,k):result = np.zeros((k,dataSet.shape[1])) #两对括号 不然会报错 TypeError: data type not understoodfor i in range(1,k+1):oneCluster = dataSet[dataSet[:,-1]==i,:-1] #对于dataset每一行如果dataset最后一个值(即label)=i,则把它的特征值X赋值给oneCluster组成一个数组array'''相当于嵌套了一个if dataSet[:-1]==i语句'''# np.meamn,axis=0对array的行求均值,axis=1对array的列求均值result[i-1,:-1] = np.mean(oneCluster,axis=0) #求均值找中心点,result即新的中心点result[i-1,-1] = i #Label分类为ireturn resultx1 = np.array([1,1])
x2 = np.array([2,1])
x3 = np.array([4,3])
x4 = np.array([5,4])testX = np.vstack((x1,x2,x3,x4)) #按垂直方向堆叠构成一个新的数组,注意两对括号result = kmeans(testX,2,10)
print('final result:\n',result)#sklearn 中也可以调用kmeans算法


)
在python3上遇到的问题)







、'zip' object is not subscriptable)
)


乘法运算)

)

![OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument:**](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument:**)