前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家。点击跳转到教程。
步骤:
1. pom文件中加 maven jar包:
<!-- ehcache 缓存 --><dependency><groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId><artifactId>ehcache</artifactId></dependency>
<!--开启缓存支持--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency>
2. 新增一个配置文件 ehcache.xml,放在resource 下面,springboot会自动扫描 :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache><!--ehcache 缓存--><cache name="department" maxElementsInMemory="1000" />
</ehcache>更多配置参考:
<ehcache><!--ehcache 缓存--><cache name="department"maxElementsInMemory="100000"eternal="true"overflowToDisk="true"maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"diskPersistent="true"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/><defaultCacheeternal="false"maxElementsInMemory="10000"overflowToDisk="false"diskPersistent="false"timeToIdleSeconds="0"timeToLiveSeconds="600"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/></ehcache>
3. 在 main 方法上加上注解 @EnableCaching,开启缓存的使用:
@EnableCaching // 开启缓存使用
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application { // extends SpringBootServletInitializerpublic static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(Application.class, "classpath*:/spring/security-*.xml");application.setWebEnvironment(true);application.run(args);}/*** HOW TO MAKE A SPRING BOOT JAR INTO A WAR TO DEPLOY ON TOMCAT*/
// @Override
// protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
// // Customize the application or call application.sources(...) to add sources
//
// application.sources(Application.class);
// return application;
// }}
4. 在方法中运用注解,实现缓存的 增、删、改、查
只要在方法上加上对应注解就可以了。
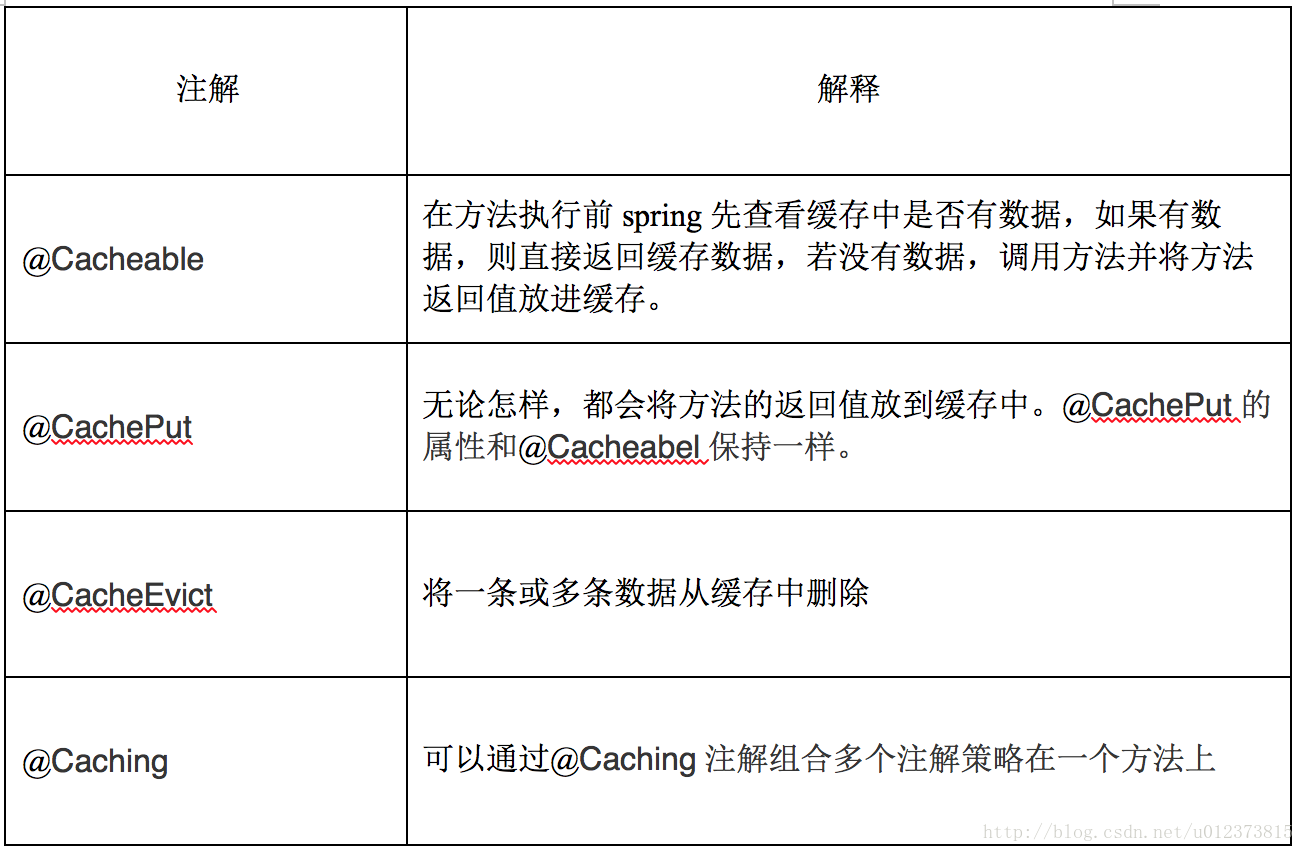
@Cacheable 查: 如果有就直接缓存中取 没有就数据库查并放入缓存。加上这个注解,调用这个方法就可以取到缓存中的值。
@CacheEvict 新增、删除、修改 :会自动清除缓存中内容。加上这注解,对数据库的update、add、delete操作都会清除对应缓存。
如:缓存名为“ department ”,当调用此方法时会先判断是否有缓存。有则不进入方法,直接返回缓存中的值。无缓存名为 “department” 的缓存才会进入方法内部,执行数据库查询。
@Override@Cacheable(value = "department")public List<Department> getDepartmentList() {System.out.println("--------------------------------缓存查询:查查查-树树树\n");List<Department> departmentList = departmentRepository.findAll(new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "id"));return (List<Department>) buildDepartmentTree(departmentList, null);}
可以给缓存中的具体项起个键值:key
@Override@Cacheable(value = "department", key = "#departmentId")public Object findOne(String departmentId) {return departmentRepository.findOne(departmentId);}
当缓存key没有全部命中时,要确保缓存全部清除,就要加上
allEntries = true ,默认为false @Override@Transactional(readOnly = false)@CacheEvict(value = "department", allEntries = true) // 新增、删除、修改 all is it.public Object updateDepartmentById(String id, Department departmentDto) {Department department = departmentRepository.findOne(id);if (department == null) {return "不存在该部门";}BeanHelper.mapPartOverrider(department, departmentDto);departmentRepository.save(department);return department;}
spring提供了4个注解来声明缓存规则(又是使用注解式的AOP的一个生动例子),如表。
事实上,新增、删除、修改都可以用@CacheEvict ,不建议使用 @ CachePut ,用法完全如上查的方法,只是注解名字不一样。
// 查:存key为cache_department 的数据缓存到departmentList中,如果没有指定key则方法参数作为key保存到缓存中。department只是缓存的名字。
//不指定 key 会默认使用参数名或者方法名,作为缓存的key。
5. 测试
第一次访问是没有缓存的,执行sql从数据库查,执行了查询方法,输出写在方法中的输出语句。
第二次访问,已有缓存,不进入方法,直接从缓存得数据并作为方法的返回值,不运行sql。如下:












)

概念的理解)

- go的数据基本数据类型及变量定义方式)
 PipelinesMultiplexers)


)
