例子
- aes_generic.c - crypto/aes_generic.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
static struct crypto_alg aes_alg = {.cra_name = "aes",.cra_driver_name = "aes-generic",.cra_priority = 100,.cra_flags = CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_CIPHER,.cra_blocksize = AES_BLOCK_SIZE,.cra_ctxsize = sizeof(struct crypto_aes_ctx),.cra_module = THIS_MODULE,.cra_u = {.cipher = {.cia_min_keysize = AES_MIN_KEY_SIZE,.cia_max_keysize = AES_MAX_KEY_SIZE,.cia_setkey = crypto_aes_set_key,.cia_encrypt = crypto_aes_encrypt,.cia_decrypt = crypto_aes_decrypt}}
};
- 从上述定义可知AES算法的属性信息,如下所示:
- a)算法名为"aes",算法驱动名为"aes-generic"。
- b)算法的优先级为100 使用的时候,如未特殊指定,按照优先级高低进行使用
- c)算法的分组长度为AES_BLOCK_SIZE(16)字节
- d)算法类型为CRYPTO_ALG_TYPE_CIPHER(即分组算法),其个性化属性数据结构为struct cipher_alg,定义如下所示:
cipher_alg
/*** DOC: Block Cipher Algorithm Definitions** These data structures define modular crypto algorithm implementations,* managed via crypto_register_alg() and crypto_unregister_alg().*//*** struct cipher_alg - single-block symmetric ciphers definition* @cia_min_keysize: Minimum key size supported by the transformation. This is* the smallest key length supported by this transformation* algorithm. This must be set to one of the pre-defined* values as this is not hardware specific. Possible values* for this field can be found via git grep "_MIN_KEY_SIZE"* include/crypto/* @cia_max_keysize: Maximum key size supported by the transformation. This is* the largest key length supported by this transformation* algorithm. This must be set to one of the pre-defined values* as this is not hardware specific. Possible values for this* field can be found via git grep "_MAX_KEY_SIZE"* include/crypto/* @cia_setkey: Set key for the transformation. This function is used to either* program a supplied key into the hardware or store the key in the* transformation context for programming it later. Note that this* function does modify the transformation context. This function* can be called multiple times during the existence of the* transformation object, so one must make sure the key is properly* reprogrammed into the hardware. This function is also* responsible for checking the key length for validity.* @cia_encrypt: Encrypt a single block. This function is used to encrypt a* single block of data, which must be @cra_blocksize big. This* always operates on a full @cra_blocksize and it is not possible* to encrypt a block of smaller size. The supplied buffers must* therefore also be at least of @cra_blocksize size. Both the* input and output buffers are always aligned to @cra_alignmask.* In case either of the input or output buffer supplied by user* of the crypto API is not aligned to @cra_alignmask, the crypto* API will re-align the buffers. The re-alignment means that a* new buffer will be allocated, the data will be copied into the* new buffer, then the processing will happen on the new buffer,* then the data will be copied back into the original buffer and* finally the new buffer will be freed. In case a software* fallback was put in place in the @cra_init call, this function* might need to use the fallback if the algorithm doesn't support* all of the key sizes. In case the key was stored in* transformation context, the key might need to be re-programmed* into the hardware in this function. This function shall not* modify the transformation context, as this function may be* called in parallel with the same transformation object.* @cia_decrypt: Decrypt a single block. This is a reverse counterpart to* @cia_encrypt, and the conditions are exactly the same.** All fields are mandatory and must be filled.*/
struct cipher_alg {unsigned int cia_min_keysize;unsigned int cia_max_keysize;int (*cia_setkey)(struct crypto_tfm *tfm, const u8 *key,unsigned int keylen);void (*cia_encrypt)(struct crypto_tfm *tfm, u8 *dst, const u8 *src);void (*cia_decrypt)(struct crypto_tfm *tfm, u8 *dst, const u8 *src);
};
分组算法个性化属性包括2个参数和3个算法 接口,如上所示:
2个参数
- 分组算法输入密钥长度的下限cia_min_keysize和上限cia_max_keysize
- AES算法密钥长度的下限和上限分别为AES_MIN_KEY_SIZE(16)、AES_MAX_KEY_SIZE(32),但实际上AES算法只支持16B(128bit)、24B(192bit)和32B(256bit)三种密钥长度,如果输入密钥的长度为其他值,在进行密钥扩展(crypto_aes_expand_key)时将返回参数错误,如下所示:

三个算法接口
- 分组算法的算法接口,包括密钥设置接口cia_setkey、加密接口cia_encrypt和解密接口cia_decrypt,算法运行的上下文空间由算法实例tfm提供。
- AES算法的三个算法接口分别为crypto_aes_set_key、aes_encrypt和aes_decrypt。从AES算法加密接口和解密接口的实现流程来看,每次处理一个分组(16B)的数据。
- AES算法运行的上下文空间是数据结构struct crypto_aes_ctx的一个实例,该数据结构定义(root/include/crypto/aes.h)如下所示:
- aes.h - include/crypto/aes.h - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
crypto_aes_ctx
/** Please ensure that the first two fields are 16-byte aligned* relative to the start of the structure, i.e., don't move them!*/
struct crypto_aes_ctx {u32 key_enc[AES_MAX_KEYLENGTH_U32];u32 key_dec[AES_MAX_KEYLENGTH_U32];u32 key_length;
};
- AES算法上下文数据结构包括密钥扩展后的加密密钥key_enc和解密密钥key_dec以及输入的密钥长度key_length。
- 注:由于算法应用不会直接使用AES算法的算法接口,因此其算法说明aes_alg未设置算法类型常量cra_type。
crypto_aes_set_key

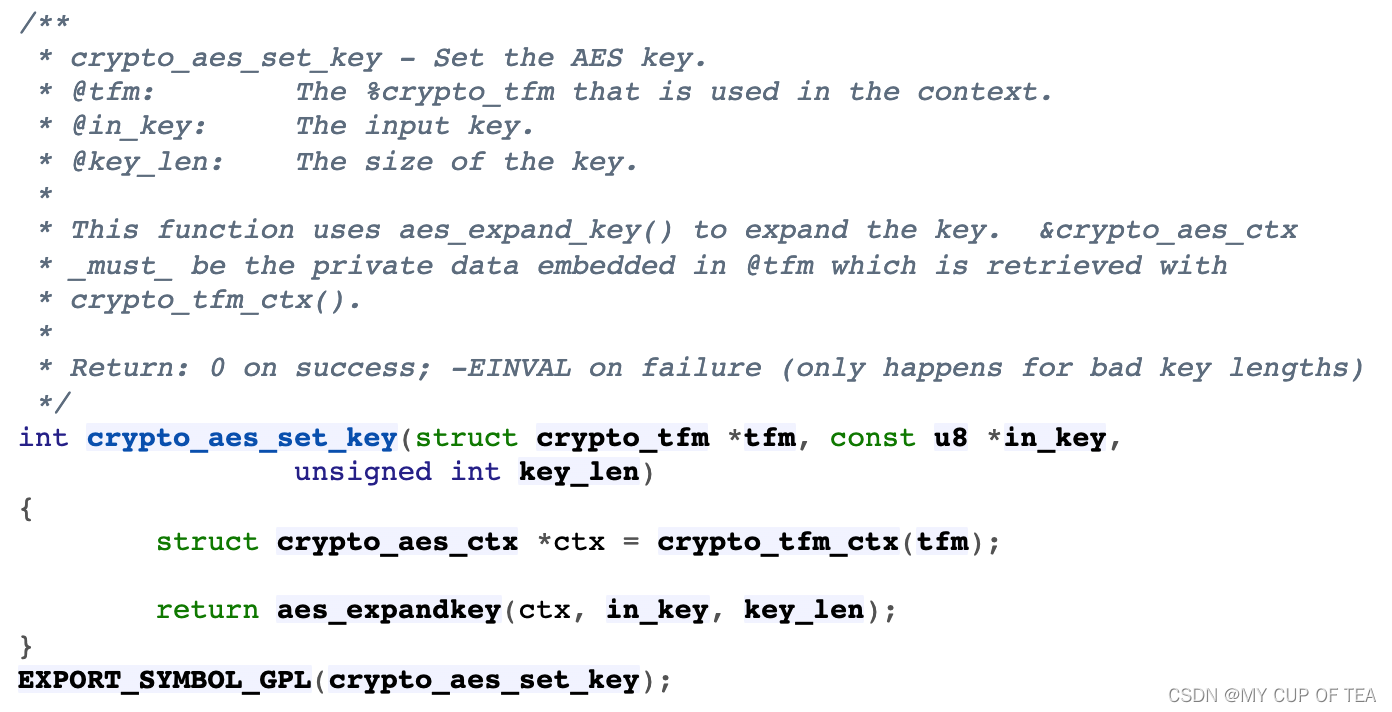
aes_expandkey
- aes.c - lib/crypto/aes.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
/*** aes_expandkey - Expands the AES key as described in FIPS-197* @ctx: The location where the computed key will be stored.* @in_key: The supplied key.* @key_len: The length of the supplied key.** Returns 0 on success. The function fails only if an invalid key size (or* pointer) is supplied.* The expanded key size is 240 bytes (max of 14 rounds with a unique 16 bytes* key schedule plus a 16 bytes key which is used before the first round).* The decryption key is prepared for the "Equivalent Inverse Cipher" as* described in FIPS-197. The first slot (16 bytes) of each key (enc or dec) is* for the initial combination, the second slot for the first round and so on.*/
int aes_expandkey(struct crypto_aes_ctx *ctx, const u8 *in_key,unsigned int key_len)
{u32 kwords = key_len / sizeof(u32);u32 rc, i, j;int err;err = aes_check_keylen(key_len);if (err)return err;ctx->key_length = key_len;for (i = 0; i < kwords; i++)ctx->key_enc[i] = get_unaligned_le32(in_key + i * sizeof(u32));for (i = 0, rc = 1; i < 10; i++, rc = mul_by_x(rc)) {u32 *rki = ctx->key_enc + (i * kwords);u32 *rko = rki + kwords;rko[0] = ror32(subw(rki[kwords - 1]), 8) ^ rc ^ rki[0];rko[1] = rko[0] ^ rki[1];rko[2] = rko[1] ^ rki[2];rko[3] = rko[2] ^ rki[3];if (key_len == AES_KEYSIZE_192) {if (i >= 7)break;rko[4] = rko[3] ^ rki[4];rko[5] = rko[4] ^ rki[5];} else if (key_len == AES_KEYSIZE_256) {if (i >= 6)break;rko[4] = subw(rko[3]) ^ rki[4];rko[5] = rko[4] ^ rki[5];rko[6] = rko[5] ^ rki[6];rko[7] = rko[6] ^ rki[7];}}/** Generate the decryption keys for the Equivalent Inverse Cipher.* This involves reversing the order of the round keys, and applying* the Inverse Mix Columns transformation to all but the first and* the last one.*/ctx->key_dec[0] = ctx->key_enc[key_len + 24];ctx->key_dec[1] = ctx->key_enc[key_len + 25];ctx->key_dec[2] = ctx->key_enc[key_len + 26];ctx->key_dec[3] = ctx->key_enc[key_len + 27];for (i = 4, j = key_len + 20; j > 0; i += 4, j -= 4) {ctx->key_dec[i] = inv_mix_columns(ctx->key_enc[j]);ctx->key_dec[i + 1] = inv_mix_columns(ctx->key_enc[j + 1]);ctx->key_dec[i + 2] = inv_mix_columns(ctx->key_enc[j + 2]);ctx->key_dec[i + 3] = inv_mix_columns(ctx->key_enc[j + 3]);}ctx->key_dec[i] = ctx->key_enc[0];ctx->key_dec[i + 1] = ctx->key_enc[1];ctx->key_dec[i + 2] = ctx->key_enc[2];ctx->key_dec[i + 3] = ctx->key_enc[3];return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(aes_expandkey);
aes_encrypt
- aes.c - lib/crypto/aes.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
/*** aes_encrypt - Encrypt a single AES block* @ctx: Context struct containing the key schedule* @out: Buffer to store the ciphertext* @in: Buffer containing the plaintext*/
void aes_encrypt(const struct crypto_aes_ctx *ctx, u8 *out, const u8 *in)
{const u32 *rkp = ctx->key_enc + 4;int rounds = 6 + ctx->key_length / 4;u32 st0[4], st1[4];int round;st0[0] = ctx->key_enc[0] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in);st0[1] = ctx->key_enc[1] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in + 4);st0[2] = ctx->key_enc[2] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in + 8);st0[3] = ctx->key_enc[3] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in + 12);/** Force the compiler to emit data independent Sbox references,* by xoring the input with Sbox values that are known to add up* to zero. This pulls the entire Sbox into the D-cache before any* data dependent lookups are done.*/st0[0] ^= aes_sbox[ 0] ^ aes_sbox[ 64] ^ aes_sbox[134] ^ aes_sbox[195];st0[1] ^= aes_sbox[16] ^ aes_sbox[ 82] ^ aes_sbox[158] ^ aes_sbox[221];st0[2] ^= aes_sbox[32] ^ aes_sbox[ 96] ^ aes_sbox[160] ^ aes_sbox[234];st0[3] ^= aes_sbox[48] ^ aes_sbox[112] ^ aes_sbox[186] ^ aes_sbox[241];for (round = 0;; round += 2, rkp += 8) {st1[0] = mix_columns(subshift(st0, 0)) ^ rkp[0];st1[1] = mix_columns(subshift(st0, 1)) ^ rkp[1];st1[2] = mix_columns(subshift(st0, 2)) ^ rkp[2];st1[3] = mix_columns(subshift(st0, 3)) ^ rkp[3];if (round == rounds - 2)break;st0[0] = mix_columns(subshift(st1, 0)) ^ rkp[4];st0[1] = mix_columns(subshift(st1, 1)) ^ rkp[5];st0[2] = mix_columns(subshift(st1, 2)) ^ rkp[6];st0[3] = mix_columns(subshift(st1, 3)) ^ rkp[7];}put_unaligned_le32(subshift(st1, 0) ^ rkp[4], out);put_unaligned_le32(subshift(st1, 1) ^ rkp[5], out + 4);put_unaligned_le32(subshift(st1, 2) ^ rkp[6], out + 8);put_unaligned_le32(subshift(st1, 3) ^ rkp[7], out + 12);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(aes_encrypt);
aes_decrypt
- aes.c - lib/crypto/aes.c - Linux source code (v5.15.11) - Bootlin
/*** aes_decrypt - Decrypt a single AES block* @ctx: Context struct containing the key schedule* @out: Buffer to store the plaintext* @in: Buffer containing the ciphertext*/
void aes_decrypt(const struct crypto_aes_ctx *ctx, u8 *out, const u8 *in)
{const u32 *rkp = ctx->key_dec + 4;int rounds = 6 + ctx->key_length / 4;u32 st0[4], st1[4];int round;st0[0] = ctx->key_dec[0] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in);st0[1] = ctx->key_dec[1] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in + 4);st0[2] = ctx->key_dec[2] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in + 8);st0[3] = ctx->key_dec[3] ^ get_unaligned_le32(in + 12);/** Force the compiler to emit data independent Sbox references,* by xoring the input with Sbox values that are known to add up* to zero. This pulls the entire Sbox into the D-cache before any* data dependent lookups are done.*/st0[0] ^= aes_inv_sbox[ 0] ^ aes_inv_sbox[ 64] ^ aes_inv_sbox[129] ^ aes_inv_sbox[200];st0[1] ^= aes_inv_sbox[16] ^ aes_inv_sbox[ 83] ^ aes_inv_sbox[150] ^ aes_inv_sbox[212];st0[2] ^= aes_inv_sbox[32] ^ aes_inv_sbox[ 96] ^ aes_inv_sbox[160] ^ aes_inv_sbox[236];st0[3] ^= aes_inv_sbox[48] ^ aes_inv_sbox[112] ^ aes_inv_sbox[187] ^ aes_inv_sbox[247];for (round = 0;; round += 2, rkp += 8) {st1[0] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st0, 0)) ^ rkp[0];st1[1] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st0, 1)) ^ rkp[1];st1[2] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st0, 2)) ^ rkp[2];st1[3] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st0, 3)) ^ rkp[3];if (round == rounds - 2)break;st0[0] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st1, 0)) ^ rkp[4];st0[1] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st1, 1)) ^ rkp[5];st0[2] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st1, 2)) ^ rkp[6];st0[3] = inv_mix_columns(inv_subshift(st1, 3)) ^ rkp[7];}put_unaligned_le32(inv_subshift(st1, 0) ^ rkp[4], out);put_unaligned_le32(inv_subshift(st1, 1) ^ rkp[5], out + 4);put_unaligned_le32(inv_subshift(st1, 2) ^ rkp[6], out + 8);put_unaligned_le32(inv_subshift(st1, 3) ^ rkp[7], out + 12);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(aes_decrypt);





预测未来值)







)








