前言
虽然在.Net Framework 中我们不必考虑内在管理和垃圾回收(GC),但是为了优化应用程序性能我们始终需要了解内存管理和垃圾回收(GC)。另外,了解内存管理可以帮助我们理解在每一个程序中定义的每一个变量是怎样工作的。
简介
继续上篇未完成的“参数传递对堆栈的影响”。
引用类型传递
传递引用类型跟上一节所示例中用引用的方式传递值类型相似。
如果使用引用类型(原文可能笔误,写的是值类型):
-
public class MyInt -
{ -
public int MyValue; -
}
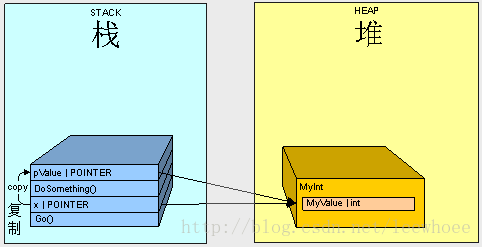
然后调用Go()方法,MyInt会被放到堆里因为它是一个引用类型。
-
public void Go() -
{ -
MyInt x = new MyInt(); -
}
如果执行下面代码中的Go():
-
public void Go() -
{ -
MyInt x = new MyInt(); -
x.MyValue = 2; -
DoSomething(x); -
Console.WriteLine(x.MyValue.ToString()); -
} -
public void DoSomething(MyInt pValue) -
{ -
pValue.MyValue = 12345; -
}
会发生这种情况:
- 开始调用Go(),栈分配一块内存空间给x。
- 执行行到DoSomething(),栈分配一块内在空间给pValue。
- x的值是堆中MyInt对应在栈里的内存地址,复制x给pValue。
因此,我们用pValue改变MyInt的MyValue的值时,x最终也会获得这个改变的值"12345“。
如果我们用引用的方式传递一个引用类型变量呢?
用引用的方式传递引用类型
我们有一个类Thing, 类 Animal和Vegetables衍生于Thing:
-
public class Thing -
{ -
} -
public class Animal:Thing -
{ -
public int Weight; -
} -
public class Vegetable:Thing -
{ -
public int Length; -
}
执行下面的Go()方法:
-
public void Go() -
{ -
Thing x = new Animal(); -
Switcharoo(ref x); -
Console.WriteLine( -
"x is Animal : " -
+ (x is Animal).ToString()); -
Console.WriteLine( -
"x is Vegetable : " -
+ (x is Vegetable).ToString()); -
} -
public void Switcharoo(ref Thing pValue) -
{ -
pValue = new Vegetable(); -
}
x最终变成 Vegetable。
打印结果:
x is Animal : False
x is Vegetable : True
让我们看看堆栈里到底发生了什么情况
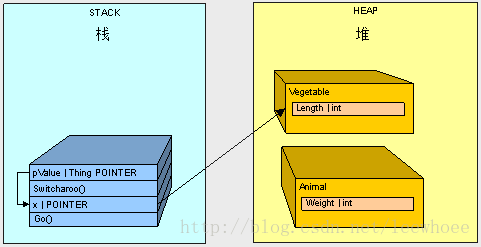
- 调用Go()方法,栈分配一块内存空间给x。
- 堆分配一块内存空间给Animal。
- 开始执行Switcharoo()方法,栈分配一块内存空间给pValue并指向x。
- 栈分配一块内存空间给Vegetable。
- pValue改变了x的值使其指向Vegetable的内在地址。
如果我们不是用ref传递的,打印结果正相反。
总结
我们已经演示了参数传递是怎么在内在中处理的。在接下来的文章里,存储在栈中的引用变量会产生什么情况以及怎么解决对象复制带来的问题。
翻译: http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/rmcochran/csharp_memory2B01142006125918PM/csharp_memory2B.aspx



 VS Stack(ing) 第五节 引用类型复制问题及用克隆接口ICloneable修复)

 VS Stack(ing) 第六节 理解垃圾回收GC,提搞程序性能****)
...)



用于提取字符串s中的特定字符操作)


方法的一些使用细节)


)


)

)