问题描述
如果写一段代码,让程序从 1 开始一直执行 ++ 操作,在规定的 10s 钟内,你能输出的最大数是多少?并将它打印到屏幕上。
乍一看,你会觉得它是一道算法题,再细想:不对!这可能是一道性能题。
题目拆解
首先,定义一个变量 i,并赋值为 1, 接着进入 while 循环,执行 i++. 需要注意的是,这个变量可能非常大,超出了类型的最大值,那么就需要用一个数组来存储这个变量,数组中的每个元素分别表示这个数的每一位。
其次,单线程处理时,每次进入 while 循环时,都需要获取程序运行时间,当程序运行时间快到 10s 时得赶紧退出循环,并将这个“大数”打印到屏幕上。否则,如果没来得及输出到屏幕,就前功尽弃了。
进阶
看起来,上述思路已经足以解决这个问题了。然而,这也许并不是最优解。这里,我们采用多线程机制试试。具体步骤如下:
- 在主线程里开辟两个新进程 A 和 B;
- 在线程 A 里执行 ++ 操作;
- 在线程 B 里实时获取程序运行时间;
- 在线程 A 里判断是否运行超时,并及时退出并输出结果。
测试结果
- 硬件信息
如图所示,intel 处理器 i5,4核。

硬件信息
- 性能数据
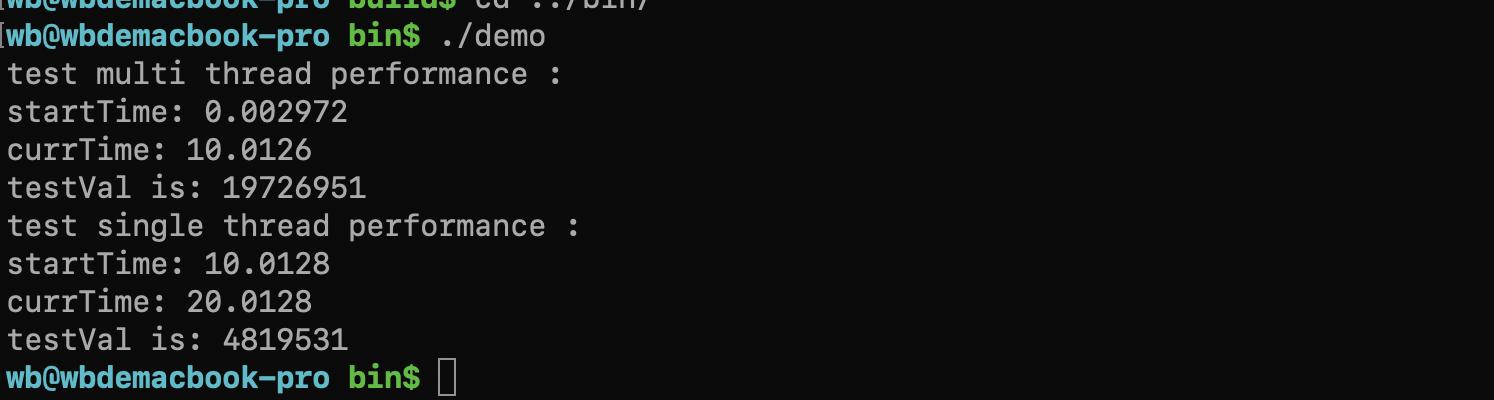
测试结果
单线程时:10s 时间内 C++ 程序能够输出的最大值为 4819531;
多线程时:10s 时间内 C++ 程序能够输出的最大值为 19726951;
多线程性能是单线程性能的 4 倍!
原因分析
很可能是因为多核,不同线程跑在不同的核上,充分利用 CPU。
软件性能是每个程序员都要面临的问题,从基本的代码级性能优化,到数据 cache miss、指令 cache miss 优化,再到多线程协同、绑核、资源调度算法,甚至对二进制目标文件的内容进行重排。。。等等,所涉及的面非常广,也可以非常深。
附录:C++ 代码,供参考
main.cpp
#include "Global.h"#include "ProcessInfo.h"#include "Test.h"#include #include #include namespace Single {void SinglePrint(std::vector& val){ std::cout << "testVal is: "; unsigned int i = 0; for (; i < val.size(); i++) { if (val[i] != 0) { break; } } for (unsigned int j = i; j < val.size(); j++) { std::cout << val[j]; } std::cout << std::endl;}void SingleTestAdd(){ std::vector testVal(Global::bitNum, 0); while (true) { int flag = 0; int tmp; for (int i = Global::bitNum - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (i == Global::bitNum - 1) { tmp = testVal[i] + 1 + flag; } else { tmp = testVal[i] + flag; } if (tmp >= 10) { flag = 1; } else { flag = 0; } testVal[i] = (tmp % 10); } clock_t t = clock(); ProcessInfo::currTime = (double)t / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; if ((ProcessInfo::currTime - ProcessInfo::startTime) > Global::expireTime) { std::cout << "currTime: " << ProcessInfo::currTime << std::endl; SinglePrint(testVal); break; } } return;};}int main(){ std::cout << "test multi thread performance : " << std::endl; ProcessInfo::GetProcessStartTime(); std::cout << "startTime: " << ProcessInfo::startTime << std::endl; std::thread t1(ProcessInfo::GetProcessCurrTime); std::thread t2(Test::TestAdd); t1.detach(); t2.join(); std::cout << "test single thread performance : " << std::endl; ProcessInfo::GetProcessStartTime(); std::cout << "startTime: " << ProcessInfo::startTime << std::endl; Single::SingleTestAdd(); return 0;}Global.h - 单例类,定义全局变量:
#ifndef _GLOBAL_H_#define _GLOBAL_H_#include class Global {private: Global(){}; static Global* global;public: static Global* GetGlobalInstance() { if (global == NULL) { global = new Global(); } return global; }public: static int bitNum; static int expireTime;};#endifGlobal.cpp
#include "Global.h"int Global::bitNum = 64;int Global::expireTime = 10;ProcessInfo.h - 程序运行信息类
#ifndef _PROCESSINFO_H_#define _PROCESSINFO_H_#include class ProcessInfo{public: ProcessInfo(){}; static double startTime; static double currTime; static void GetProcessStartTime() { clock_t tmp = clock(); startTime = (double)tmp / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; }; static void GetProcessCurrTime() { while(1) { clock_t tmp = clock(); currTime = (double)tmp / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; } };};#endifProcessInfo.cpp
#include "ProcessInfo.h"double ProcessInfo::startTime = 0;double ProcessInfo::currTime = 0;Test.h - 测试类
#ifndef _TEST_H_#define _TEST_H_#include "../module1/ProcessInfo.h"#include "../module1/Global.h"#include #include #include class Test{public: Test(){}; static void TestAdd() { std::vector testVal(Global::bitNum, 0); while (true) { int flag = 0; int tmp; for (int i = Global::bitNum - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (i == Global::bitNum - 1) { tmp = testVal[i] + 1 + flag; } else { tmp = testVal[i] + flag; } if (tmp >= 10) { flag = 1; } else { flag = 0; } testVal[i] = (tmp % 10); } if ((ProcessInfo::currTime - ProcessInfo::startTime) > Global::expireTime) { std::cout << "currTime: " << ProcessInfo::currTime << std::endl; PrintTestVal(testVal); break; } } return; }; static void PrintTestVal(std::vector& val) { std::cout << "testVal is: "; unsigned int i = 0; for (; i < val.size(); i++) { if (val[i] != 0) { break; } } for (unsigned int j = i; j < val.size(); j++) { std::cout << val[j]; } std::cout << std::endl; }};#endif







-类型、方法与继承)











