/*
字符串:
一、概述:1.字符串在JAVA中,使用""表示2.java.lang.String类3.只要写""就是字符串对象。不需要new二、空参构造器new Sting();private final char value[];public String() {this.value = "".value;}
三、String类一个参数构造器:字节数组采用平台(操作系统)默认字符集解码数组--编码表GBKbyte[] = {};将字节数组转成字符串public String(byte bytes[]) {this(bytes, 0, bytes.length);}
四、String类两个参数构造器:指定一个编码表【I/O更新】五、String类三个参数构造器:字节数组,开始下标,获取几个
java.lang.String @Contract(pure = true)
public String(@NotNull byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
六、String类一个参数构造器:字符数组
public String(char value[]) {this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);}
七、String类三个参数构造器:字符数组,开始下标,获取几个public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {if (offset < 0) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);}if (count <= 0) {if (count < 0) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);}if (offset <= value.length) {this.value = "".value;return;}}// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.if (offset > value.length - count) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);}this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);}
八、String类三个参数构造器:整数数组,开始下标,获取几个(基本不用)
九、 String类三个参数构造器:字符串(基本不用)
public String(String original) {this.value = original.value;this.hash = original.hash;}十、字符串一旦创建,就是常量,不能修改。
"abc"是对象---不能改变
s 是引用型变量
s 的指向对象可以改变十一、在堆中,如果
String s1 = new String('a','b','c');
String s2 = new String('a','b','c');
System.out.println(s1==s2);-------true但
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1==s2);-------Fals:创建对象不同String s5 = "efg";
System.out.println(s4==(s4+s5));---- f-------常量与变量相加,不知道结果,重新建立空间,比较的是内存地址
System.out.println(s4==("abc"+"def"));---- t------常量与常量相加,比较的是具体数值*/
1.双引号代表String类对象
2.String类空参构造器
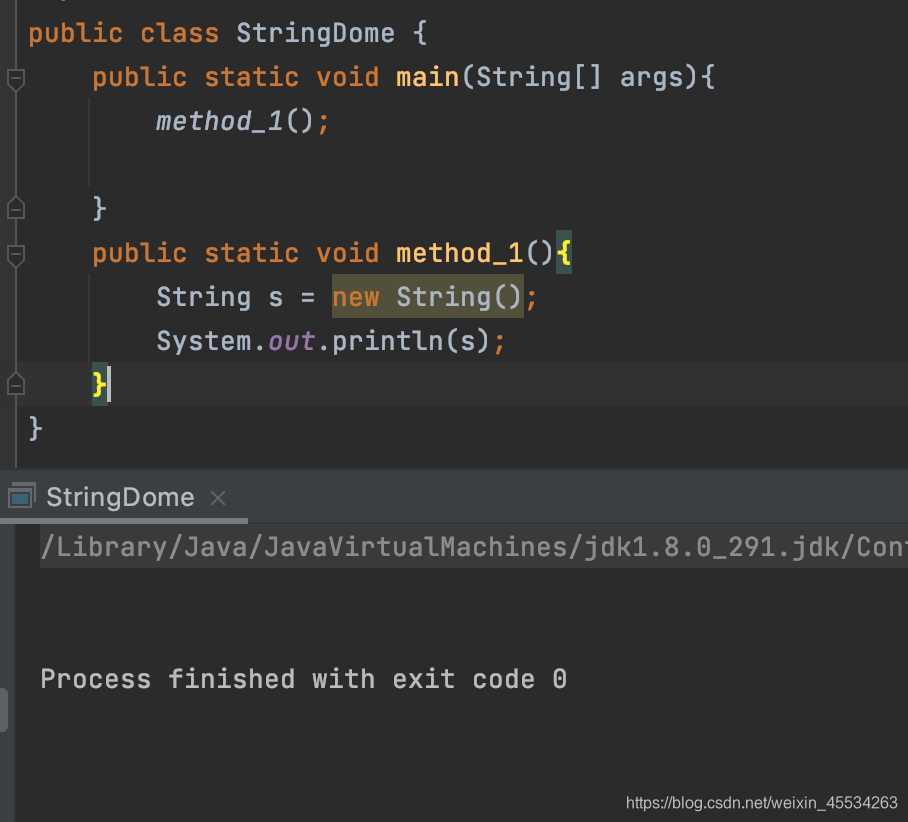
3.String类一个参数构造器
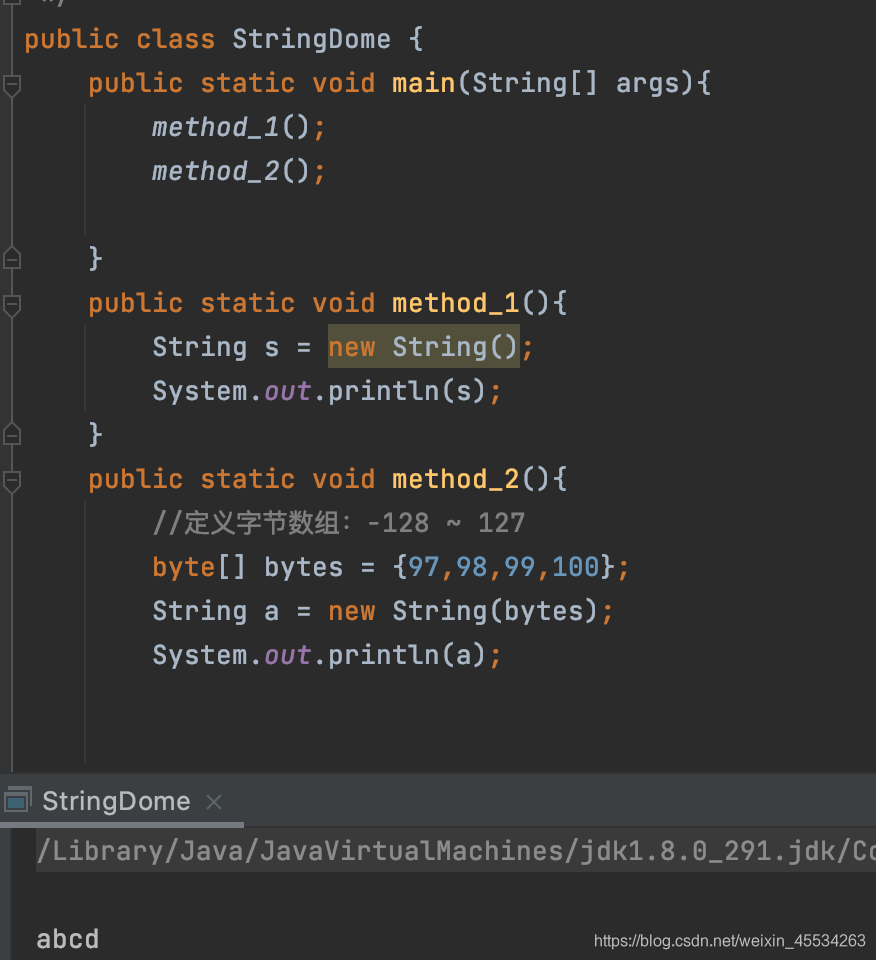


:数组导读)

String类之比较方法)
:数组的概念)
创建数组)
String类之比较方法(2))



StringBuffer类)
:数组新增元素)


StringBuffer类(练习))
)


二分法)

Arrays数组工具类)