大家好,我是烤鸭:
- 根据官方文档翻译并精简部分内容。建议有时间的朋友下载原版查看,全文106页pdf,快的话1-2天就能看完。自己翻译的有些地方可能不完整,欢迎指正。
- 官方pdf下载,需登录:
- https://www.mysql.com/cn/why-mysql/presentations/tune-mysql-queries-performance/
- csdn下载地址:
- https://download.csdn.net/download/angry_mills/10953302
- 简化版地址:
- https://blog.csdn.net/Angry_Mills/article/details/88081834
[官方] mysql 性能优化文档(中英文自译)
- How to Analyze and Tune MySQL Queries for Better Performance `如何分析和调整MySQL查询以获得更好的性能`
- Program Agenda `目录`
- Cost-based query optimization in MySQL `MySQL中基于成本的查询优化`
- Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries `用于监视,分析和调整查询的工具 `
- Data access and index selection `数据访问和索引选择`
- Join optimizer `连接优化器`
- Subqueries `子查询`
- Sorting `排序`
- Influencing the optimizer `影响优化器`
How to Analyze and Tune MySQL Queries for Better Performance 如何分析和调整MySQL查询以获得更好的性能
Program Agenda 目录
Cost-based query optimization in MySQL MySQL中基于成本的查询优化
MySQL Optimizer mysql优化器
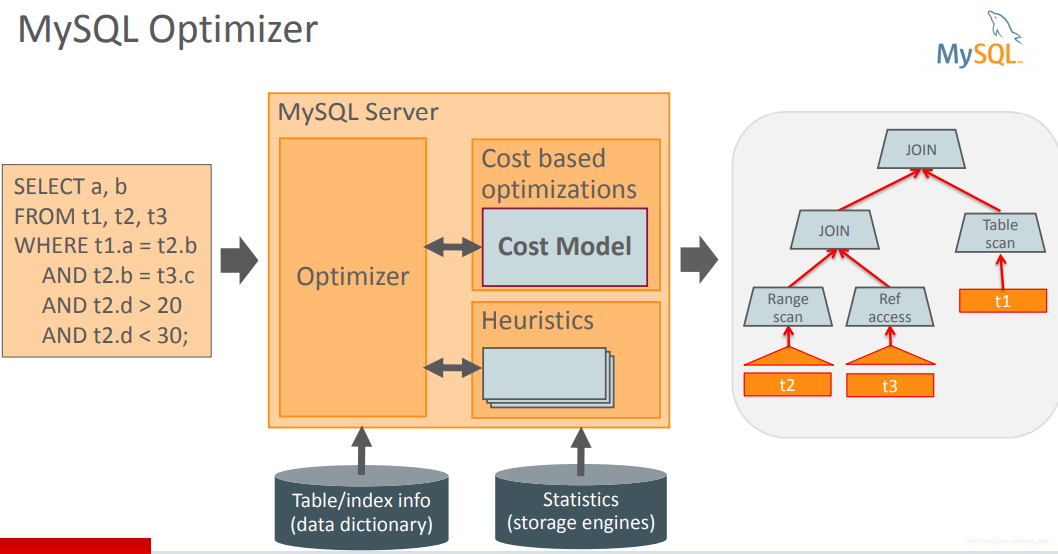
通常的想法:
- Assign cost to operations
将成本分配到操作 - Assign cost to partial or alternative plans
将成本分配到部分或替代计划 - Search for plan with lowest cost
搜索成本最低的计划 - Cost-based optimizations
基于成本的优化 - Access method
访问方式Subquery strategy子查询策略Join order连接顺序
mysql优化的特点:
- Produce the query plan that uses least resources IO and CPU
尽量减少CPU和I/O操作 - Optimizes a single query No inter-query optimizations
使用简单的查询,尽量少用嵌套的查询 - Produces left-deep linear query execution plan
生成以左连接为主的线性查询执行计划
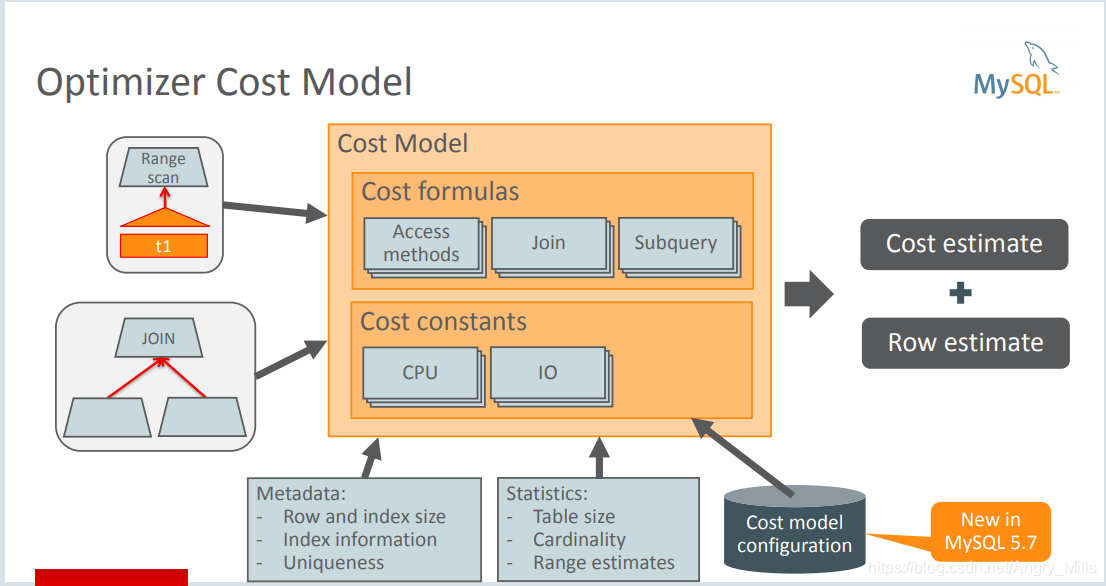
Optimizer Cost Model 优化器成本模型
图 Optimizer Cost Mode
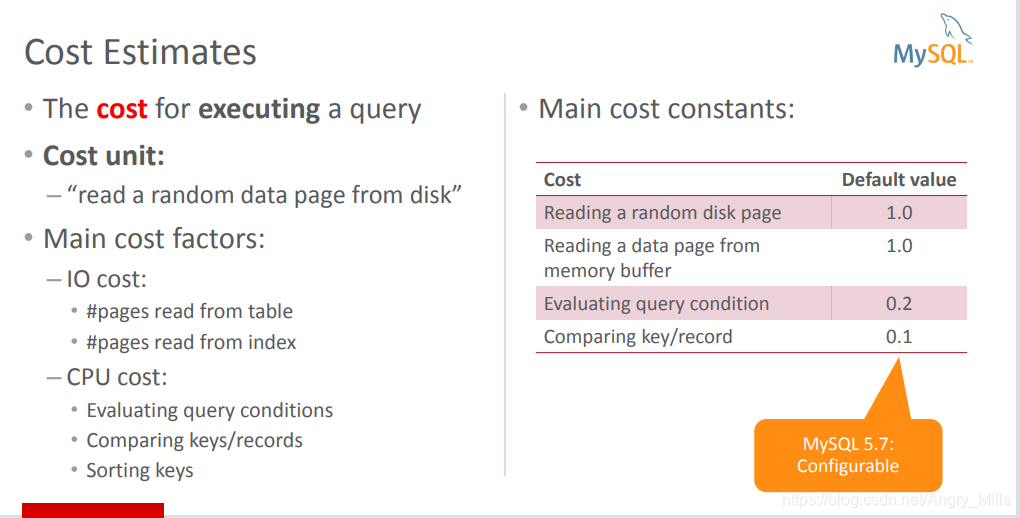
Cost Estimates 成本估算
- Cost unit:
“read a random data page from disk”随机从硬盘获取"一页"的数据
Main cost factors: - IO cost:
pages read from table:默认 1.0
pages read from index:默认 1.0 - CPU cost:
Evaluating query conditions:默认 0.2
Comparing keys/records :默认 0.1,mysql 5.7以后可配置
图 Cost Estimates
Cost Model Example 成本模型实例
- Table scan:
全表扫描- IO-cost: #pages in table * IO_BLOCK_READ_COST
IO成本:表中的pages * IO阻塞读取成本 - CPU cost: #rows * ROW_EVALUATE_COST
CPU成本: 行 * 行计算成本
- IO-cost: #pages in table * IO_BLOCK_READ_COST
- Range scan (on secondary index):
范围扫描(第二索引)- IO-cost: #rows_in_range * IO_BLOCK_READ_COST
IO成本:范围中的行 * IO阻塞读取成本 - CPU cost: #rows_in_range * ROW_EVALUATE_COST
IO成本:范围中的行 * 行计算成本
- IO-cost: #rows_in_range * IO_BLOCK_READ_COST
图 Cost Model Example
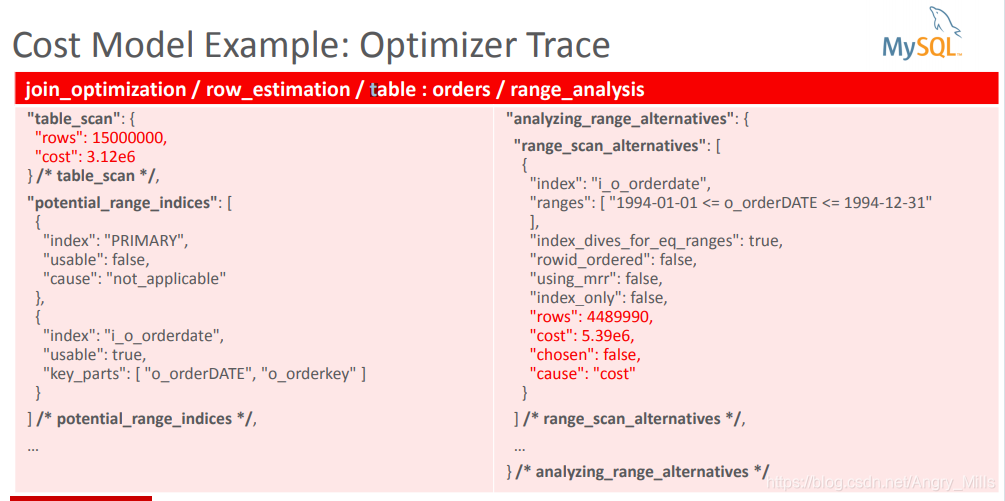
图 Cost Model Example: Optimizer Trace
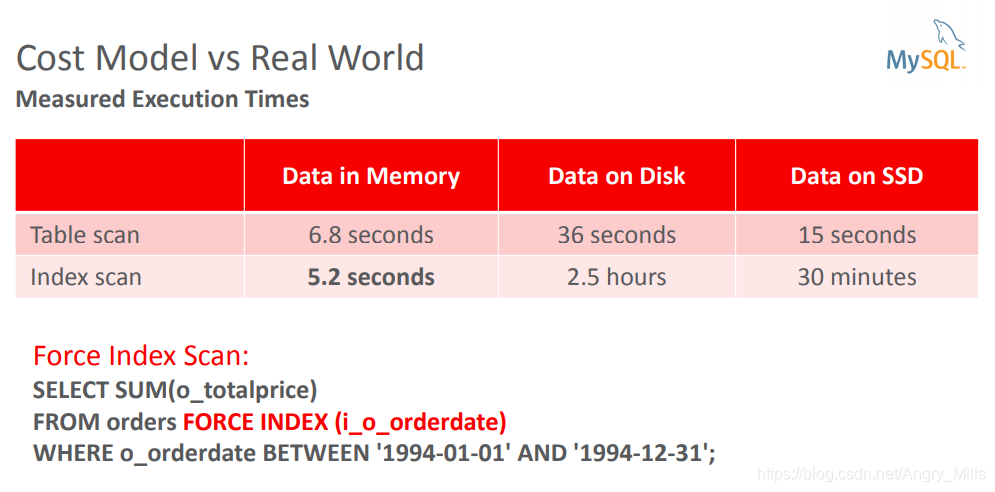
图 Cost Model vs Real World
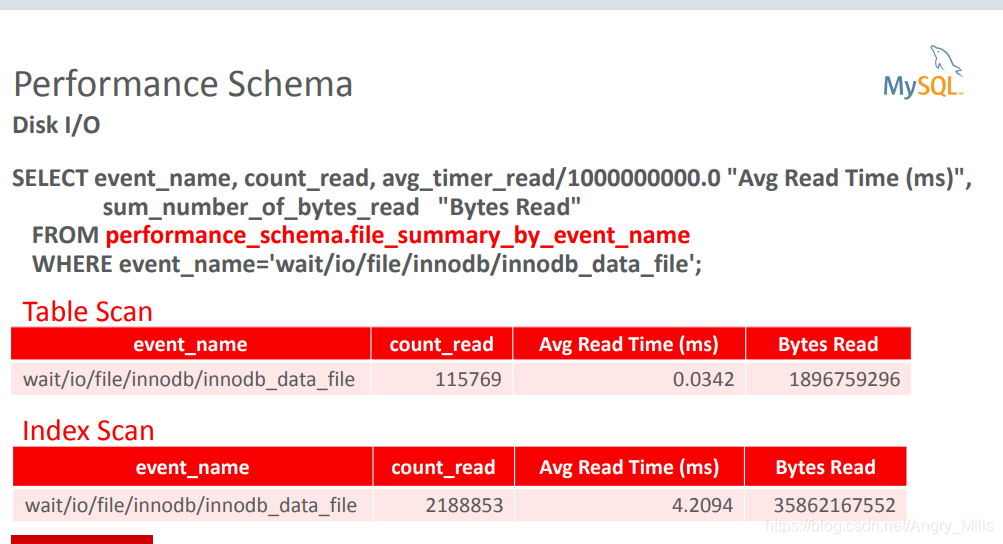
图 Cost Model Performance Schema
Tools for monitoring, analyzing, and tuning queries 用于监视,分析和调整查询的工具
- Useful tools
- MySQL Enterprise Monitor (MEM), Query Analyzer Commercial
product付费产品 - Performance schema, MySQL sys schema
执行计划,MySQL 系统计划
- MySQL Enterprise Monitor (MEM), Query Analyzer Commercial
- EXPLAIN
- Tabular EXPLAIN 表格式EXPLAIN
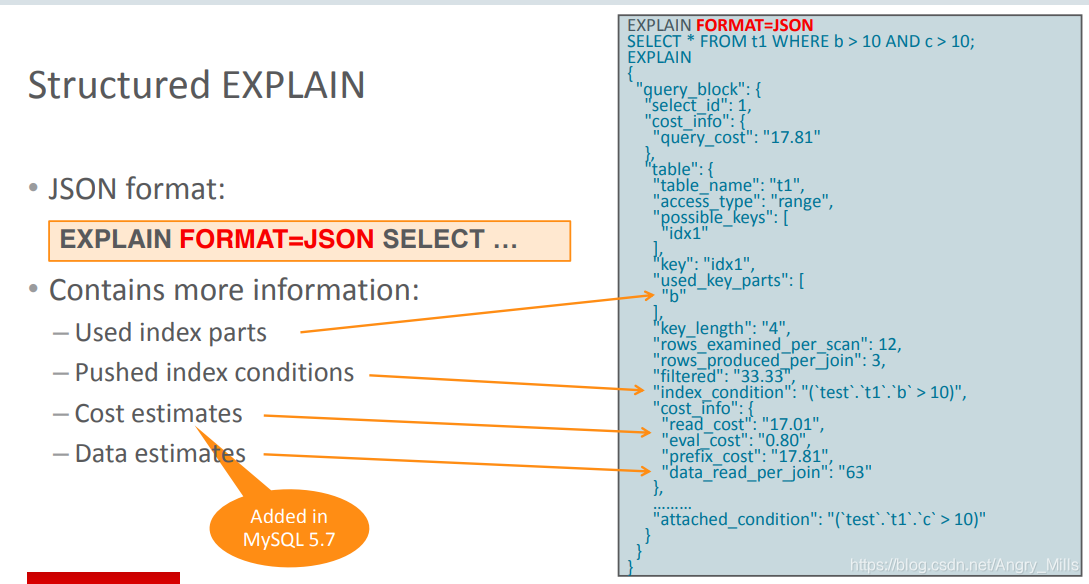
- Structured EXPLAIN (FORMAT=JSON)结构式EXPLAIN 图*2

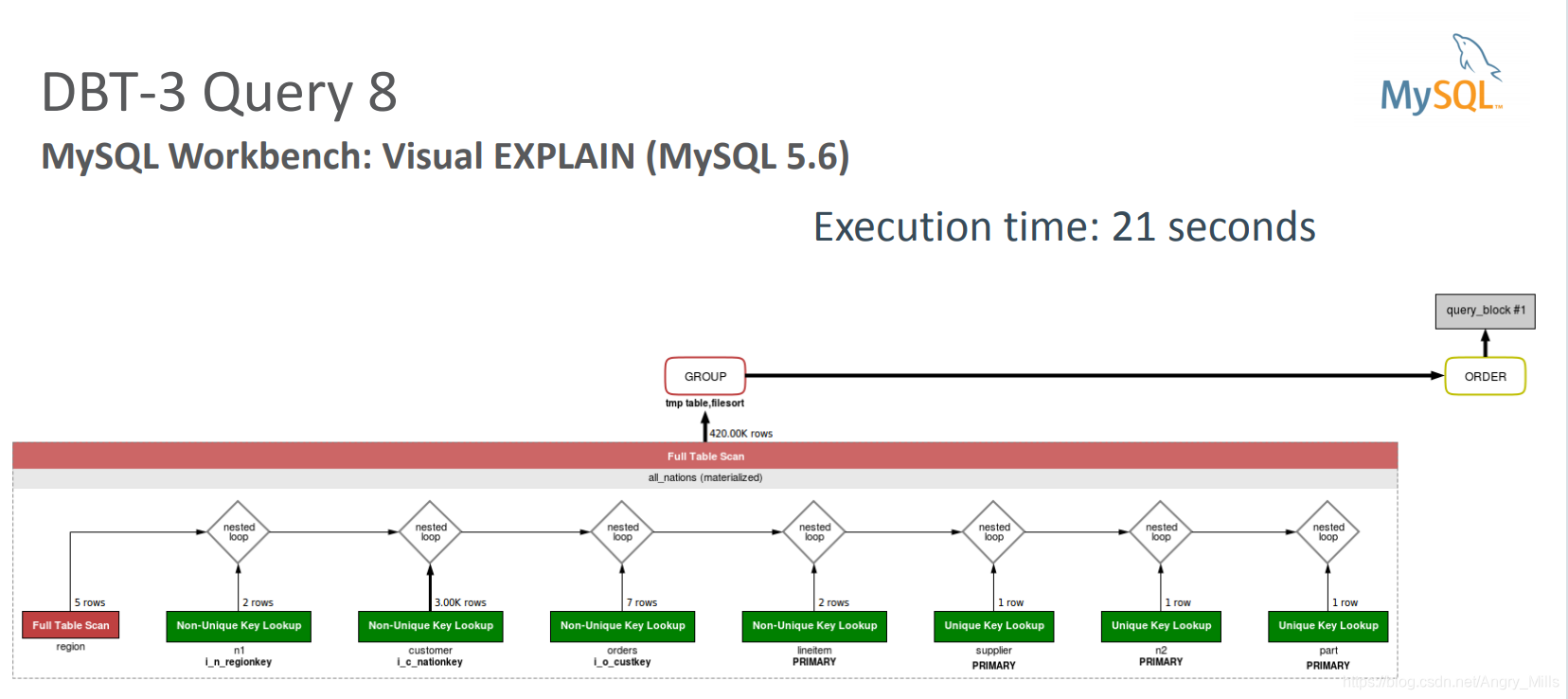
- Visual EXPLAIN (MySQL Workbench)
可视化EXPLAIN
- Optimizer trace
优化器跟踪 - Slow log
日志 - Status variables (SHOW STATUS LIKE ‘Sort%’)
状态变量
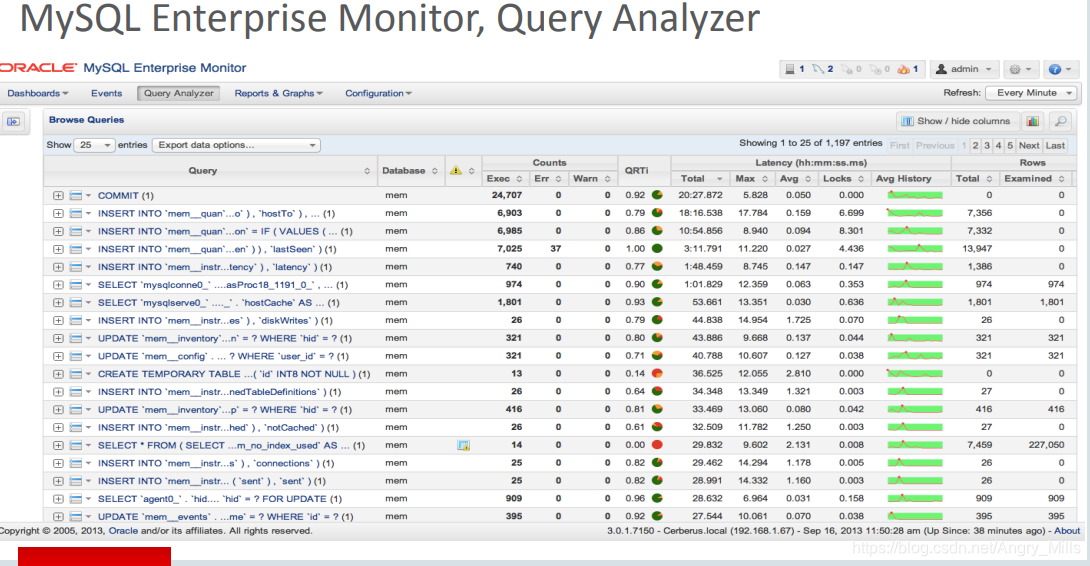
MEM 图形化界面,收费的,暂时不考虑了,看下面的例图
图 Query Analyzer
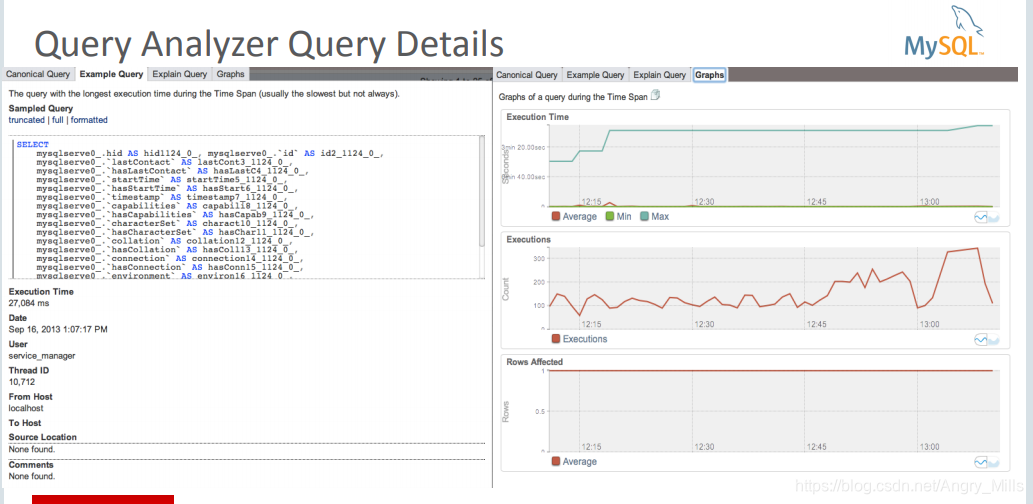
图 Query Analyzer Query Details
Performance schema 执行计划
一些有用的表:
-
events_statements_history,events_statements_history_long Most
recent statements executed大部分最近执行的statement -
events_statements_summary_by_digest Summary for similar statements
(same statement digest)总结相似操作(相同的statement合并) -
file_summary_by_event_name
-
Interesting event: wait/io/file/innodb/innodb_data_file
-
table_io_waits_summary_by_table
-
table_io_waits_summary_by_index_usage
-
Statistics on storage engine access per table and index
统计存储引擎的每个表和索引
Statement events
-
Tables:(Current statement for each thread)
每个线程当前执行的statement -
events_statements_history (10 most recent statements per thread)
每个线程最近执行的最多10条statement -
events_statements_history_long (10000 most recent statements)
最近执行的最多10000statement -
Statement digest
statement合并 -
Normalization of queries to group statements that are similar to be
grouped and summarized:规范化的按statement分组的查询,类似于分组和汇总、如下:
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_custkey=10 AND o_totalprice>20
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_custkey = 20 AND o_totalprice > 100
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_custkey = ? AND o_totalprice > ?
events_statements_summary_by_digest
MySQL sys Schema 系统计划
- A collection of views, procedures and functions, designed to make
reading raw Performance Schema data easier
一组视图,过程和函数,旨在简化读取原始性能模式数据 - Implements many common DBA and Developer use cases
实现许多常见的DBA和Developer用例- File IO usage per user
每个用户的文件IO使用 - Which indexes is never used?
哪个索引从未被使用 - Which queries use full table scans?
哪些查询是全表扫描
- File IO usage per user
- Examples of very useful functions:
非常有用的函数示例- format_time() , format_bytes(), format_statement()
- Included with MySQL 5.7
包含mysql 5.7 - Bundled with MySQL Workbench
与MySQL Workbench捆绑在一起
MySQL sys Schema MySQL 系统计划
- statement_analysis :Lists a normalized statement view with aggregated
statistics, ordered by the total execution time per normalized
statement (SELECT * FROM sys.statement_analysis LIMIT 1\G)
列出带聚合的规范化语句视图统计信息,按每个规范化语句的总执行时间排序
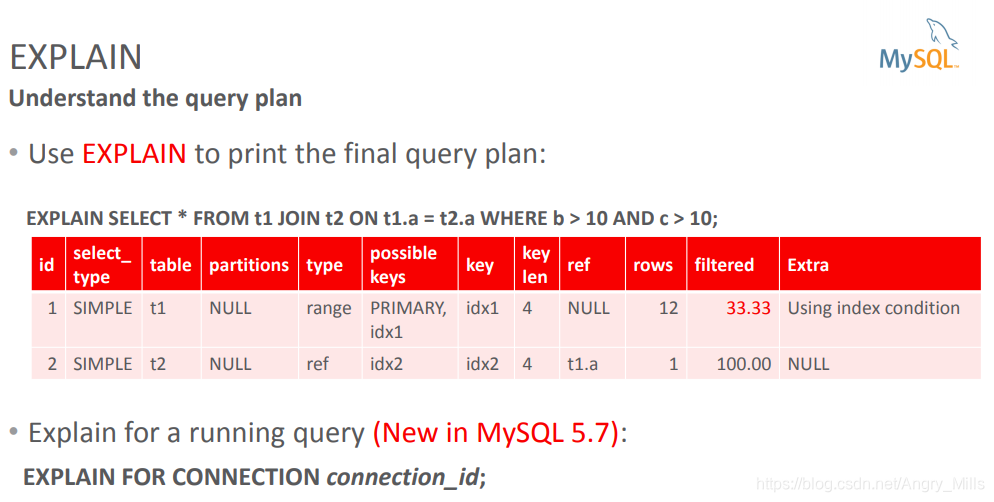
EXPLAIN Understand the query plan
图 EXPLAIN
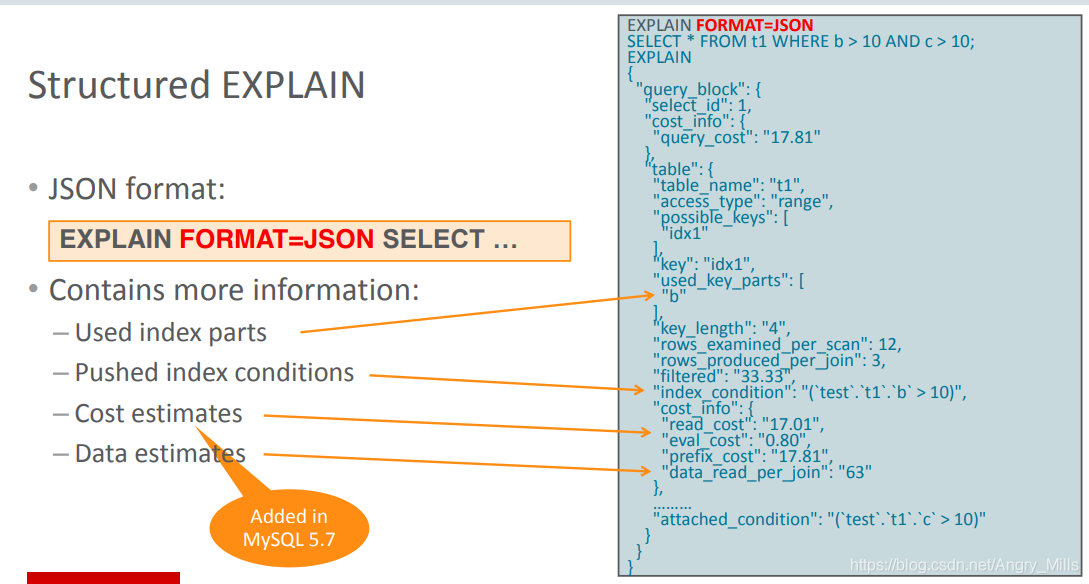
Structured EXPLAIN (EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON SELECT …)
图 Structured EXPLAIN
Contains more information:
- Used index parts
- Pushed index conditions
触发索引的条件 - Cost Estimates
成本估算 - Data estimates
数据估算
- Pushed index conditions
图 Structured EXPLAIN
图 MySQL sys Schema Example
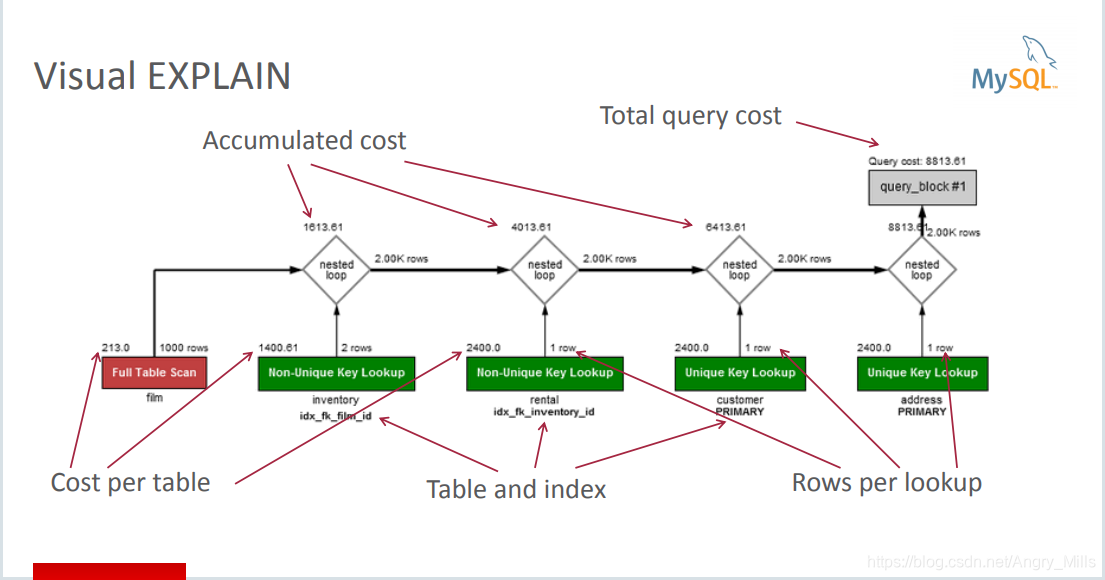
Visual EXPLAIN 可视化EXPLAIN
图 Visual EXPLAIN
Optimizer Trace: Query Plan Debugging 优化程序跟踪:查询计划调试
- EXPLAIN shows the selected plan EXPLAIN
展示了选择的计划 - Optimizer trace shows WHY the plan was selected
优化跟踪展示了为什么选这个计划SELECT * FROM t1,t2 WHERE f1=1 AND f1=f2 AND f2>0;SELECT trace FROM information_schema.optimizer_trace INTO OUTFILE <filename> LINES TERMINATED BY '';```SET optimizer_trace="enabled=off";
图 Optimizer Trace Debugging
Data access and index selection 数据访问和索引选择
- Finding the optimal method to read data from storage engine
找到最合适的方式从储存引擎读取数据 - For each table, find the best access method:
对于每个表,找到最佳访问方法- Check if the access method is useful
检查访问方法是否有用 - Estimate cost of using access method
估算使用访问方法的成本 - Select the cheapest to be used
选择最便宜的使用
- Check if the access method is useful
- Choice of access method is cost based
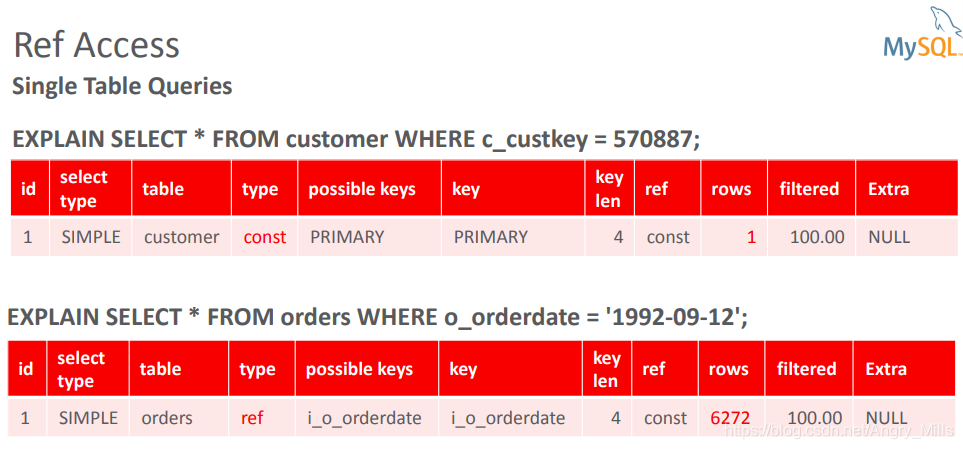
访问方法的选择是基于成本的 - Ref Access
参考访问 - Single Table Queries
单表查询
图 Ref Access Single Table Queries
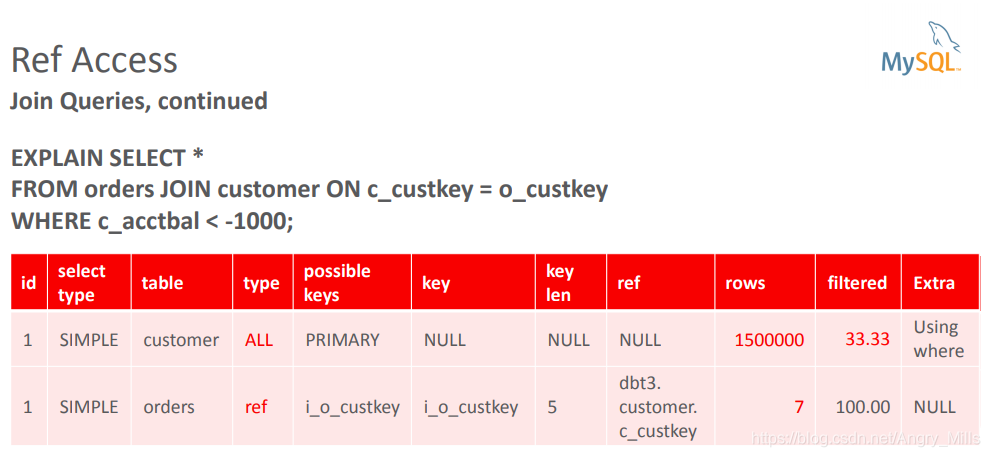
Join Queries 连接查询
图 Ref Access Single Join Queries
Join Queries, continued 未命中的索引的连接查询
图 Ref Access Join Queries continued
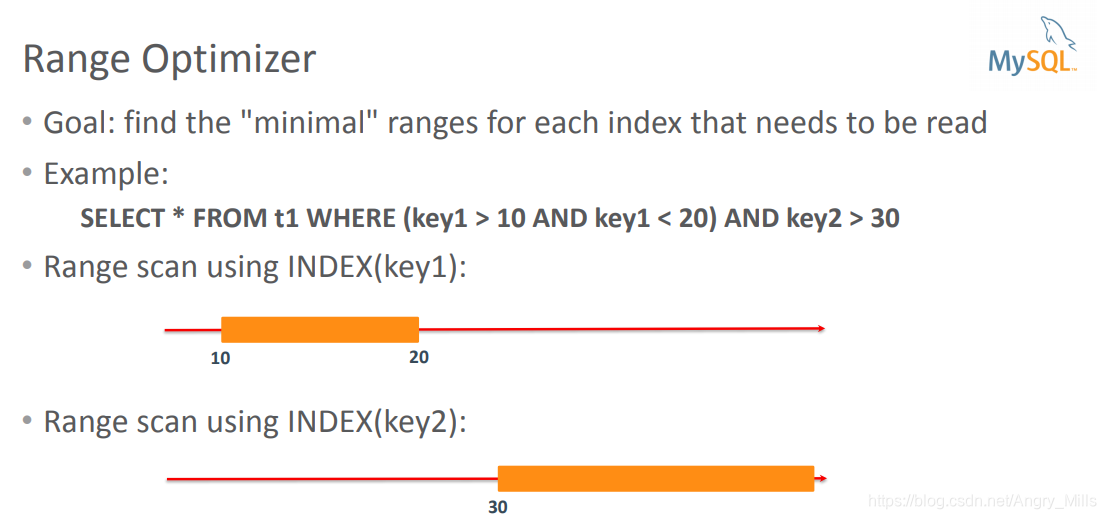
- Range Optimizer
范围优化器- Goal: find the “minimal” ranges for each index that needs to be read
目的: 找到需要读取索引的"最小"变化
Example:
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE (key1 > 10 AND key1 < 20) AND key2 > 30 - Goal: find the “minimal” ranges for each index that needs to be read
图 Ref Access Range Optimizer
- Range Optimizer, cont
范围优化器,常量- Range optimizer selects the “useful” parts of the WHERE condition:
范围优化器选择WHERE条件"有用的"部分- Conditions comparing a column value with a constant:
条件是一列和常量比较的数据 - Nested AND/OR conditions are supported
嵌套的AND/OR 是支持的
- Conditions comparing a column value with a constant:
- Result: list of disjoint ranges that need to be read from index:
结果: 没有交集的范围从索引读取
- Range optimizer selects the “useful” parts of the WHERE condition:
- Cost estimate based on number of records in each range:
成本估算基于每个范围的记录数量- Record estimate is found by asking the Storage Engine (“index dives”)
记录估算通过询问存储引擎("指数潜水")获取
- Record estimate is found by asking the Storage Engine (“index dives”)
Optimizer Trace show ranges 优化程序跟踪显示范围
图 Optimizer Trace show ranges
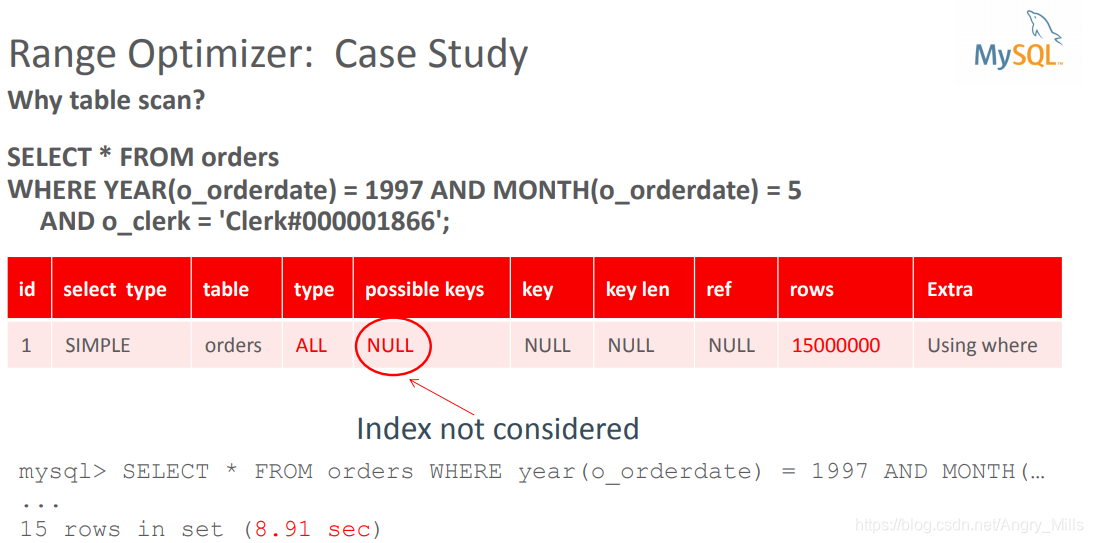
Range Optimizer: Case Study 范围优化:案例学习
- Why table scan?
为什么全表扫描?
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE YEAR(o_orderdate) = 1997 AND MONTH(o_orderdate) = 5
AND o_clerk = 'Clerk#000001866';
图 Range Optimizer Case Study1
possible keys NULL未使用索引
- Some Reasons Why Index can not be Used
一些未使用索引的原因-
ndexed column is used as argument to function
索引列使用函数计算YEAR(o_orderdate) = 1997 -
Looking for a suffix
寻找前缀name LIKE '%son' -
First column(s) of compound index NOT used
符合索引的前置列未被使用b = 10 when index defined over (a, b)
当复合索引(a,b),但是查询条件是b = 10 -
Type mismatch
类型不匹配my_string = 10 -
Character set / collation mismatch
字符集/排序规则不匹配t1 LEFT JOIN t2 ON t1.utf8_string = t2. latin1_string
-
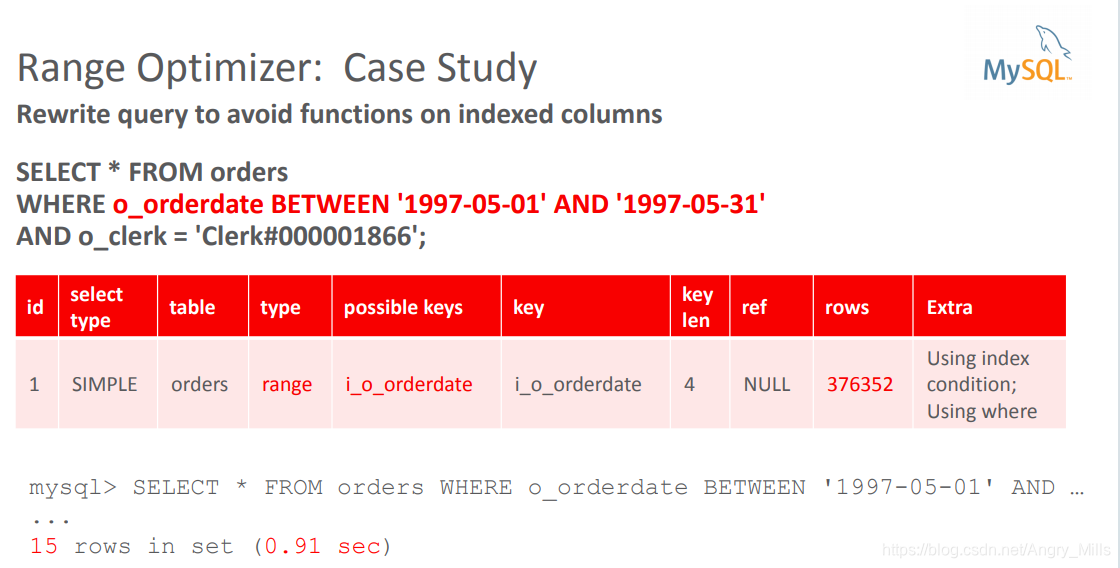
案例学习:
- Rewrite query to avoid functions on indexed columns
重写查询以避免索引列上的函数
例如:
i_o_orderdateSELECT * FROM orders WHERE o_orderdate BETWEEN '1997-05-01' AND '1997-05-31' AND o_clerk = 'Clerk#000001866';命中索引
图 Case Optimizer Case Study2
- Adding another index
添加另一个索引mysql> CREATE INDEX i_o_clerk ON orders(o_clerk); 就上面的例子,添加 o_clerk 索引
图 Range Optimizer Case Study3
-
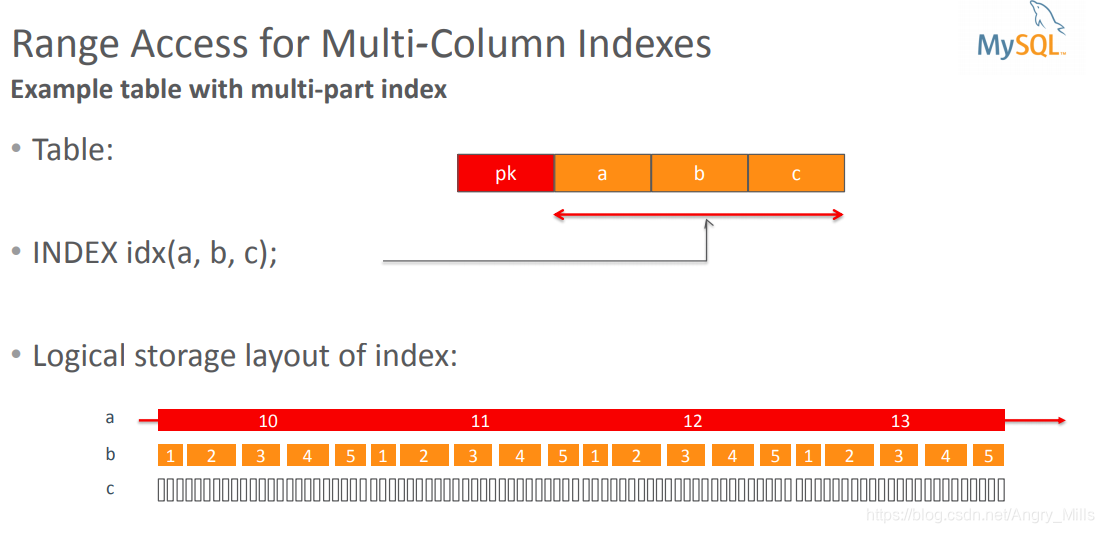
Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes
多列索引的范围访问 -
Example table with multi-part index
具有多部分索引的示例表 有索引abc ,index(a,b,c) -
Logical storage layout of index:
索引的逻辑存储布局:
图 Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes
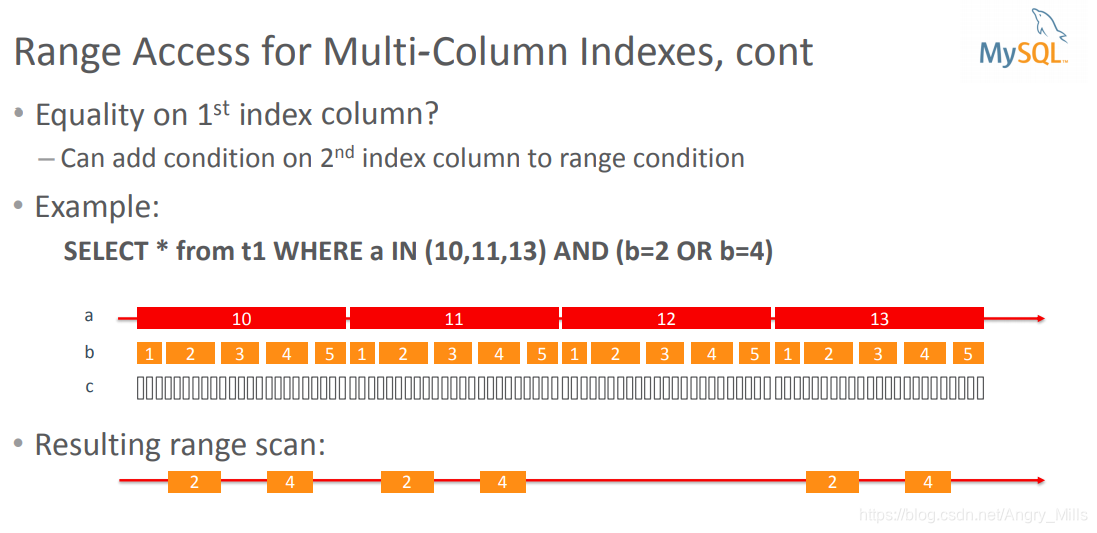
Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes, cont 多列索引的范围访问,常量
-
Equality on 1st index column?
第一个索引列上的平等? -
Can add condition on 2nd index column to range
condition?可以在第二个索引列上添加条件到范围条件?例如:
SELECT * from t1 WHERE a IN (10,11,13) AND (b=2 OR b=4)
Resulting range scan 结果范围扫描:
图 Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes, cont
-
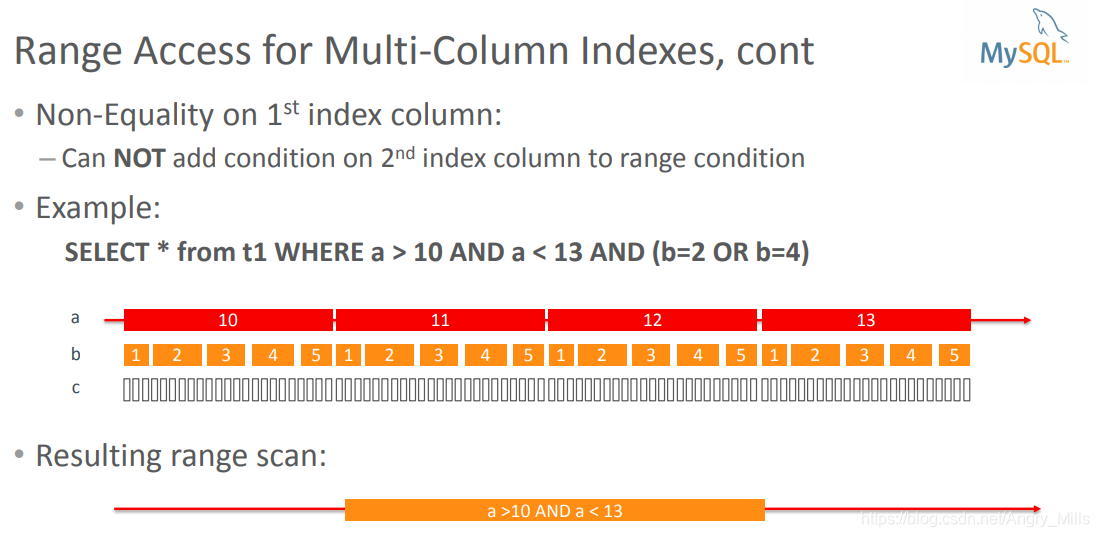
Non-Equality on 1st index column?
第一个索引列上不平等? -
Can NOT add condition on 2nd index column to range
condition?可以不在第二个索引列上添加条件到范围条件?例如:
SELECT * from t1 WHERE a > 10 AND a < 13 AND (b=2 OR b=4)
Resulting range scan 结果范围扫描:
图 Range Access for Multi-Column Indexes, cont+
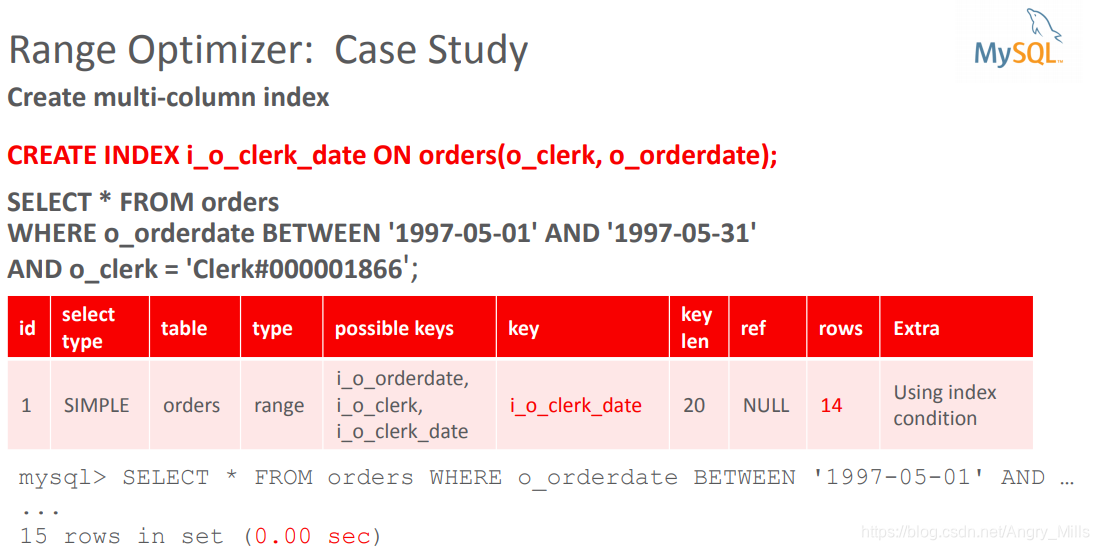
案例学习:
- Create multi-column index
创建多列索引CREATE INDEX i_o_clerk_date ON orders(o_clerk, o_orderdate);
图 Range Optimizer Case Study4
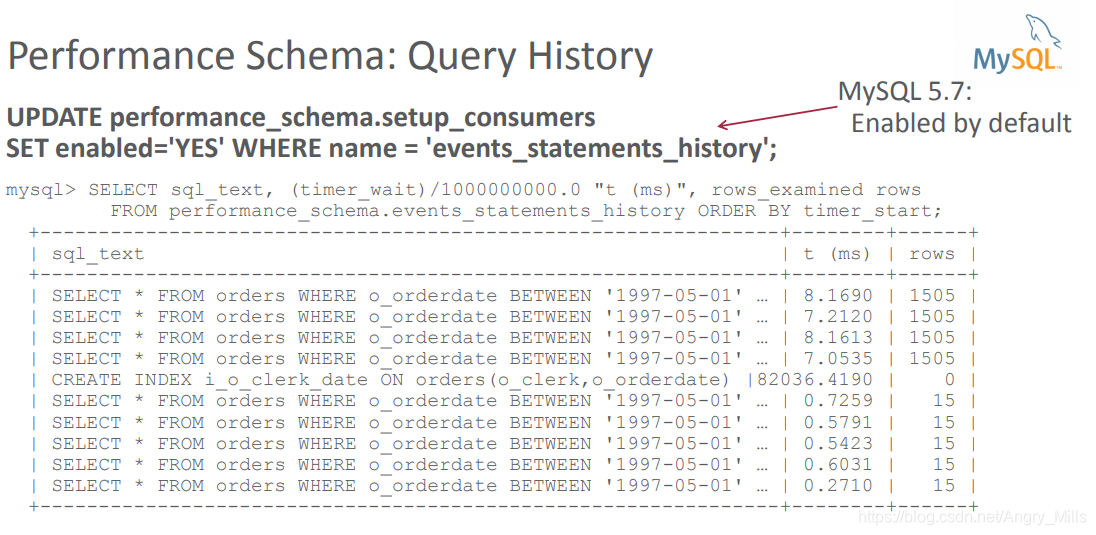
Performance Schema: Query History 执行计划:查询历史
mysql5.7 默认enabled的。
UPDATE performance_schema.setup_consumers SET enabled='YES' WHERE name = 'events_statements_history'; SELECT sql_text, (timer_wait)/1000000000.0 "t (ms)", rows_examined rowsFROM performance_schema.events_statements_history ORDER BY timer_start;
图 Performance Schema: Query History
Index Merge 索引合并
- Uses multiple indexes on the same table
同一张表使用多重索引 - Implemented index merge strategies
实施索引合并策略- Index Merge Union
索引合并并集- OR-ed conditions between different indexes
不同的索引之间使用OR条件
- OR-ed conditions between different indexes
- Index Merge Intersection
索引合并交集- AND conditions between different indexes
不同的索引之间的情况
- AND conditions between different indexes
- Index Merge Union
- Index Merge Sort-Union
索引合并排序并集 - OR-ed conditions where condition is a range
WHERE范围条件使用OR
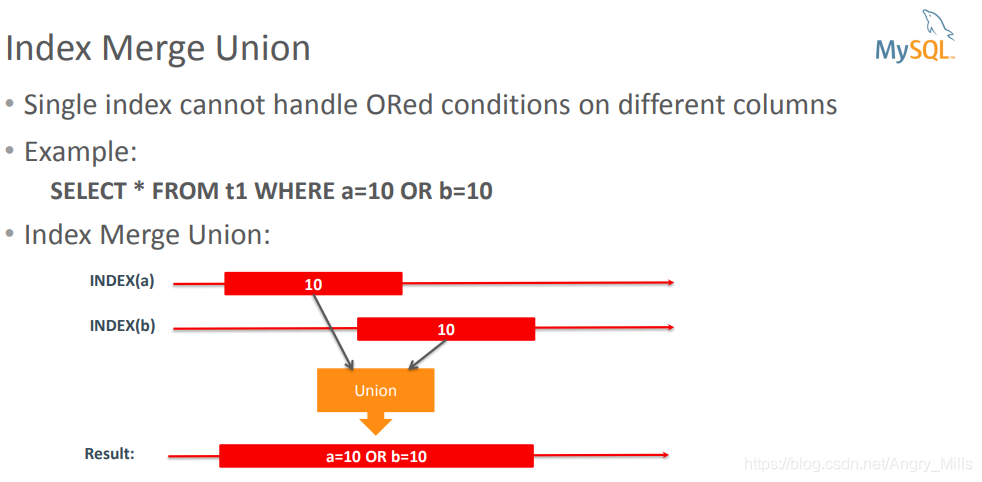
Index Merge Union 索引合并并集
- Single index cannot handle ORed conditions on different columns
单一索引不能处理不同列使用OR的情况
例如:
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a=10 OR b=10
INDEX(a) a = 10 INDEX(b) b = 10
Result: a= 10 OR b = 10
图 Index Merge Union
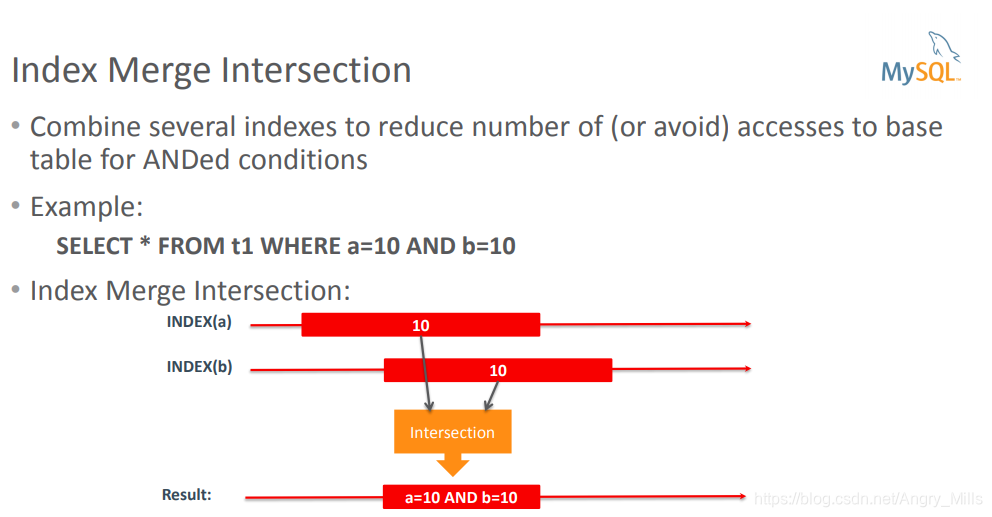
Index Merge Intersection 索引合并交集
- Combine several indexes to reduce number of (or avoid) accesses to base table for ANDed conditions
在AND条件下组合多个索引以减少(或避免)对基表访问次数
例如:
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a=10 AND b=10
INDEX(a) a = 10 INDEX(b) b = 10
Result: a= 10 AND b = 10
图 Index Merge Intersection
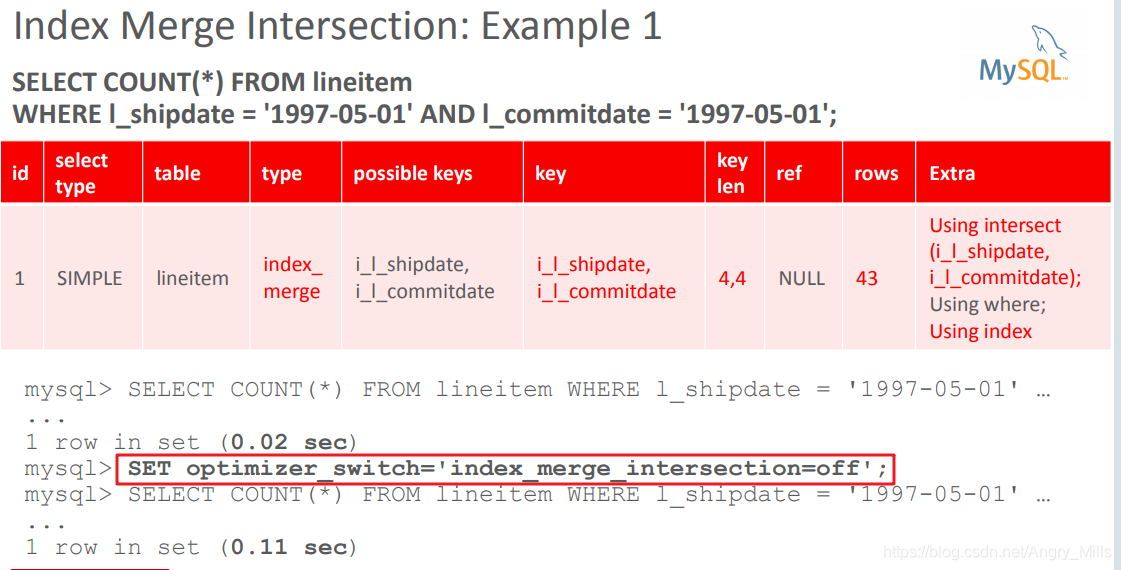
Example1:
图 Index Merge Intersection Example 1
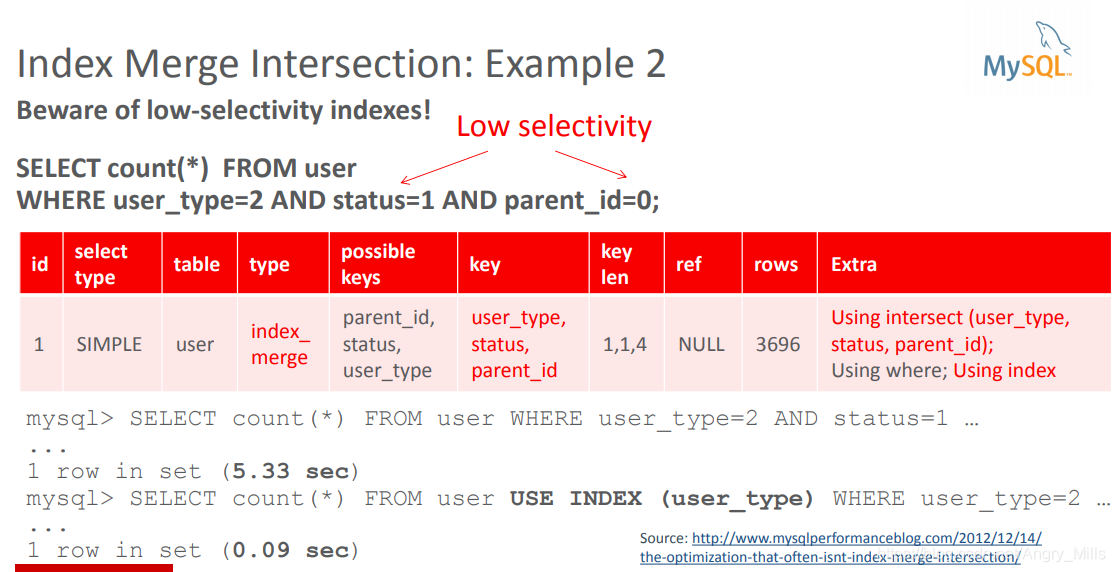
Example2:
Beware of low-selectivity indexes! 注意低选择性索引!
图 Index Merge Intersection Example 2
Example3:
Handler status variables 处理程序状态变量
图 Index Merge Intersection Example 2+
Join optimizer 连接优化器
”Greedy search strategy” 贪婪的搜索策略
目的: Given a JOIN of N tables, find the best JOIN ordering N张表中找到最好的连接排序
- Strategy: 策略:
- Start with all 1-table plans (Sorted based on size and key dependency)
从所有1表计划开始(根据大小和密钥依赖性排序) - Expand each plan with remaining tables
用剩余的表扩展每个计划- Depth-first
深度优先
- Depth-first
- If “cost of partial plan” > “cost of best plan”:
如果"部分计划成本" > "最好的计划成本"- “prune” plan
精简计划
- “prune” plan
- Start with all 1-table plans (Sorted based on size and key dependency)
- Heuristic pruning:
探索式精简- Prune less promising partial plans
精简没什么用的部分计划 - May in rare cases miss most optimal plan (turn off with set optimizer_prune_level = 0)
可能在极少数情况下错过最佳计划 (关闭并设置 optimizer_prune_level = 0)
- Prune less promising partial plans
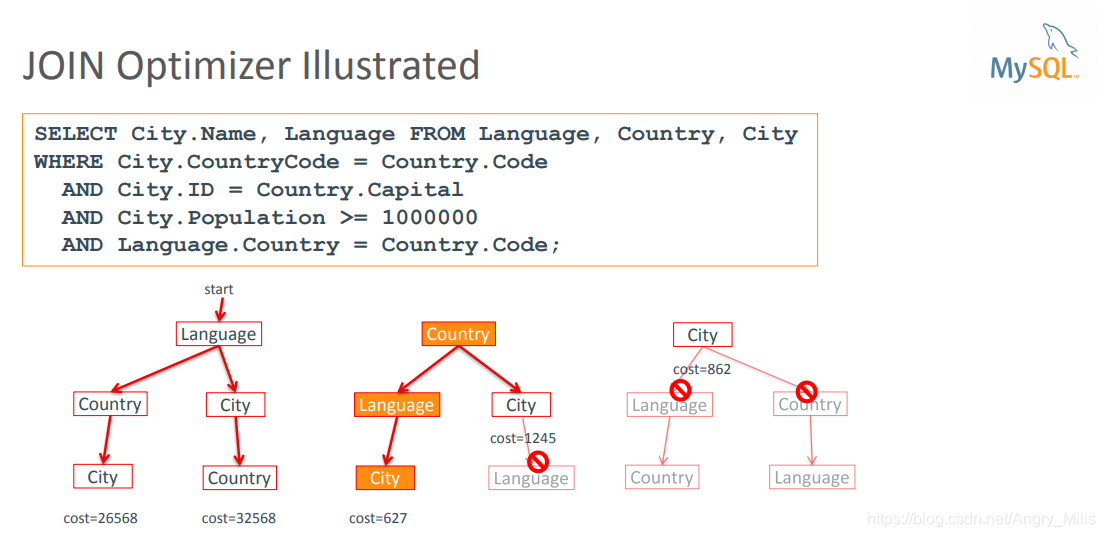
JOIN Optimizer Illustrated 连接优化器插图
图 Join Optimizer
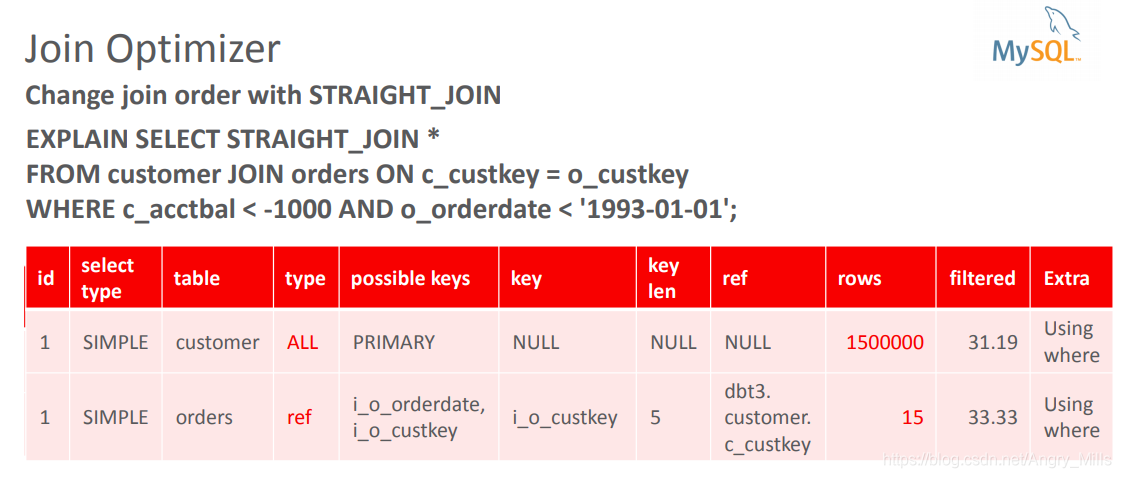
Change join order with STRAIGHT_JOIN 使用STRAIGHT_JOIN更改连接顺序
图 Join Optimizer+
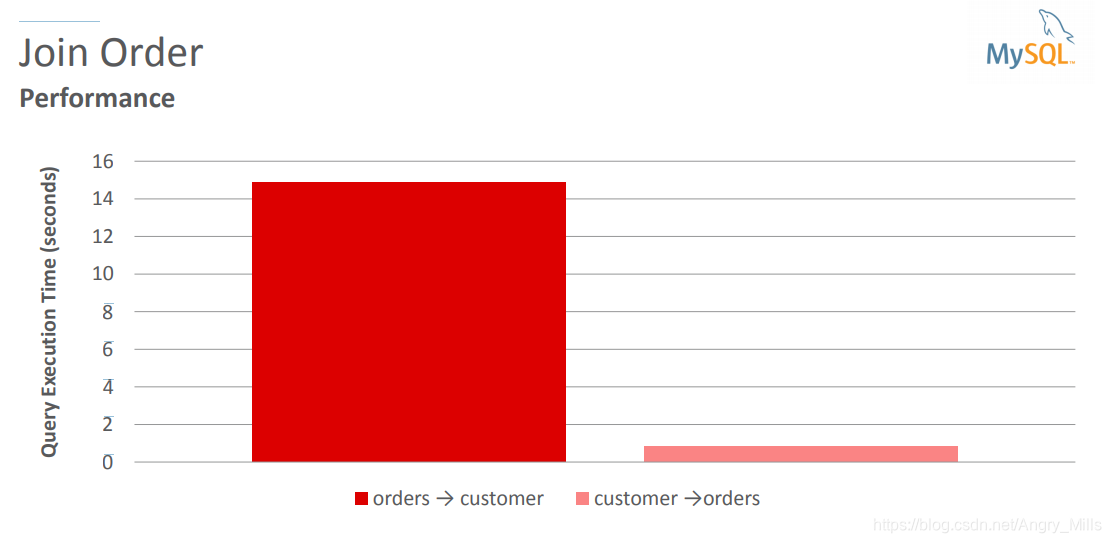
Join Order 连接顺序
图 Join Order
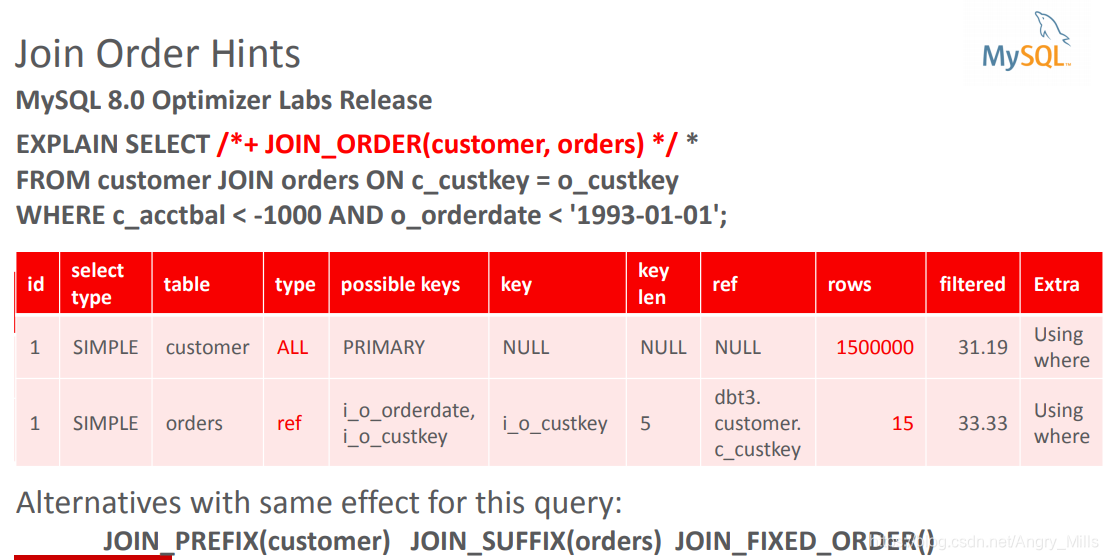
Join Order Hints 连接顺序提示
MySQL 8.0 Optimizer Labs Release MySQL 8.0优化工具实验室发布
- Alternatives with same effect for this query:
对此查询具有相同效果的替代方案
JOIN_PREFIX(customer) JOIN_SUFFIX(orders) JOIN_FIXED_ORDER()
图 Join Order Hints
National Market Share Query 全国市场份额查询
SELECT o_year, SUM(CASE WHEN nation = 'FRANCE' THEN volume ELSE 0 END) / SUM(volume) AS mkt_shareFROM (SELECT EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o_orderdate) AS o_year, l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) AS volume, n2.n_name AS nationFROM partJOIN nation n2 ON s_nationkey = n2.n_nationkey JOIN region ON n1.n_regionkey = r_regionkey JOIN nation n1 ON c_nationkey = n1.n_nationkey JOIN customer ON o_custkey = c_custkey JOIN orders ON l_orderkey = o_orderkey JOIN supplier ON s_suppkey = l_suppkey JOIN lineitem ON p_partkey = l_partkey WHERE r_name = 'EUROPE' AND o_orderdate BETWEEN '1995-01-01' AND '1996-12-31' AND p_type = 'PROMO BRUSHED STEEL') AS all_nations GROUP BY o_year ORDER BY o_year;
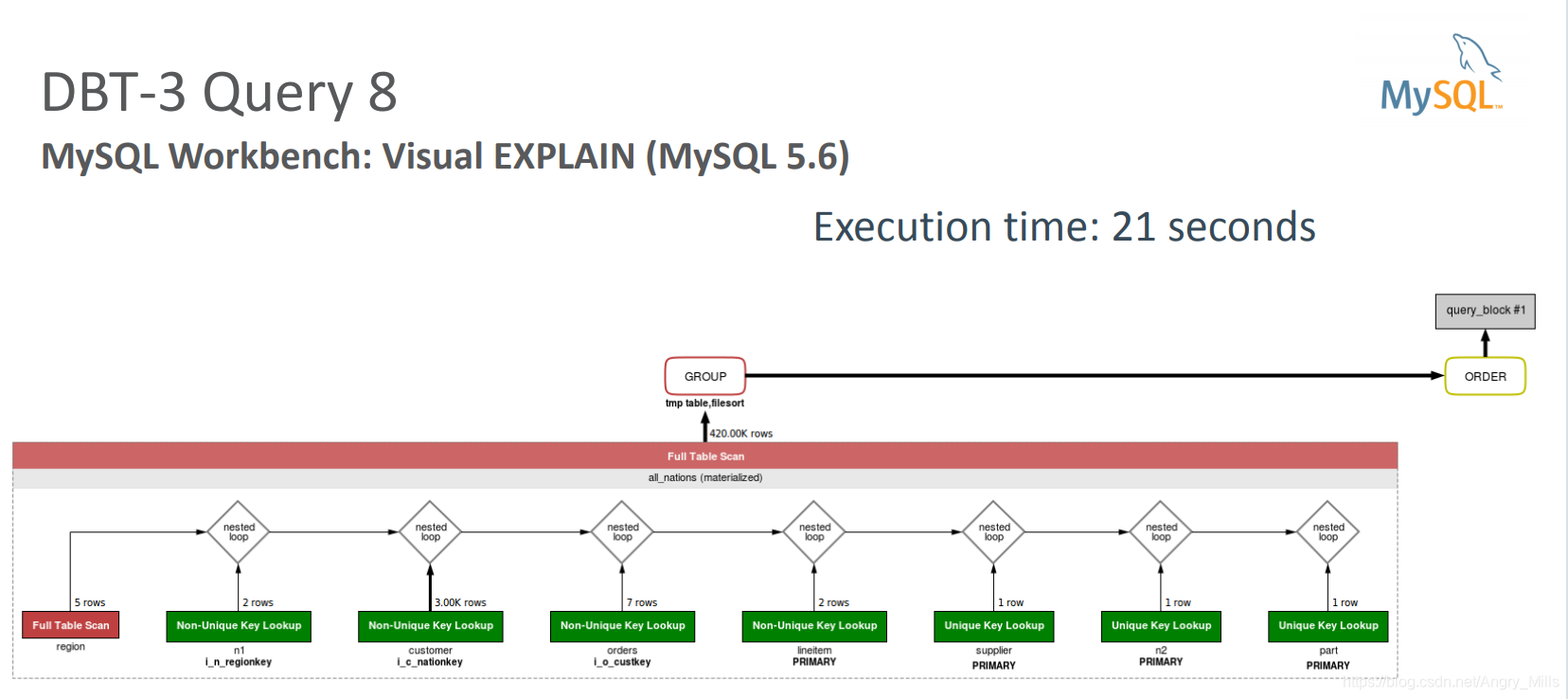
MySQL Workbench Visual EXPLAIN MySQL Workbench 可视化 EXPLAIN
图 MySQL Workbench: Visual EXPLAIN
Force early processing of high selectivity conditions 强制早期处理高选择性条件
图 Force early processing of high selectivity conditions
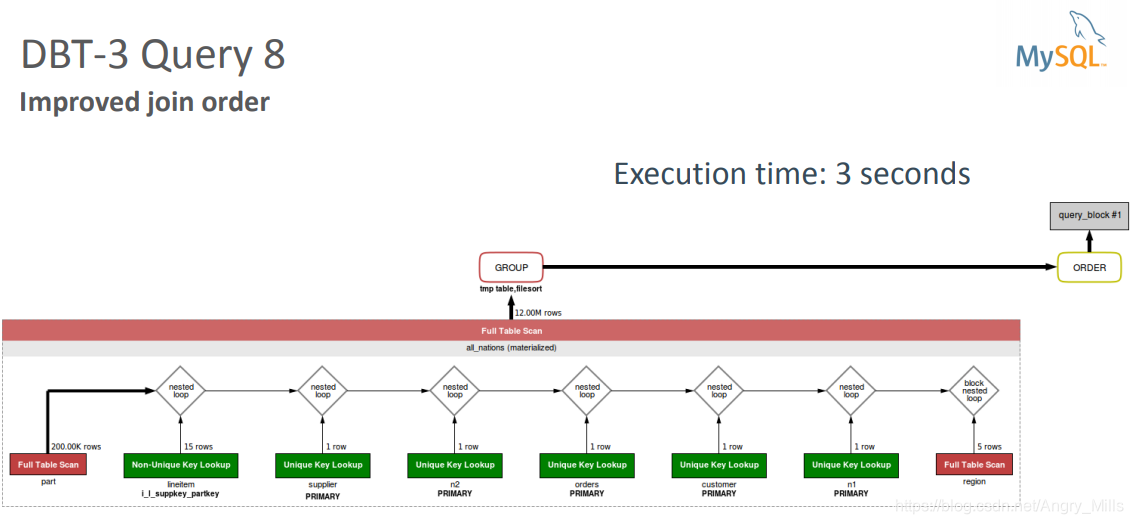
Improved join order 优化连接顺序
图 Improved join order
- Improvements to Query 8 in MySQL 5.7:
mysql 5.7 对Query8的优化 - Filtering on non-indexed columns are taken into account
考虑对非索引列进行过滤 - No need for hint to force part table to be processed early
部分表强制提前处理无需提示 - Merge derived tables into outer query
将派生表合并到外部查询中 - No temporary table
无临时表
Subqueries 子查询
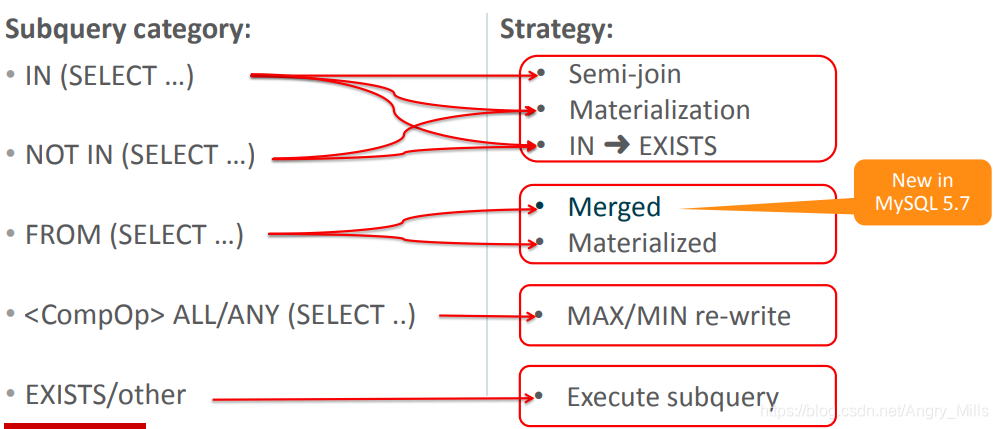
Overview of Subquery Optimizations 子查询优化概述
Subquery category: 子查询分类 | Strategy:策略 |
|---|---|
| IN (SELECT …) | Semi-join 半连接Materialization 实体化 |
| NOT IN (SELECT …) | IN ➜ EXISTS |
| FROM (SELECT …) | Merged 合并 Materialized 实体化 |
| ALL/ANY (SELECT …) | MAX/MIN re-write 最大/最小化 重写 |
| EXISTS/other | Execute subquery 执行子查询 |
图 Subquery category
- Traditional Optimization of IN Subqueries
IN子查询的传统优化- IN -> EXISTS transformation
IN 转化为 EXISTS
- IN -> EXISTS transformation
- Convert IN subquery to EXISTS subquery by “push-down” IN-equality to
subquery从IN子查询转化为EXISTS子查询通过"向下"的同等子查询
优化为 =>SELECT title FROM film WHERE film_id IN (SELECT film_id FROM actor WHERE name=“Bullock”)SELECT title FROM filmWHERE EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM actor WHERE name=“Bullock” AND film.film_id = actor.film_id) - Benefit: subquery will evaluate fewer records
优点:子查询将计算更少的记录 - Note: Special handling if pushed down expressions can be NULL
注意:如果"向下"表达式为NULL,则可特殊处理
Semi-join 半连接
-
Convert subquery to inner join, BUT Need some way to remove duplicates
将子查询转换为内连接 但需要一些方法去重 -
Different strategies for duplicate removal:
去重的不同策略- FirstMatch (equivalent to IN→EXISTS execution)
匹配优先(等价于IN—>EXISTS的方式) - LooseScan (index scan, skip duplicates)
懒扫描(索引扫描,跳过重复) - Materialization: MatLookup (like subquery materialization), MatScan
(materialized table is first in join order)
实体化:MatLookup(像子查询实体化),MatScan(实体化表在连接顺序的第一位) - Duplicate WeedOut (insert result rows of semi-join query into
temporary table with unique index; duplicate rows will be rejected.
Any join order.)去重(用唯一索引将半连接的行插入临时表;重复列将会被拒绝。无论连接顺序)
- FirstMatch (equivalent to IN→EXISTS execution)
-
If duplicate removal is not necessary:
如果去重是非必须的话- Table pull-out
表将删掉
- Table pull-out
Main advantage : 主要优势:
- Opens up for more optimal ”join orders”
有更多优化"连接顺序"的选择
例如:SELECT o_orderdate, o_totalprice FROM orders WHERE o_orderkey IN (SELECT l_orderkey FROM lineitem WHERE l_shipDate='1996-09-30');- Will process less rows if starting with lineitem instead of orders
使用行代替排序会经过较少的行
- Will process less rows if starting with lineitem instead of orders
- Restriction: 限制:
- Cannot use semi-join if subquery contains union or aggregation
如果子查询包含union(并集)或者aggregation(聚合)不能使用半连接
- Cannot use semi-join if subquery contains union or aggregation
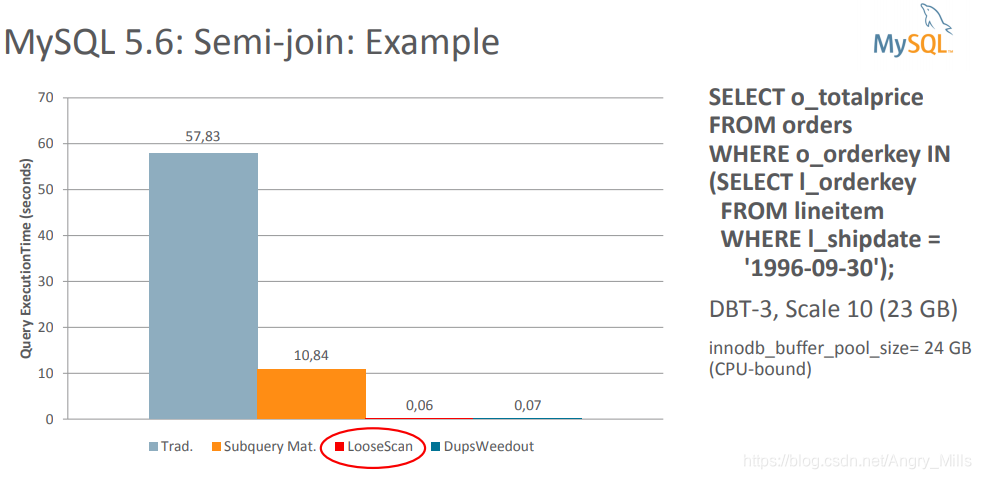
MySQL 5.6: Semi-join: Example mysql5.6 半拦截的例子:
图 MySQL 5.6: Semi-join: Example
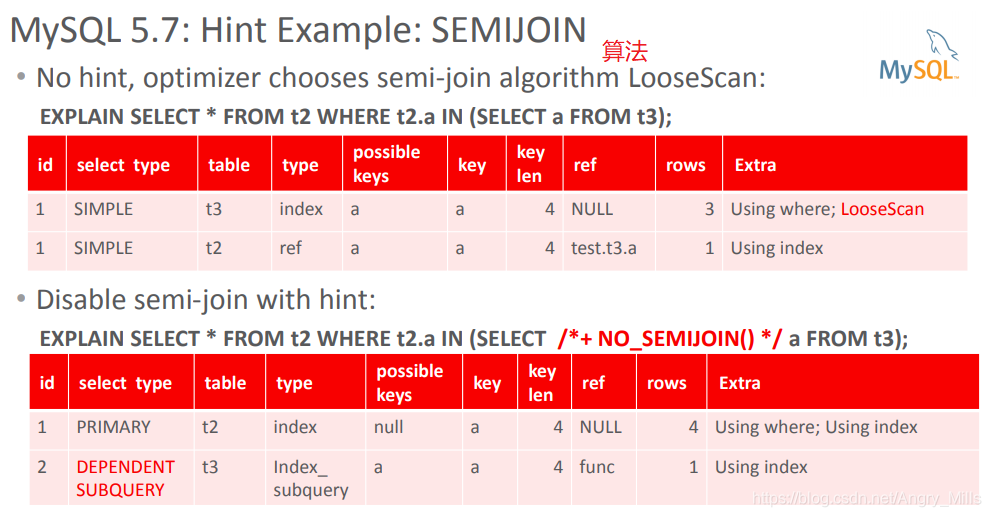
MySQL 5.7: Hint Example: SEMIJOIN 提示示例: 半连接
- No hint, optimizer chooses semi-join algorithm LooseScan:
没有提示,优化器选择半连接算法LooseScan - Disable semi-join with hint:
使用提示禁用半连接:
图 Hint Example: SEMIJOIN
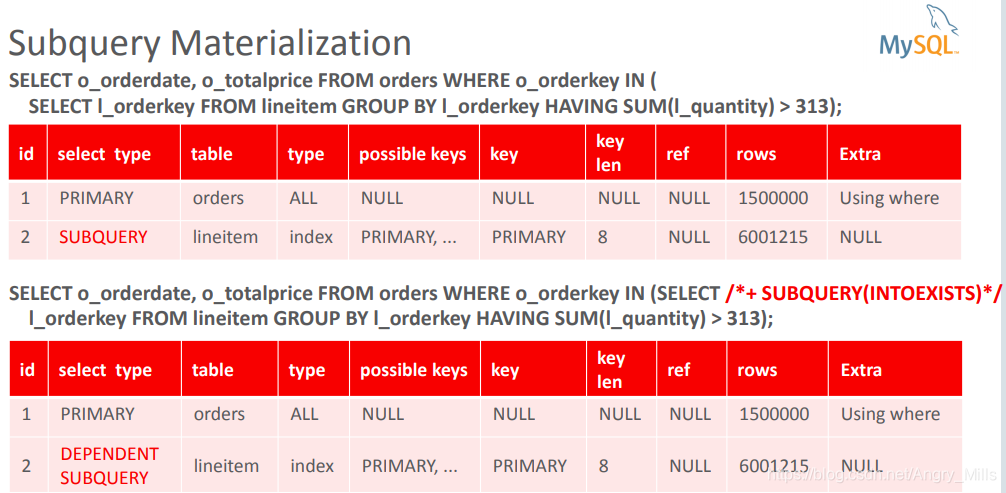
- Subquery Materialization
子查询实体化- Execute subquery once and store result in a temporary table
执行一次子查询并在临时表中存结果 - Table has unique index for quick look-up and duplicate removal
表有唯一索引可以快速查找并去重
- Execute subquery once and store result in a temporary table
- Execute outer query and check for matches in temporary table
执行外部查询并检查临时表中的匹配项
图 Subquery Materialization
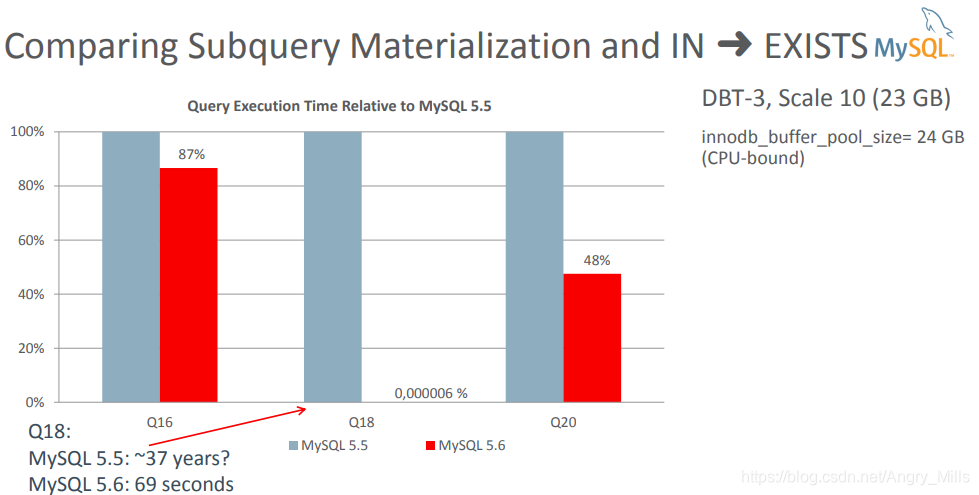
比较子查询实现和IN➜EXISTS 比较IN —> EXISTS的实现
图 Comparing Subquery Materialization
图 Subquery Materialization+
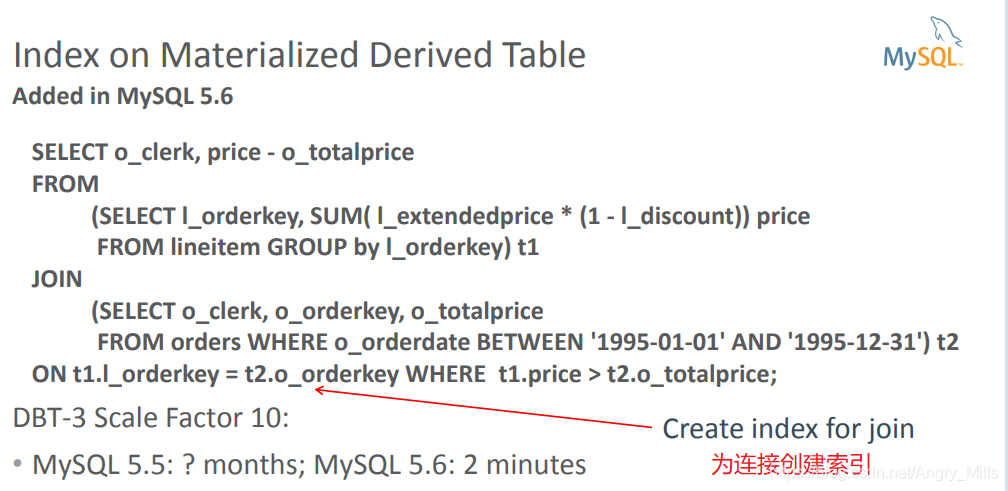
Derived Tables 派生表
- Subquery in FROM clause
FROM子句中的子查询SELECT AVG(o_totalprice) FROM ( SELECT * FROM orders ORDER BY o_totalprice DESC LIMIT 100000 ) td; - MySQL 5.6 and earlier: Executed separately and result stored in a
temporary table (materialization)MySQL 5.6及更早版本:单独执行并将结果存储在临时表中(实现) - MySQL 5.7: Treat derived tables like views: May be merged with outer
query blockMySQL 5.7:处理类似于视图的派生表:可以与外部查询块合并
图 Index on Materialized Derived Table
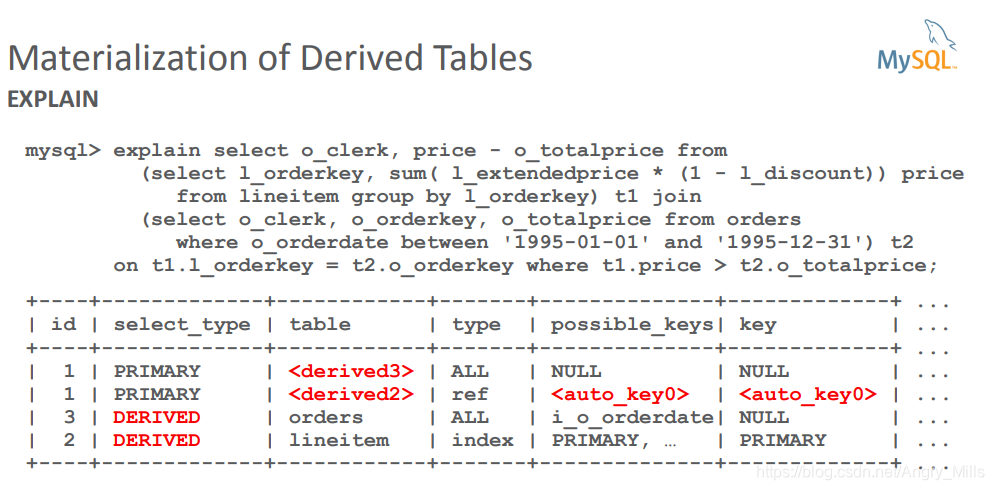
图 Materialization of Derived Tables EXPLAIN
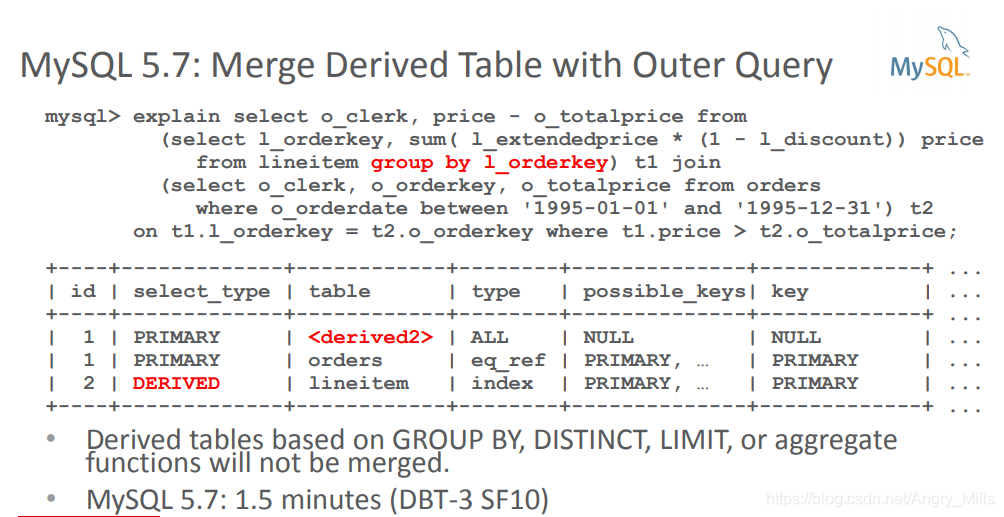
- Merge Derived Table with Outer Query
用外部连接合并派生表- Derived tables based on GROUP BY, DISTINCT, LIMIT, or aggregate
functions will not be merged基于GROUP BY,DISTINCT,LIMIT或聚合函数的派生表将不会合并
- Derived tables based on GROUP BY, DISTINCT, LIMIT, or aggregate
图 Merge Derived Table with Outer Query
Hint: Merge/Materialize Derived Table or View 暗示:合并/实现派生表或视图
- MySQL 8.0.0 optimizer labs release
MySQL 8.0.0优化器实验室发布-
Derived tables/views are, if possible, merged into outer query
如果可能,派生表/视图将合并到外部查询中 -
NO_MERGE hint can be used to override default behavior:
NO_MERGE提示可用于覆盖默认行为:SELECT /*+ NO_MERGE(dt) */ * FROM t1 JOIN (SELECT x, y FROM t2) dt ON t1.x = dt.x;
-
MERGE hint will force a merge
MERGE提示将强制合并SELECT /*+ MERGE(dt) */ * FROM t1 JOIN (SELECT x, y FROM t2) dt ON t1.x = dt.x;
-
Can also use MERGE/NO_MERGE hints for views
也可以使用MERGE / NO_MERGE提示查看视图SELECT /*+ NO_MERGE(v) */ * FROM t1 JOIN v ON t1.x = v.x;
-
Sorting 排序
ORDER BY Optimizations 排序优化
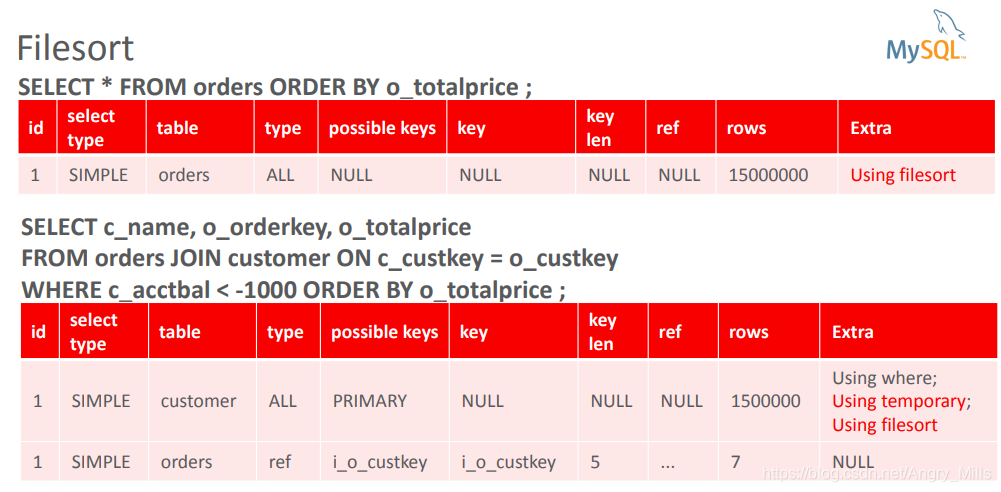
- General solution; “Filesort”:
通常的解决方案;"文件排序"- Store query result in temporary table before sorting
在排序之前将查询结果存储在临时表中 - If data volume is large, may need to sort in several passes with intermediate storage on disk.
如果数据量很大,可能需要在磁盘上使用中间存储进行多次传递排序
- Store query result in temporary table before sorting
- Optimizations :
优化- Take advantage of index to generate query result in sorted order
利用索引按排序顺序生成查询结果 - For ”LIMIT n” queries, maintain priority queue of n top items in
memory instead of filesort. (MySQL 5.6)
对于"LIMIT n查询,保留内存中n个顶级项的优先级队列而不是文件排序。 (MySQL 5.6)
- Take advantage of index to generate query result in sorted order
Filesort 文件排序:
图 Filesort
Status variables 状态变量
图 Filesort+
Performance Schema 执行计划
图 Filesort Performance Schema
Sorting status per statement available from Performance Schema可从执行计划中对每个语句进行排序
案例1
图 Filesort Case Study1
案例2
图 Filesort Case Study2
案例3
图 Filesort Case Study3
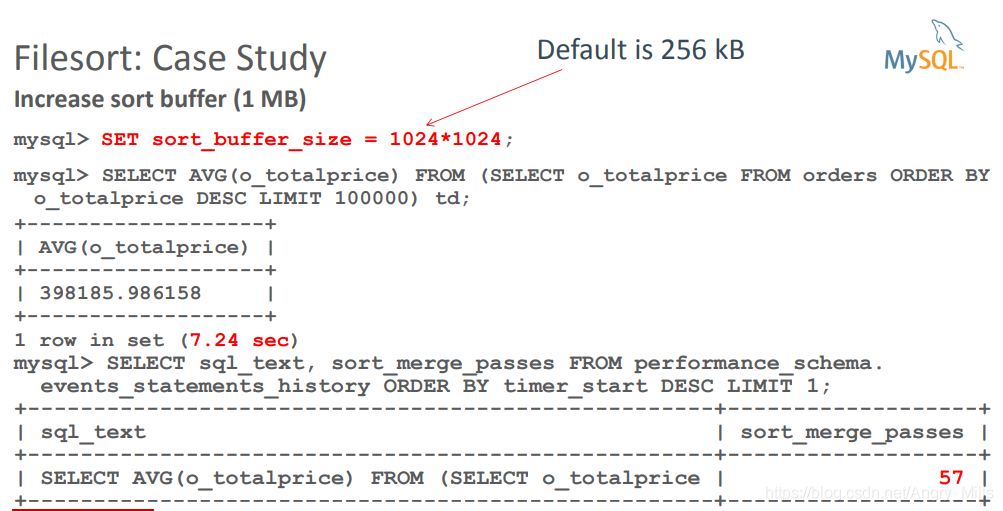
Increase sort buffer增加排序缓冲区
SET sort_buffer_size = 1024*1024默认256 KB。
案例4
图 Filesort Case Study4
Increase sort buffer even more (8MB)进一步增加排序缓冲区 (8MB)
SET sort_buffer_size = 8*1024*1024;
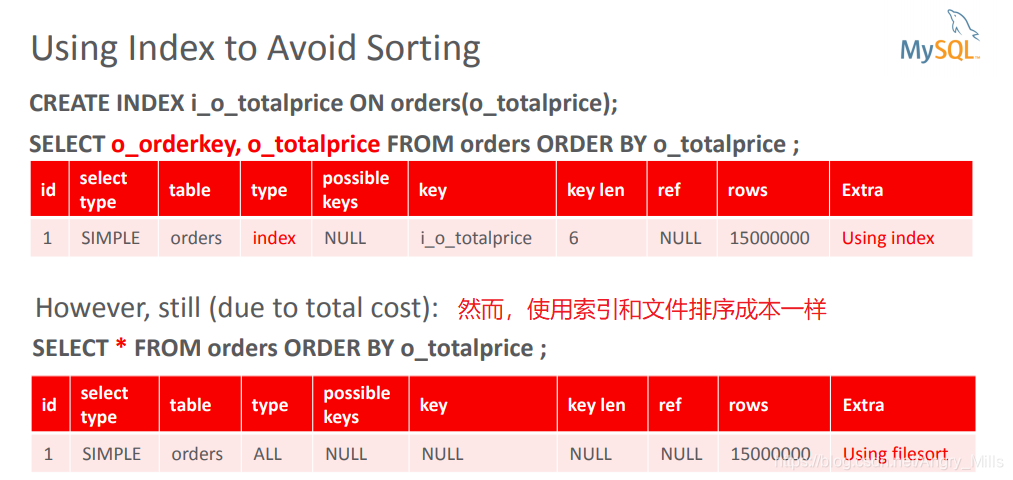
图 Using Index to Avoid Sorting
Using Index to Avoid Sorting使用索引来避免排序
图 Using Index to Avoid Sorting Case study
Case study revisited重新研究案例
Influencing the optimizer 影响优化器
- Add indexes
添加索引 - Force use of specific indexes:
强制使用特定的索引- USE INDEX, FORCE INDEX, IGNORE INDEX
使用索引,强制索引,忽略索引
- USE INDEX, FORCE INDEX, IGNORE INDEX
- Force specific join order:
强制特定的关联顺序- STRAIGHT_JOIN
- Adjust session variables
调整会话变量- optimizer_switch flags: set optimizer_switch=“index_merge=off”
- Buffer sizes: set sort_buffer=810241024;
- Other variables: set optimizer_search_depth = 10;
MySQL 5.7: New Optimizer Hints MySQL 5.7:新的优化器暗示
-
Ny hint syntax:
暗示语法:
SELECT /*+ HINT1(args) HINT2(args) */ … FROM … -
New hints:
新的暗示:- BKA(tables)/NO_BKA(tables), BNL(tables)/NO_BNL(tables)
- Batched Key Access (BKA)
批量key访问Block Nested-Loop (BNL)阻塞嵌套循环算法
- Batched Key Access (BKA)
- MRR(table indexes)/NO_MRR(table indexes)
(表的索引) - SEMIJOIN/NO_SEMIJOIN(strategies), SUBQUERY(strategy)
- NO_ICP(table indexes)
- Index Condition Pushdown (ICP)
索引命中情况下推 - NO_RANGE_OPTIMIZATION(table indexes)
索引情况下该范围没有可优化的 - QB_NAME(name)
Query Block 查询阻塞
- BKA(tables)/NO_BKA(tables), BNL(tables)/NO_BNL(tables)
-
Finer granularilty than optimizer_switch session variable
比optimizer_switch会话变量更精细
Optimizer Hints
- Future :
- New hints in 8.0.0 Optimizer Labs Release
Optimizer Labs 8.0.0 版本中的新暗示 - Enable/disable merge of views and derived tables:
启用/禁用视图和派生表的合并
- New hints in 8.0.0 Optimizer Labs Release
- MERGE() NO_MERGE()
- Join order
连接顺序JOIN_ORDER(tables)JOIN_PREFIX(tables)JOIN_SUFFIX(tables)JOIN_FIXED_ORDER()
- Hints we consider to add
考虑添加的暗示:- Force/ignore index_merge Alternatives
强制/忽略index_merge替代方案 - Reimplement index hints in new syntax
重新实现新语法中的索引暗示 - Temporarily set session variables for just one query
暂时为一个查询设置会话变量
- Force/ignore index_merge Alternatives
MySQL 5.7: Query Rewrite Plugin 查询重写插件
-
Rewrite problematic queries without the need to make application
changes无需更改应用程序即可重写有问题的查询 -
Add hints
添加暗示- Modify join order
更新连接顺序 - Much more …
更多
- Modify join order
-
Add rewrite rules to table:
向表中添加重写规则:
图 Query Rewrite Plugin
- New pre- and post-parse query rewrite APIs
新的解析前和解析后查询重写API
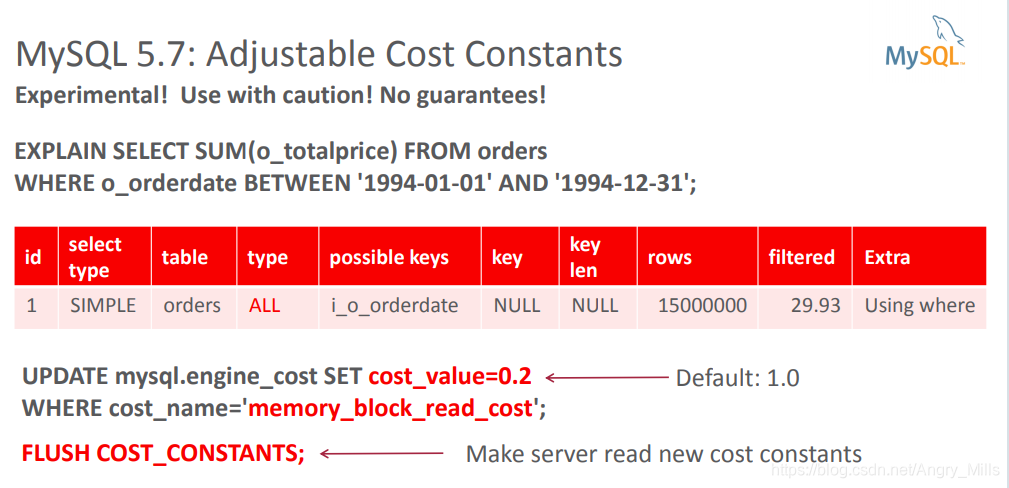
MySQL 5.7: Adjustable Cost Constants 可调成本常量
Experimental! Use with caution! No guarantees 实验! 谨慎使用! 不保证!!
图 Adjustable Cost Constants
图 Adjustable Cost Constants+
- More information 更多信息:
-
- MySQL Server Team blog
- http://mysqlserverteam.com/
官方博客 -
- My blog:
- http://oysteing.blogspot.com/
作者博客 -
- Optimizer team blog:
- http://mysqloptimizerteam.blogspot.com/
优化团队博客 -
- MySQL forums:
- Optimizer & Parser: http://forums.mysql.com/list.php?115/
- Performance: http://forums.mysql.com/list.php?24/
论坛




















![[css] transition、animation、transform三者有什么区别?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[css] transition、animation、transform三者有什么区别?)


![[css] 如何使用css3实现一个div设置多张背景图片?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[css] 如何使用css3实现一个div设置多张背景图片?)
-理论-操作系统)

![[css] 你有用过IE css的expression表达式吗?说说你对它的理解和它有什么作用呢?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[css] 你有用过IE css的expression表达式吗?说说你对它的理解和它有什么作用呢?)
——java基础)

![[css] 有哪些方式可以对一个DOM设置它的CSS样式?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[css] 有哪些方式可以对一个DOM设置它的CSS样式?)


![[css] 举例说明实现圆角的方式有哪些?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[css] 举例说明实现圆角的方式有哪些?)


![[css] 有用过scss和sass吗?说说它们之间的区别是什么?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[css] 有用过scss和sass吗?说说它们之间的区别是什么?)

![[css] absolute的containing block(容器块)计算方式和正常流有什么区别?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[css] absolute的containing block(容器块)计算方式和正常流有什么区别?)
