计算机指令格式
指令格式 (Instruction format )
Instruction format describes the internal structures (layout design) of the bits of an instruction, in terms of its constituent parts.
指令格式按照指令的组成部分描述指令位的内部结构(布局设计)。
An Instruction format must include an opcode, and address is dependent on an availability of particular operands.
指令格式必须包含操作码,并且地址取决于特定操作数的可用性。
The format can be implicit or explicit which will indicate the addressing mode for each operand.
格式可以是隐式或显式的,这将指示每个操作数的寻址模式。
Designing of an Instruction format is very complex. As we know a computer uses a variety of instructional. There are many designing issues which affect the instructional design, some of them are given are below:
指令格式的设计非常复杂。 众所周知,计算机使用各种指令。 有许多影响教学设计的设计问题,下面列出其中一些:
- Instruction length: It is a most basic issue of the format design. A longer will be the instruction it means more time is needed to fetch the instruction.指令长度:这是格式设计的最基本问题。 指令越长,则意味着需要更多的时间来提取指令。
- Memory size: If larger memory range is to be addressed then more bits will be required in the address field.存储器大小:如果要寻址更大的存储器范围,则地址字段中将需要更多位。
- Memory organization: If the system supports the virtual memory then memory range which needs to be addressed by the instruction, is larger than the physical memory.内存组织:如果系统支持虚拟内存,则该指令需要解决的内存范围大于物理内存。
- Memory transfer length: Instruction length should be equal to the data bus length or it should be multiple of it.内存传输长度:指令长度应等于数据总线长度,或者应为数据总线长度的倍数。
Instruction formats are classified into 5 types based on the type of the CPU organization. CPU organization is divided into three types based on the availability of the ALU operands, which are as follows here:
根据CPU组织的类型, 指令格式分为5种类型。 根据ALU操作数的可用性,CPU的组织分为三种类型,如下所示:
1) STACK CPU
1)堆栈CPU
In this organization, ALU operands are performed only on a stack data. This means that both of the ALU operations are always required in the stack. The same stack is also used as the destination. In the stack, we can perform insert and deletion operation at only one end which is called as the top of a stack. So in this format, there is no need of address because in this TOS becomes the default location.
在这种组织中,仅对堆栈数据执行ALU操作数。 这意味着在堆栈中始终需要两个ALU操作。 相同的堆栈也用作目标。 在堆栈中,我们只能在称为堆栈顶部的一端执行插入和删除操作。 因此,以这种格式,不需要地址,因为在此TOS中,它成为默认位置。
In this organization, only the ALU operands are zero address operation whereas data transfer instructions are not a zero address instruction. The computable instruction format of STACK CPU is Zero Address Instruction Format.
在这种组织中,只有ALU操作数是零地址操作,而数据传输指令不是零地址指令。 STACK CPU的可计算指令格式为零地址指令格式 。

2) Accumulator CPU
2)累加器CPU
In this organization, one of the ALU operands is always present in the accumulator. The same accumulator is also used as the destination. Another ALU operand is present either in the register or in memory. In processor design, only one accumulator is present so it becomes the default location.
在这种组织中,累加器中始终存在一个ALU操作数。 同一累加器也用作目标。 寄存器或存储器中存在另一个ALU操作数。 在处理器设计中,仅存在一个累加器,因此它成为默认位置。
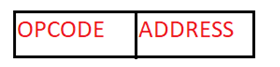
The computable instruction format of Accumulator CPU is One Address Instruction Format.
累加器CPU的可计算指令格式为“ 一个地址指令格式” 。
3) General Register CPU
3)通用寄存器CPU
Based on the number of the registers possible in the processors, the architecture is divided into two types:
根据处理器中可能存在的寄存器数量,该体系结构分为两种类型:
Register-Memory references CPU
寄存器存储器参考CPU
Register-Register references CPU
寄存器-寄存器引用CPU
i) Register-Memory Reference CPU
i)寄存器存储器参考CPU
In this architecture, processors support less number of registers. Therefore register file size is small. In this organization, the first ALU operand is always required in the register. The same register can also be used as the destination. The second ALU operand is present either in a register or in memory. The computable instruction format of the register to memory reference CPU is Two Address Instruction Format.
在这种体系结构中,处理器支持较少数量的寄存器。 因此,寄存器文件的大小很小。 在这种组织中,寄存器中始终需要第一个ALU操作数。 相同的寄存器也可用作目标。 第二个ALU操作数存在于寄存器或存储器中。 寄存器到存储器参考CPU的可计算指令格式为“ 两个地址指令格式” 。
ii) Register-Register Reference CPU
ii)寄存器-寄存器参考CPU
In this architecture, processors support number of registers, therefore, register file size is large. In this organization, ALU operands are performed only on a registers data that means both of the ALU operands are required in the register. Due to more number of register present in the CPU, the separate register is used to store the result. The computable instruction format of Register-Register Reference CPU is Three Address Instruction Format.
在这种体系结构中,处理器支持寄存器的数量,因此,寄存器文件的大小很大。 在这种组织中,仅对寄存器数据执行ALU操作数,这意味着寄存器中需要两个ALU操作数。 由于CPU中存在更多的寄存器,因此使用单独的寄存器存储结果。 寄存器-寄存器参考CPU的可计算指令格式为三地址指令格式。
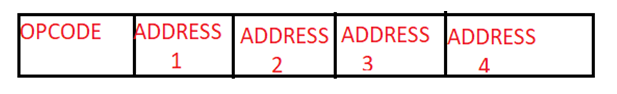
Four Address instruction format
四地址指令格式
This format contains the 4 different address fields with an opcode. Since PC is used as the mandatory register in the CPU design which is used to hold the next instruction address. So four instruction format is not in the use.
此格式包含4个不同的地址字段和一个操作码。 由于PC被用作CPU设计中的强制寄存器,用于保存下一条指令地址。 因此没有使用四种指令格式。
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/cso/instruction-format.aspx
计算机指令格式




)

松弛委托和可为空类型语法增强)









的文本与背景色的改变)
![fckeditor文件管理器添加查看、修改、删除文件功能[php]修正下载地址](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/fckeditor文件管理器添加查看、修改、删除文件功能[php]修正下载地址)

