官网API
一、线性回归
针对的是损失函数loss faction
Ⅰ、Lasso Regression
采用L1正则,会使得w值整体偏小;w会变小从而达到降维的目的
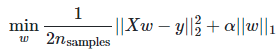
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressorX = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * X + np.random.randn(100, 1)lasso_reg = Lasso(alpha=0.15, max_iter=10000)
lasso_reg.fit(X, y)
print("w0=",lasso_reg.intercept_)
print("w1=",lasso_reg.coef_)sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(penalty='l1', max_iter=10000)
sgd_reg.fit(X, y.ravel())
print("w0=",sgd_reg.intercept_)
print("w1=",lasso_reg.coef_)
Ⅱ、Ridge Regression(岭回归)
采用L2正则,会使得有的w趋近1,有的w趋近0;当w趋近于0的时候,相对于可以忽略,w会变少也可以达到降维的目的(深度学习模型建立首选)
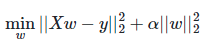
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor#随机梯度下降回归#模拟数据
X = 2 * np.random.rand(100,1)
y = 4 + 3 * X + np.random.randn(100,1)ridge_reg = Ridge(alpha=1,solver='auto')#创建一个ridge回归模型实例,alpha为惩罚项前的系数
ridge_reg.fit(X,y)
print("w0=",ridge_reg.intercept_)#w0
print("w1=",ridge_reg.coef_)#w1sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(penalty='l2')
sgd_reg.fit(X,y.ravel())
print("w0=",sgd_reg.intercept_)#w0
print("w1=",sgd_reg.coef_)#w1
Ⅲ、Elastic Net回归
当你不清楚使用L1正则化还是L2正则化的时候,可以采用Elastic Net
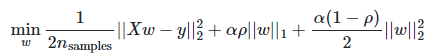
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressorX = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * X + np.random.randn(100, 1)elastic_net = ElasticNet(alpha=0.0001, l1_ratio=0.15)
elastic_net.fit(X, y)
#print(elastic_net.predict(1.5))
print("w0=",elastic_net.intercept_)
print("w1=",elastic_net.coef_)sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(penalty='elasticnet', max_iter=1000)
sgd_reg.fit(X, y.ravel())
#print(sgd_reg.predict(1.5))
print("w0=",sgd_reg.intercept_)
print("w1=",sgd_reg.coef_)
Ⅳ、总结
①算法选择顺序,Ridge Regression (L2正则化) --> ElasticNet (即包含L1又包含L2) --> Lasso Regression (L1正则化)
②正则化L1和L2有什么区别?
答:L1是w绝对值加和,L2是w平方加和。L1的有趣的现象是会使得w有的接近于0,有的接近于1,
L1更多的会用在降维上面,因为有的是0有的是1,我们也称之为稀疏编码。
L2是更常用的正则化手段,它会使得w整体变小
超参数alpha 在Rideg类里面就直接是L2正则的权重
超参数alpha 在Lasso类里面就直接是L1正则的权重
超参数alpha 在ElasticNet和SGDRegressor里面是损失函数里面的alpha
超参数l1_ration 在ElasticNet和SGDRegressor里面是损失函数的p
二、多项式回归
针对的是数据预处理进行特征处理,跟归一化一样,都是针对的是数据
多项式回归其实是线性回归的一种拓展。
多项式回归:叫回归但并不是去做拟合的算法
PolynomialFeatures是来做预处理的,来转换我们的数据,把数据进行升维!
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
m = 100#100个样本
X = 6 * np.random.rand(m, 1) - 3#m行1列的数,数的取值范围在[-3,3]
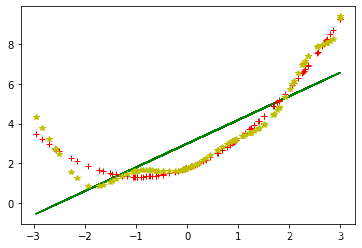
y = 0.5 * X ** 2 + X + 2 + np.random.randn(m, 1)plt.plot(X, y, 'b.')
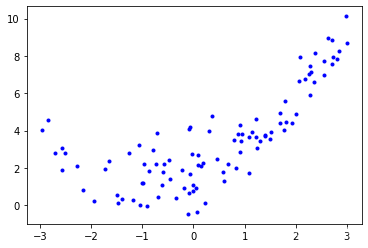
d = {1: 'g-', 2: 'r+', 10: 'y*'}
for i in d:poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=i, include_bias=False)#degree超参数可以改变,当然若太大会出现过拟合现象,导致效果更加糟糕X_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(X)print(X[0])print(X_poly[0])print(X_poly[:, 0])lin_reg = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)lin_reg.fit(X_poly, y)print(lin_reg.intercept_, lin_reg.coef_)y_predict = lin_reg.predict(X_poly)plt.plot(X_poly[:, 0], y_predict, d[i])plt.show()
"""
[-1.17608282]
[-1.17608282]
[-1.17608282 0.84008756 -0.47456115 1.09332609 -0.08048591 2.56227793-2.16089094 2.9934595 -0.97719578 -0.35093548 -0.01833382 -2.578095490.90594767 1.23236141 0.5809494 -1.03761487 1.07926559 -1.015365042.08713351 1.68679419 0.36108667 0.0739686 -0.60676473 -0.09778250.93322126 -0.98029008 1.80329174 -2.7079627 2.27067075 -0.23098381-2.84414673 2.80368239 1.13965085 0.60386564 1.5068452 0.084835792.54605719 2.25506764 -0.57412233 1.40321778 0.08664762 1.79293147-0.72311264 -1.39573162 0.15066435 -2.56825076 1.6992054 0.306551442.27792527 0.05690445 1.91725839 2.70744724 -0.46459041 1.24513038-0.90932212 2.71793477 -1.64319111 1.49955188 2.17534115 -2.505103912.72835224 -0.17797949 -0.07305404 -0.60531858 0.90754969 0.1864542.63700818 2.00439925 -1.26906332 -0.03326623 0.95249887 2.988010311.39131364 -1.46984234 0.67347918 1.30899516 -0.68746311 -0.078952172.847029 -1.94670177 -0.73970148 -1.05884194 -2.95987324 -2.27319748-0.01555128 -0.86999284 0.45600536 1.21528784 -1.72581767 0.22440468-1.50353748 2.36782931 2.30633509 1.76346603 -0.79567338 -0.061536510.87272525 0.78535366 2.36179793 2.05667417]
[2.99104579] [[1.19669575]]
[-1.17608282]
[-1.17608282 1.38317079]
[-1.17608282 0.84008756 -0.47456115 1.09332609 -0.08048591 2.56227793-2.16089094 2.9934595 -0.97719578 -0.35093548 -0.01833382 -2.578095490.90594767 1.23236141 0.5809494 -1.03761487 1.07926559 -1.015365042.08713351 1.68679419 0.36108667 0.0739686 -0.60676473 -0.09778250.93322126 -0.98029008 1.80329174 -2.7079627 2.27067075 -0.23098381-2.84414673 2.80368239 1.13965085 0.60386564 1.5068452 0.084835792.54605719 2.25506764 -0.57412233 1.40321778 0.08664762 1.79293147-0.72311264 -1.39573162 0.15066435 -2.56825076 1.6992054 0.306551442.27792527 0.05690445 1.91725839 2.70744724 -0.46459041 1.24513038-0.90932212 2.71793477 -1.64319111 1.49955188 2.17534115 -2.505103912.72835224 -0.17797949 -0.07305404 -0.60531858 0.90754969 0.1864542.63700818 2.00439925 -1.26906332 -0.03326623 0.95249887 2.988010311.39131364 -1.46984234 0.67347918 1.30899516 -0.68746311 -0.078952172.847029 -1.94670177 -0.73970148 -1.05884194 -2.95987324 -2.27319748-0.01555128 -0.86999284 0.45600536 1.21528784 -1.72581767 0.22440468-1.50353748 2.36782931 2.30633509 1.76346603 -0.79567338 -0.061536510.87272525 0.78535366 2.36179793 2.05667417]
[1.77398327] [[0.96156952 0.516698 ]]
[-1.17608282]
[-1.17608282 1.38317079 -1.6267234 1.91316143 -2.25003628 2.64622901-3.11218446 3.66018667 -4.30468264 5.06266328]
[-1.17608282 0.84008756 -0.47456115 1.09332609 -0.08048591 2.56227793-2.16089094 2.9934595 -0.97719578 -0.35093548 -0.01833382 -2.578095490.90594767 1.23236141 0.5809494 -1.03761487 1.07926559 -1.015365042.08713351 1.68679419 0.36108667 0.0739686 -0.60676473 -0.09778250.93322126 -0.98029008 1.80329174 -2.7079627 2.27067075 -0.23098381-2.84414673 2.80368239 1.13965085 0.60386564 1.5068452 0.084835792.54605719 2.25506764 -0.57412233 1.40321778 0.08664762 1.79293147-0.72311264 -1.39573162 0.15066435 -2.56825076 1.6992054 0.306551442.27792527 0.05690445 1.91725839 2.70744724 -0.46459041 1.24513038-0.90932212 2.71793477 -1.64319111 1.49955188 2.17534115 -2.505103912.72835224 -0.17797949 -0.07305404 -0.60531858 0.90754969 0.1864542.63700818 2.00439925 -1.26906332 -0.03326623 0.95249887 2.988010311.39131364 -1.46984234 0.67347918 1.30899516 -0.68746311 -0.078952172.847029 -1.94670177 -0.73970148 -1.05884194 -2.95987324 -2.27319748-0.01555128 -0.86999284 0.45600536 1.21528784 -1.72581767 0.22440468-1.50353748 2.36782931 2.30633509 1.76346603 -0.79567338 -0.061536510.87272525 0.78535366 2.36179793 2.05667417]
[1.75155522] [[ 0.96659081 1.47322289 -0.32379381 -1.09309828 0.22053653 0.3517641-0.03986542 -0.04423885 0.00212836 0.00193739]]
"""
完整代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionm = 100#100个样本
X = 6 * np.random.rand(m, 1) - 3#m行1列的数,m = 100#100个样本
X = 6 * np.random.rand(m, 1) - 3#m行1列的数,数的取值范围在[-3,3]
y = 0.5 * X ** 2 + X + 2 + np.random.randn(m, 1)plt.plot(X, y, 'b.')#数的取值范围在[-3,3]
y = 0.5 * X ** 2 + X + 2 + np.random.randn(m, 1)plt.plot(X, y, 'b.')d = {1: 'g-', 2: 'r+', 10: 'y*'}
for i in d:poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=i, include_bias=False)X_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(X)print(X[0])print(X_poly[0])print(X_poly[:, 0])lin_reg = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)lin_reg.fit(X_poly, y)print(lin_reg.intercept_, lin_reg.coef_)y_predict = lin_reg.predict(X_poly)plt.plot(X_poly[:, 0], y_predict, d[i])plt.show()
三、案例实战
保险公司的一份数据集,里面含有多人的age、sex、bmi、children、smoker、region、charges。
年龄、性别、BMI肥胖指数、有几个孩子、是否吸烟、居住区域、医疗开销。
很显然,这是个有监督的学习,保险公司肯定是想通过其他因素来确定处某个人的医疗开销,来一个人,我可以通过他的年龄、性别、BMI肥胖指数、有几个孩子、是否吸烟、居住区域来推测出这个人的医疗开销。
故,这里的y为charges,各因素为age、sex、bmi、children、smoker、region。
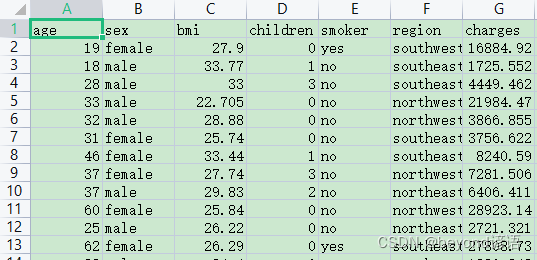
免费保险公司用户信息数据集下载,这里采用的是CSV文件,也就是数据之间通过逗号隔开的数据集。
逗号分隔值(Comma-Separated Values,CSV,有时也称为字符分隔值,因为分隔字符也可以不是逗号)
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
data = pd.read_csv('./insurance.csv')#该路径为数据集的路径
print(type(data))
print(data.head())#输出前5条数据
print(data.tail())#输出后5条数据
# describe做简单的统计摘要
print(data.describe())
"""
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>age sex bmi children smoker region charges
0 19 female 27.900 0 yes southwest 16884.92400
1 18 male 33.770 1 no southeast 1725.55230
2 28 male 33.000 3 no southeast 4449.46200
3 33 male 22.705 0 no northwest 21984.47061
4 32 male 28.880 0 no northwest 3866.85520age sex bmi children smoker region charges
1333 50 male 30.97 3 no northwest 10600.5483
1334 18 female 31.92 0 no northeast 2205.9808
1335 18 female 36.85 0 no southeast 1629.8335
1336 21 female 25.80 0 no southwest 2007.9450
1337 61 female 29.07 0 yes northwest 29141.3603age bmi children charges
count 1338.000000 1338.000000 1338.000000 1338.000000
mean 39.207025 30.663397 1.094918 13270.422265
std 14.049960 6.098187 1.205493 12110.011237
min 18.000000 15.960000 0.000000 1121.873900
25% 27.000000 26.296250 0.000000 4740.287150
50% 39.000000 30.400000 1.000000 9382.033000
75% 51.000000 34.693750 2.000000 16639.912515
max 64.000000 53.130000 5.000000 63770.428010
"""
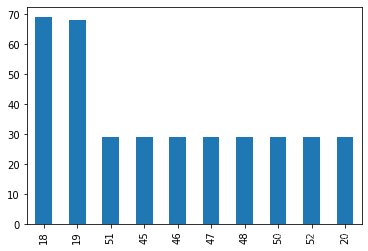
# 采样要均匀
data_count = data['age'].value_counts()#看看age有多少个不同的年龄,各个年龄的人一共有几个人
print(data_count)
data_count[:10].plot(kind='bar')#将年龄的前10个进行柱状图展示
plt.show()
# plt.savefig('./temp')#可以指定将图进行保存的路径
"""
18 69
19 68
51 29
45 29
46 29
47 29
48 29
50 29
52 29
20 29
26 28
54 28
53 28
25 28
24 28
49 28
23 28
22 28
21 28
27 28
28 28
31 27
29 27
30 27
41 27
43 27
44 27
40 27
42 27
57 26
34 26
33 26
32 26
56 26
55 26
59 25
58 25
39 25
38 25
35 25
36 25
37 25
63 23
60 23
61 23
62 23
64 22
Name: age, dtype: int64
"""
print(data.corr())
"""age bmi children charges
age 1.000000 0.109272 0.042469 0.299008
bmi 0.109272 1.000000 0.012759 0.198341
children 0.042469 0.012759 1.000000 0.067998
charges 0.299008 0.198341 0.067998 1.000000
"""
reg = LinearRegression()
x = data[['age', 'sex', 'bmi', 'children', 'smoker', 'region']]
y = data['charges']
# python3.6 报错 sklearn ValueError: could not convert string to float: 'northwest',加入一下几行解决
x = x.apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='coerce')#有的数据集类型是字符串,需要通过to_numeric方法转换为数值型
y = y.apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='coerce')
x.fillna(0, inplace=True)#数据集中为空的地方填充为0
y.fillna(0, inplace=True)poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3, include_bias=False)
X_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(x)reg.fit(X_poly, y)
print("w0=",reg.intercept_)#w0
print("w1=",reg.coef_)#w1
"""
w0= 14959.173791946276
w1= [ 5.86755877e+02 -8.66943361e-09 -2.43090741e+03 2.46877353e+03-2.34731345e-09 6.66457112e-10 -1.20823237e+01 2.22654961e-096.99860524e+00 -1.94583589e+02 -2.67144085e-10 4.64133620e-107.31601446e-11 3.21392690e-10 -1.89132265e-10 7.45785655e-113.91901267e-09 9.19625484e+01 -1.49720497e+02 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 2.76208814e+03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 9.96980980e-020.00000000e+00 4.50579510e-02 3.12743917e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -2.30842696e-01 -1.20554724e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -4.28257797e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -9.34651320e-015.89748395e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -5.02728643e+010.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 -2.25687557e+02 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+000.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
"""
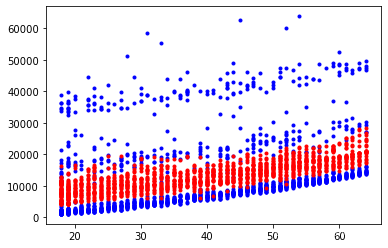
y_predict = reg.predict(X_poly)plt.plot(x['age'], y, 'b.')
plt.plot(X_poly[:, 0], y_predict, 'r.')
plt.show()
完整代码如下:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressiondata = pd.read_csv('./insurance.csv')
print(type(data))
print(data.head())#输出前5条数据
print(data.tail())#输出后5条数据
# describe做简单的统计摘要
print(data.describe())# 采样要均匀
data_count = data['age'].value_counts()#看看age有多少个不同的年龄,各个年龄的人一共有几个人
print(data_count)
data_count[:10].plot(kind='bar')#将年龄的前10个进行柱状图展示
plt.show()
# plt.savefig('./temp')#将图进行保存print(data.corr())#输出列和列之间的相关性reg = LinearRegression()
x = data[['age', 'sex', 'bmi', 'children', 'smoker', 'region']]
y = data['charges']
# python3.6 报错 sklearn ValueError: could not convert string to float: 'northwest',加入一下几行解决
x = x.apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='coerce')
y = y.apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='coerce')
x.fillna(0, inplace=True)
y.fillna(0, inplace=True)poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3, include_bias=False)
X_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(x)reg.fit(X_poly, y)
print(reg.coef_)
print(reg.intercept_)y_predict = reg.predict(X_poly)plt.plot(x['age'], y, 'b.')
plt.plot(X_poly[:, 0], y_predict, 'r.')
plt.show()
四、总结
Ⅰ多项式回归:叫回归但并不是去做拟合的算法,PolynomialFeatures是来做预处理的,来转换我们的数据,把数据进行升维!
Ⅱ升维有什么用?
答:升维就是增加更多的影响Y结果的因素,这样考虑的更全面,最终的目的是要增加准确率!
还有时候,就像PolynomialFeatures去做升维,是为了让线性模型去拟合非线性的数据!
ⅢPolynomialFeatures是怎么升维的?
答:可以传入degree超参数,如果等于2,那么就会在原有维度基础之上增加二阶的数据变化!更高阶的以此类推
Ⅳ如果数据是非线性的变化,但是就想用线性的模型去拟合这个非线性的数据,怎么办?
答:1,非线性的数据去找非线性的算法生成的模型去拟合
2,可以把非线性的数据进行变化,变成类似线性的变化,然后使用线性的模型去拟合
PolynomialFeatures类其实就是这里说的第二种方式
Ⅴ保险的案例:
目的:未来来个新的人,可以通过模型来预测他的医疗花销,所以,就把charges列作为y,其他列作为X维度
Ⅵ为什么每行没有人名?
答:人名不会对最终的Y结果产生影响,所以可以不用
Ⅶ为什么要观测注意数据多样性,采样要均匀?
答:就是因为你要的模型的功能是对任何年龄段的人都有一个好的预测,那么你的模型在训练的时候 读取的数据集,就得包含各个年龄段的数据,而且各个年龄段也得数据均匀,防止过拟合!
Ⅷ什么是Pearson相关系数?
答:Pearson相关系数是来测量两组变量之间的线性相关性的!Pearson相关系数的区间范围是-1到1之间
如果越接近于-1,说明两组变量越负相关,一个变大,另一个变小,反之如果越接近于1,说明两组变量越正相关,一个变大,另一个也跟着变大,如果越接近于0,说明越不相关,即一个变大或变小,另一个没什么影响!
通过Pearson相关系数,如果发现两个维度之间,相关系数接近于1,可以把其中一个去掉,做到降维!
通过Pearson相关系数,如果发现某个维度和结果Y之间的相关系数接近于0,可以把这个维度去掉,降维!

)






---讲解)





---小练习)



方法与示例)
