数据科学和统计学
统计 (Statistics)
Statistics are utilized to process complex issues in reality with the goal that Data Scientists and Analysts can search for important patterns and changes in Data. In straightforward words, Statistics can be utilized to get significant experiences from information by performing scientific calculations on it. A few Statistical capacities, standards and calculations are executed to break down crude information, fabricate a Statistical Model and construe or foresee the outcome. The motivation behind this is to give an extensive review of the fundamentals of statistics that you’ll need to start your data science journey.
统计数据用于处理现实中的复杂问题,其目标是数据科学家和分析师可以搜索数据的重要模式和变化。 简而言之,可以通过对统计信息进行科学计算,利用统计信息来获得重要的经验。 执行一些统计能力,标准和计算以分解原始信息,构建统计模型并解释或预见结果。 其背后的动机是对开始进行数据科学之旅所需的统计基础知识进行广泛的回顾。
资料类型 (Data Types)
Numerical:
数值 :
Data communicated with digits; is quantifiable. It can either be discrete (limited number of qualities) or consistent (interminable number of qualities).
用数字传达的数据; 是可量化的。 它可以是离散的(有限数量的质量)或一致的(无限数量的质量)。
Downright:
完全 :
Qualitative data grouped into classes. It tends to be ostensible (no structure) or ordinal (requested data).
定性数据分为几类。 它倾向于表面上的(无结构)或顺序的(请求的数据)。
集中趋势测度 (Measures of Central Tendency)
Mean: The normal of a dataset.
平均值 :数据集的法线。
Medium: The center of an arranged dataset; less defenseless to anomalies.
中 :排列的数据集的中心; 对异常情况缺乏防御力。
Mode: The most widely recognized incentive in a dataset; just significant for discrete information.
模式 :数据集中最广泛认可的激励; 对于离散信息而言意义重大。
变异量度 (Measures of Variability)
Range: The distinction between the most elevated and least incentive in a dataset.
范围 :数据集中最高激励和最低激励之间的区别。
Variance (σ2): Apportions on how to spread a lot of data is comparative with the mean.
方差(σ2) :关于如何分散大量数据的方式与均值比较。
Standard Deviation (σ): Another estimation of how to spread out numbers are in data collection; it is the square foundation of variance
标准偏差(σ) :关于如何分散数字的另一种估计是在数据收集中。 它是方差的平方根
Z-score: Decides the number of the standard deviations data point is from the mean.
Z分数 :确定标准差数据点与平均值的数量。
R-Squared: A factual proportion of fit that demonstrates how much variety of a reliant variable is clarified by the free variable(s); just helpful for straightforward direct relapse.
R平方 :拟合的实际比例,它表明自由变量阐明了多少依赖变量; 有助于直接复发。
Balanced R-squared: A changed variant of r-squared that has been balanced for the number of indicators in the model; it increments if the new term improves the model more than would be normal by some coincidence and the other way around.
平衡的R平方 : R平方的已更改变体,已经针对模型中的指标数量进行了平衡; 如果新术语对模型的改进程度比正常情况好一些(反之亦然),则它会增加。
变量之间关系的度量 (Measurement of Relationships between Variables)
Covariance: Measures the fluctuation between (at least two) factors. On the off chance that it's sure, at that point they will move in a similar way, in the event that it's negative, at that point they will in general move in inverse bearings, and on the off chance that they're zero, they have no connection to one another.
协方差 :衡量(至少两个)因素之间的波动。 可以肯定的是,到那时它们将以类似的方式运动,如果它为负,则通常它们将反向移动,而当它们为零时,它们将以相反的方向运动。没有任何联系。
Correlation: Measures the quality of a connection between two factors and ranges from - 1 to 1; the standardized adaptation of covariance. By and large, a connection of +/ - 0.7 speaks to a solid connection between two factors. On the other side, connections between - 0.3 and 0.3 show that there is almost no connection between factors.
相关 :测量两个因素之间的连接质量,范围为-1到1; 协方差的标准化适应。 总的来说,+ /-0.7的连接表示两个因素之间的牢固连接。 另一方面,-0.3和0.3之间的联系表明因素之间几乎没有联系。
概率分布函数 (Probability Distribution Functions)
Probability Density Function (PDF): A capacity for ceaseless data where the incentive anytime can be deciphered as giving a relative probability that the estimation of the irregular variable would rise to that example.
概率密度函数(PDF) :一种不间断数据的能力,在这种能力下,可以随时将激励解释为给出不规则变量的估计将上升到该示例的相对概率。
Probability Mass Function (PMF): A capacity for discrete information that gives the likelihood of a given worth happening.
概率质量函数(PMF) :离散信息的能力,给出给定价值发生的可能性。
Cumulative Density Function (CDF): A capacity that reveals to us the probability that an irregular variable is not exactly a specific worth; the basis of the PDF.
累积密度函数(CDF) :一种能力,向我们揭示不规则变量不完全是特定价值的可能性; PDF的基础。
连续数据分配 (Continuous Data Distributions)
Uniform Distribution: Probability dissemination where all results are similarly likely.
均匀分布 :概率分布 ,所有结果都有可能相似。
Normal/Gaussian Distribution: Regularly alluded to as the bell curve and is identified with central limit theorem; has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
正态/高斯分布 :通常被称为钟形曲线,并通过中心极限定理进行标识; 平均值为0,标准偏差为1。
T-Distribution: Probability dissemination used to evaluate populace parameters when the example size is little and/r when the populace change is obscure.
T分布 :当样本量较小时和/或在人口变化不明显时,用于评估人口参数的概率分布 。
Chi-Square Distribution: Dissemination of the chi-square measurement.
卡方分布 :传播卡方测量。
离散数据分布 (Discrete Data Distributions)
Poisson Distribution: Probability dissemination that communicates the likelihood of a given number of occasions happening inside a fixed timeframe.
泊松分布 :概率分布 ,用于传达在固定时间范围内发生给定次数的情况的可能性。
Binomial Distribution: Probability dissemination of the number of achievements in a succession of n autonomous encounters each with its Boolean-esteemed result (p, 1-p).
二项式分布 :概率分布 n次连续的自动遭遇中每个成就的数量,每个自主遭遇都有布尔值估计的结果(p,1-p)。
片刻 (Moments)
Moments portray various parts of nature and state of circulation. The principal moment is the mean, the subsequent moment is the fluctuation, the third moment is the skewness, and the fourth moment is the kurtosis.
时刻刻画了自然的各个部分和循环状态。 主力矩是均值,随后力矩是波动,第三力矩是偏度,第四力矩是峰度。
可能性 (Probability)
Conditional Probability [P(A|B)] is the probability of an occasion happening, in light of the event of a past occasion.
条件概率[P(A | B)]是根据过去的事件发生的情况的概率。
Independent Event whose result doesn't impact the likelihood of the result of another occasion; P(A|B) = P(A).
独立事件,其结果不会影响其他情况下结果的可能性; P(A | B)= P(A)。
Mutually Exclusive events are events that can't happen at the same time; P(A|B) = 0.
互斥事件是不能同时发生的事件。 P(A | B)= 0。
Bayes' Theorem: A scientific recipe for deciding restrictive likelihood. "The probability of A given B is equal to the probability of B given A times the probability of A over the probability of B".
贝叶斯定理 :决定限制性可能性的科学方法。 “ A给定B的概率等于B给定A的概率乘以A的概率对B的概率”。
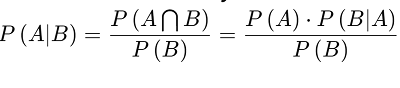
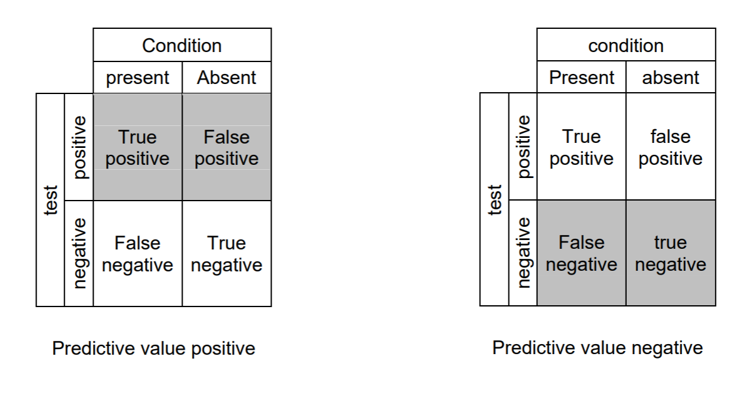
准确性 (Accuracy)
True positive: Identifies the condition when the condition is available.
真实肯定 :在条件可用时标识条件。
True negative: doesn't distinguish the condition when the condition is absent.
真否定 :不存在条件时不区分条件。
False-positive: distinguishes the condition when the condition is missing.
假阳性 :缺少条件时区分条件。
False-negative: doesn't distinguish the condition when the condition is available.
假阴性 :在条件可用时不区分条件。
Sensitivity: otherwise called recall; quantifies the capacity of a test to distinguish the condition when the condition is available; sensitivity = TP/(TP+FN)
敏感性 :否则称为召回; 在条件可用时量化测试区分条件的能力; 灵敏度= TP /(TP + FN)
Specificity: quantifies the capacity of a test to accurately reject the condition when the condition is missing; Specificity = TN/(TN+FP)
特异性 :量化测试在条件缺失时准确拒绝条件的能力; 特异性= TN /(TN + FP)
Predictive value positive: otherwise called precision; the extent of positives that compare to the nearness of the condition; PVP = TP/(TP+FP)
正预测值 :否则称为精度; 与条件的接近程度相比,阳性的程度; PVP = TP /(TP + FP)
Predictive value negative: the extent of negatives that compare to the nonattendance of the condition; PVN = TN/(TN+FN)
预测值负数 :与条件的无人值守相比较的负数范围; PVN = TN /(TN + FN)
假设检验及其统计意义 (Hypothesis Testing and Statistical Significance)
Null Hypothesis: The speculation that example perceptions result absolutely from possibility.
零假设(Null Hypothesis) : 假设感知完全是由可能性引起的。
Alternative Hypothesis: The theory that example perceptions are affected by some non-irregular reason.
替代假设 :理论感知受一些非常规原因影响的理论。
P-value: the likelihood of acquiring the watched aftereffects of a test, accepting that the invalid speculation is right; a littler p-value implies that there is more grounded proof for the elective theory.
P值 :接受无效推测是正确的,获得测试的观察到的后效应的可能性; 较小的p值表示选修理论有更多扎实的证据。
Alpha: The essentialness level; the probability of dismissing the invalid theory when it is valid — otherwise called Type 1 error.
Alpha :必要性级别; 无效理论成立时被驳回的可能性-否则称为1类错误。
Beta: type 2 mistake; neglecting to dismiss the false null hypothesis.
Beta :类型2错误; 忽略了错误的虚假假设。
假设检验的步骤 (Steps to Hypothesis Testing)
Express the invalid and elective theory
表达无效选修理论
Decide the test size; is it a couple or two-tailed test?
确定测试大小; 是几尾还是两尾测试?
Register the test measurement and the likelihood value
注册测试测量值和似然值
Dissect the outcomes and either dismiss or don't dismiss the invalid speculation
剖析结果,或者驳斥或不驳斥无效的推测
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/data-science/statistics.aspx
数据科学和统计学
)




(转载))



![[Json] C#ConvertJson|List转成Json|对象|集合|DataSet|DataTable|DataReader转成Json (转载)...](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Json] C#ConvertJson|List转成Json|对象|集合|DataSet|DataTable|DataReader转成Json (转载)...)


![centos6.5安装配置LDAP服务[转]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/centos6.5安装配置LDAP服务[转])



)


)