c语言语言教程0基础
Hey, Folks here I am back with my second article on C language. Hope you are through with my previous article C language - History, Popularity reasons, Characteristics, Basic structure etc. In this one, I will cover some fundamental concepts of C Language namely Variables, Tokens, Operators in C language.
嘿,伙计们,我回来了第二篇有关C语言的文章。 希望您能读完我以前的C语言文章-历史,流行原因,特征,基本结构等 。 在这一篇中,我将介绍C语言的一些基本概念,即C语言中的变量,标记,运算符 。
Let’s get started...
让我们开始吧...
1)变量 (1) Variables)
They are temporary memory locations allocated during execution of the program. As the name suggests it is an entity whose value may change during program execution.
它们是在程序执行期间分配的临时内存位置。 顾名思义,它是一个在程序执行期间其值可能会更改的实体。
Rules for variable name
变量名规则
It does not have a space between characters.
字符之间没有空格。
Collection of alphabets, digits, and underscore (_).
字母,数字和下划线(_)的集合。
The first character should be either alphabet or underscore (_).
第一个字符应为字母或下划线(_)。
No other special symbol except underscore (_).
除下划线(_)外,没有其他特殊符号。
Keywords cannot be used as variable name.
关键字不能用作变量名。
Declaration of variable
变量声明
Syntax:
句法:
datatype variable_name;
Example:
例:
int a;
It tells the user what is the data type of a declared variable or what type of values it can hold.
它告诉用户声明的变量的数据类型是什么或它可以保存的值的类型。
Initialization of a variable
初始化变量
The process of assigning any value to any variable.
将任何值分配给任何变量的过程。
Example:
例:
int a = 5;
2)代币 (2) Token)
The basic and smallest unit of C program is token.
C程序的基本最小单位是令牌。
Token includes :
令牌包括:
Keywords
关键词
Identifier
识别码
Constants
常数
String Constant
字符串常量
Operators
经营者
Special Symbols e.g: _ , @ , *
特殊符号,例如:_,@,*
1) Keywords or Reserve words
1)关键字或保留字
These are those words whose meaning is already explained to the compiler.
这些是已经向编译器解释其含义的单词。
They can’t be used as a variable name because if we do so that means we are defining the new meaning to the compiler which the compiler does not allow.
它们不能用作变量名,因为如果这样做,则意味着我们正在为编译器定义编译器不允许的新含义。
2) Identifier
2)识别码
They are the name given to programming elements such as array, function, variable. Same rules as of variable name.
它们是诸如数组,函数,变量之类的编程元素的名称。 与变量名相同的规则。
3) Constant
3)常数
Entities whose value does not during the execution of a program.
其值在程序执行期间不存在的实体。
4) String constant
4)字符串常量
Collection of character enclosed by a double inverted comma. e.g.: "abc"
用双反逗号括起来的字符的集合。 例如: “ abc”
5) Operators
5)运营商
They are used to perform arithmetic and logical operations by ALU.
它们由ALU用于执行算术和逻辑运算。
Example:
例:
a+b
Here, a and b are operands and + is an operator.
在这里, a和b是操作数,而+是运算符。
C language has very rich operators. Many different types of operators are available in C language for different mathematical computations.
C语言具有非常丰富的运算符。 C语言提供了许多不同类型的运算符,用于不同的数学计算。
They are mainly of three types:
它们主要分为三种类型:
Operators itself is a separate topic which needs to be covered in detail.
运营商本身是一个单独的主题,需要详细介绍。
So, here we get started.
所以,我们开始。
Unary operators
一元运算符
They require only one operand for execution, it includes :
它们只需要一个操作数即可执行,其中包括:
Unary minus
一元减
Bitwise compliment
按位赞美
Logical Not
逻辑不
Increment / Decrement
增量/减量
sizeof() operator
sizeof()运算符
sizeof() Operator
sizeof()运算符
It is used to return the size of an operand. It can be applied on variable, constant, datatype.
它用于返回操作数的大小。 它可以应用于变量,常量,数据类型。
Syntax:
句法:
sizeof(operand);
Example:
例:
int a=2, b;
b = sizeof(a);
//or
b = sizeof(int);
//or
b = sizeof(5);
printf("%d\n",b);
//All of the 3 three statements will give same output.
Ternary operators
三元运算符
They are also called conditional operator. For these operators, we require 3 operands for execution. There is only and one ternary operator in C language.
它们也称为条件运算符。 对于这些运算符,我们需要3个操作数来执行。 用C语言只有一个三元运算符。
Syntax:
句法:
expression_1 ? expression_2 : expression_3 ;
If expression_1 is true expression_2 gets executed, if false then expression_3.
如果expression_1为true,则执行expression_2 ,如果为false,则执行expression_3 。
Example:
例:
int a=4 , b=7 , c;
c = ( a<7 ? a:b );
printf("%d\n", c );
Output
输出量
4
Since, a = 4, exp_1 is true and therefore exp_2 gets executed. So, c = a gets executed.
由于a = 4 , exp_1为true,因此exp_2被执行。 因此, c = a被执行。
Binary operators
二元运算符
i) Arithmetic operators
i)算术运算符
| Operator name | Operator |
| Addition | + |
| Subtraction | - |
| Multiplication | * |
| Division | / |
| Modulus | % |
| 操作员姓名 | 操作员 |
| 加成 | + |
| 减法 | -- |
| 乘法 | * |
| 师 | / |
| 模量 | % |
Modulus operator gives remainder and division operator gives quotient. All arithmetic operators can be used for integer and float values except modulus which is used for integers only.
模运算符给出余数,除法运算符给出商。 除模数仅用于整数外,所有算术运算符均可用于整数和浮点值。
b) Relational operators
b)关系运算符
They are used for comparison between two values. They return result as true or false.
它们用于两个值之间的比较。 它们返回结果为true或false。
| Operator name | Operator |
| Less than | < |
| Less than or equal to | <= |
| Greater than | > |
| Greater than or equal to | >= |
| Equal to | == |
| Not equal to | != |
| 操作员姓名 | 操作员 |
| 少于 | < |
| 小于或等于 | <= |
| 比...更棒 | > |
| 大于或等于 | > = |
| 等于 | == |
| 不等于 | != |
c) Logical operators
c)逻辑运算符
Used to combine two relational expression and they returns result as true or false.
用于组合两个关系表达式,它们返回结果为true或false。
| A | B | A && B | A || B | !A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 一个 | 乙 | A && B | A || 乙 | !一个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1个 |
| 0 | 1个 | 0 | 1个 | 1个 |
| 1个 | 0 | 0 | 1个 | 0 |
| 1个 | 1个 | 1个 | 1个 | 0 |
d) Bitwise operators
d)按位运算符
They are used to perform operation on individual bits. They can be applied on char and int.
它们用于对单个位执行操作。 它们可以应用于char和int 。
| Operators | Symbol name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| & | Ampersand | Bitwise AND |
| | | Pipe | Bitwise OR |
| ^ | Caret | Bitwise X OR |
| ~ | Tilde | Bitwise compliment |
| << | Double less than | Left shift operator |
| >> | Double greater than | Right shift operator |
| 经营者 | 符号名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 和 | &符 | 按位与 |
| | | 管 | 按位或 |
| ^ | 插入符号 | 按位X OR |
| 〜 | 蒂尔德 | 按位赞美 |
| << | 少于两倍 | 左移运算符 |
| >> | 大于 | 右移运算符 |
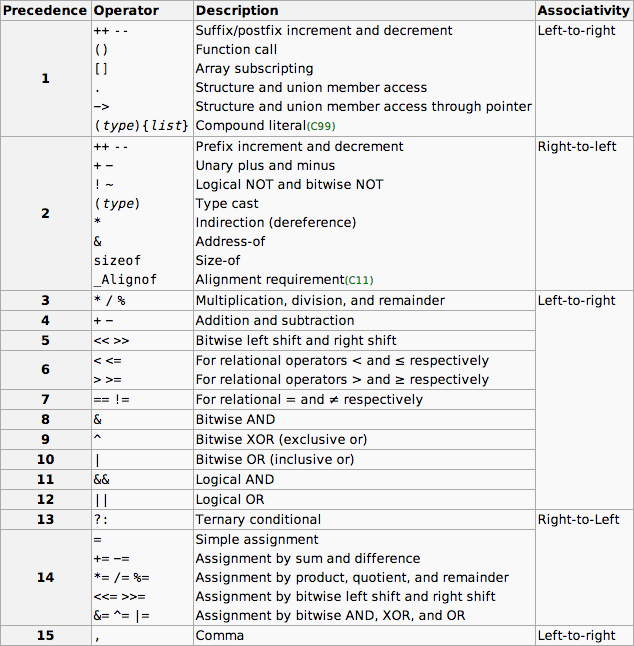
C Operator Precedence Table:
C运算符优先级表:
This page lists C operators in order of precedence (highest to lowest). Their associativity indicates in what order operators of equal precedence in an expression are applied.
本页按优先顺序(从高到低)列出C运算符。 它们的关联性指示在表达式中应用相同优先级的运算符的顺序。
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/c/basics-of-c-language.aspx
c语言语言教程0基础
















 但是 3.28.4-0ubuntu18.04.2 正要被安装解决方案)


