(给DotNet加星标,提升.Net技能)
英文:samueleresca.net
译文:cnblogs.com/Rwing/p/fast-growing
译者:Rwing
本篇文章的第一部分介绍了有关Serverless计算的基本概念。
第二部分展示了如何构建 .NET Core的Lambda函数,其中使用了AWS的Serverless框架。
Serverless 计算的好处
Serverless 技术是 FaaS(功能即服务)技术体系的一部分。随着云计算的采用,这些技术变得越来越受欢迎。如今,serverless 实现被提升为云计算提供商的首选技术,无论是私有云还是公有云。
此外,典型的软件服务和系统会通过在内存中保留大量数据并在复杂数据源中写入成批数据来完成操作。
然而一般而言,像 Serverless 一样的 FaaS 技术旨在通过尽可能快地处理许多小请求和事件,来使我们的系统保持快速响应。Serverless 组件通常与运行它们的云服务商所提供的事件紧密耦合:一个通知、一个队列调度的事件或者一个来自 API 网关的请求,都被视为此组件中包含的一小部分计算的触发器。这也就是云服务商的定价系统基于请求数而不是基于计算时间的主要原因。
再者,serverless 组件通常在执行时间上有一些限制。与每种技术一样,serverless 并不适合每一个解决方案和系统。
但是事实上它确实简化了软件工程师的一些工作,lambda 部署周期通常很快,开发人员只需要做少量工作就可以快速将新功能投入生产。
此外使用 serverless 技术构建组件意味着开发人员无需担心扩展问题或故障,让云提供商去关心这些问题吧。
最后,我们还应该知道 serverless 函数是无状态的。因此,基于此技术构建的每个系统都更加模块化和松耦合。
Serverless 的痛点
但是这种能力和敏捷性却不是没有代价的。首先,serverless 函数是在云上执行的,它们通常由与云提供商紧密耦合的事件触发,因此调试它们并不容易。
这就是为什么要使它的作用域保持尽可能小,并且始终将函数的核心逻辑与外部组件和事件分隔开的原因。此外,用单元测试和集成测试覆盖 serverless 代码非常重要。
其次,就像微服务架构一样,它具有大量的服务,但是关注的范围很小,因此很难对 serverless 的组件进行监控,某些问题也很难检测。
总之,很难对不同的 serverless 组件之间的体系结构和依赖性有一个全面的认识。因此,云提服务商和第三方公司都在提供监控和系统分析功能的一体式工具上投入了大量资金。
体验一下 serverless 计算
现如今,根据业务需求快速进化的架构以往任何时候都更为重要。数据驱动的体验是这个过程的一部分。此外,在发布新功能之前,我们应该实现MVP(译注:最小可行化产品)并在部分客户群上测试它。如果实验结果是肯定的,则值得在MVP上进行投资,以将其转化为我们产品的功能。
是的,serverless 计算提供了这样一种方法,可以在不考虑基础设施的情况下快速进化我们的架构。Serverless 轻量级开销提供了一种实现一次性 MVP 的方法,用于试验新功能和新特性。此外,它们还可以很容易地启动和关闭。
使用 .NET Core 来实现 AWS Lambda 函数
这一节将介绍使用 .NET Core 的一些 AWS Lambdas 的简单实现。该例子涉及三个关键技术:
AWS 是承载我们 serverless 功能的云服务商;
serverless 框架,它是将 Lambdas 放入 AWS 的非常有用的工具。作为一个通用的框架,它兼容所有主要的云服务商;
.NET Core 是微软提供的开源的、跨平台的框架;
我们将要讨论的示例也放在了 GitHub 上,URL 如下: https://github.com/serverless/examples/tree/master/aws-dotnet-rest-api-with-dynamodb。
该示例是 serverless 框架提供的一些模板项目的一部分。
AWS Lambda 项目遵循以下功能架构:
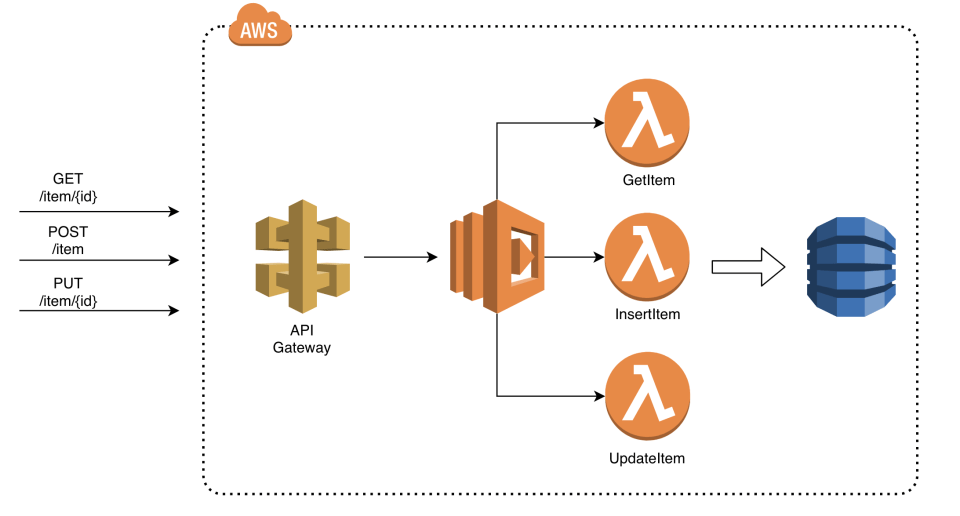
总结一下,该功能实现了对数据的一些读取/写入操作。客户端通过API网关发出HTTP请求,lambda 项目定义了三个函数:GetItem、InsertItem 和 UpdateItem。它们都对 DynamoDB 表进行操作。
项目结构
我们将要实现的解决方案具有以下项目结构:
src/DotNetServerless.Application 该项目包含了由 Serverless 执行的核心逻辑;
src/DotNetServerless.Lambda 该项目包含了 Serverless 函数的入口点以及所有与 AWS 紧密耦合的组件;
tests/DotNetServerless.Tests 该项目包含了 Serverless 功能的单元测试和集成测试;
领域项目
让我们从 application 层开始分析。项目的核心实体是 Item 类,它表示 DynamoDB(译注:AWS的一种数据库) 表中存储的实体:
using Amazon.DynamoDBv2.DataModel;
namespace DotNetServerless.Application.Entity
{
public class Item
{
[DynamoDBHashKey]
public string Id { get; set; }
[DynamoDBRangeKey]
public string Code { get; set; }
[DynamoDBProperty]
public string Description { get; set; }
[DynamoDBProperty]
public bool IsChecked { get; set; }
}
}实体的字段使用了一些特性进行修饰,以便使用 DynamoDb 存储模型映射它们。Item 实体被 IItemsRepository 接口引用,该接口定义用于存储数据的操作:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Amazon.DynamoDBv2;
using Amazon.DynamoDBv2.DataModel;
using Amazon.DynamoDBv2.DocumentModel;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Entities;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Infrastructure.Configs;
namespace DotNetServerless.Application.Infrastructure.Repositories
{
public interface IItemRepository
{
Task> GetById(string id, CancellationToken cancellationToken);Task Save(Item item, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
}public class ItemDynamoRepository : IItemRepository
{private readonly AmazonDynamoDBClient _client;private readonly DynamoDBOperationConfig _configuration;public ItemDynamoRepository(DynamoDbConfiguration configuration,
IAwsClientFactory clientFactory){
_client = clientFactory.GetAwsClient();
_configuration = new DynamoDBOperationConfig
{
OverrideTableName = configuration.TableName,
SkipVersionCheck = true
};
}public async Task Save(Item item, CancellationToken cancellationToken){using (var context = new DynamoDBContext(_client))
{await context.SaveAsync(item, _configuration, cancellationToken);
}
}public async Task> GetById(string id, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{var resultList = new List();using (var context = new DynamoDBContext(_client))
{var scanCondition = new ScanCondition(nameof(Item.Id), ScanOperator.Equal, id);var search = context.ScanAsync(new[] {scanCondition}, _configuration);while (!search.IsDone)
{var entities = await search.GetNextSetAsync(cancellationToken);
resultList.AddRange(entities);
}
}return resultList;
}
}
}IItemRepository 的实现定义了两个基本操作:
Save,允许调用者插入和更新实体;
GetById,根据 ID 返回对象;
最后,DotNetServerless.Application 的顶层是 Handler 部分。
并且整个 application 项目都基于中介模式,以保证 AWS 函数和核心逻辑之间的松散耦合。让我们以创建项目处理程序的定义为例:
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Entities;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Infrastructure.Repositories;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Requests;
using MediatR;
namespace DotNetServerless.Application.Handlers
{
public class CreateItemHandler : IRequestHandler
{private readonly IItemRepository _itemRepository;public CreateItemHandler(IItemRepository itemRepository){
_itemRepository = itemRepository;
}public async Task Handle(CreateItemRequest request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var item = request.Map();
item.Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
await _itemRepository.Save(item, cancellationToken);return item;
}
}
}如您所见,代码非常简单。CreateItemHandler 实现了 IRequestHandler,它使用内置的依赖注入来解析 IItemRepository 接口。处理程序的 Handler 方法仅将传入的请求与Item实体映射,并调用IItemRepository接口提供的Save方法。
函数项目
函数项目包含 lambda 功能的入口点。它定义了三个函数类,它们表示 AWS 的 lambda:CreateItemFunction, GetItemFunction 和 UpdateItemFunction; 稍后我们将看到,每个函数都将使用 API 网关的特定路由进行映射。
让我们以 CreateItem 函数为例,对函数定义进行一些深入探讨:
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents;
using Amazon.Lambda.Core;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Requests;
using MediatR;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace DotNetServerless.Lambda.Functions
{
public class CreateItemFunction
{
private readonly IServiceProvider _serviceProvider;
public CreateItemFunction() : this(Startup
.BuildContainer()
.BuildServiceProvider()){
}
public CreateItemFunction(IServiceProvider serviceProvider){
_serviceProvider = serviceProvider;
}
[LambdaSerializer(typeof(Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.Json.JsonSerializer))]
public async TaskRun(APIGatewayProxyRequest request){
var requestModel = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(request.Body);var mediator = _serviceProvider.GetService();var result = await mediator.Send(requestModel);return new APIGatewayProxyResponse { StatusCode = 201, Body = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(result)};
}
}
}上面提到的代码定义了函数的入口点。首先,它声明一个构造函数,并使用Startup类公开的BuildContainer和BuildServiceProvider方法。稍后我们将看到,这些方法是为初始化依赖项注入容器而提供的。CreateItem 函数的 Run 方法使用 Lambda 序列器属性进行修饰,这意味着它是函数的入口点。
此外运行函数使用 APIGatewayProxyRequest 请求和 APIGatewayProxyReposne 作为 lambda 计算的输入和输出。
依赖注入
该项目使用了 .NET Core 内置的依赖注入。Startup 类定义了 BuildContainer 静态方法,该方法返回一个新的 ServiceCollection,其中包含实体之间的依赖关系映射:
using System.IO;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Infrastructure;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Infrastructure.Configs;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Infrastructure.Repositories;
using DotNetServerless.Lambda.Extensions;
using MediatR;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace DotNetServerless.Lambda
{
public class Startup
{
public static IServiceCollection BuildContainer(){
var configuration = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.AddEnvironmentVariables()
.Build();
return ConfigureServices(configuration);
}
private static IServiceCollection ConfigureServices(IConfigurationRoot configurationRoot){
var services = new ServiceCollection();
services
.AddMediatR()
.AddTransient(typeof(IAwsClientFactory<>), typeof(AwsClientFactory<>))
.AddTransient()
.BindAndConfigure(configurationRoot.GetSection("DynamoDbConfiguration"), new DynamoDbConfiguration()).BindAndConfigure(configurationRoot.GetSection("AwsBasicConfiguration"), new AwsBasicConfiguration());return services;
}
}
}Startup使用ConfigureServices初始化新的ServiceCollection并与其一起解决依赖关系。此外,它还使用 BindAndConfigure 方法创建一些配置对象。BuildContainer方法将由函数调用,以解决依赖项。
测试我们的代码
如前所述,测试一下我们的代码,对于持续集成和交付是非常重要的,尤其是在lambda项目中。在这种情况下,测试将覆盖 IMediator 接口和处理程序之间的集成。此外,它们还覆盖了依赖项注入部分。让我们看看 CreateItemFunctionTests 的实现:
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Entities;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Infrastructure.Repositories;
using DotNetServerless.Application.Requests;
using DotNetServerless.Lambda;
using DotNetServerless.Lambda.Functions;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.Extensions;
using Moq;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Xunit;
namespace DotNetServerless.Tests.Functions
{
public class CreateItemFunctionTests
{
public CreateItemFunctionTests(){
_mockRepository = new Mock();
_mockRepository.Setup(_ => _.Save(It.IsAny(), It.IsAny())).Returns(Task.CompletedTask);var serviceCollection = Startup.BuildContainer();
serviceCollection.Replace(new ServiceDescriptor(typeof(IItemRepository), _ => _mockRepository.Object,
ServiceLifetime.Transient));
_sut = new CreateItemFunction(serviceCollection.BuildServiceProvider());
}private readonly CreateItemFunction _sut;private readonly Mock _mockRepository;
[Fact]public async Task run_should_trigger_mediator_handler_and_repository(){await _sut.Run(new APIGatewayProxyRequest {Body = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new CreateItemRequest())});
_mockRepository.Verify(_ => _.Save(It.IsAny(), It.IsAny()), Times.Once);
}
[Theory]
[InlineData(201)]public async Task run_should_return_201_created(int statusCode){var result = await _sut.Run(new APIGatewayProxyRequest {Body = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new CreateItemRequest())});
Assert.Equal(result.StatusCode, statusCode);
}
}
}如您所见,上述代码执行了我们的函数,并且对已注入的依赖项执行一些验证,并验证 IItemRepository 公开的 Save 方法是否被调用。
因为一些原因,测试类并没有覆盖 DynamoDb 的特性。此外,当我们将复杂的实体和操作结合在一起时,可以使用 Docker 容器通过一些集成测试来覆盖数据库部分。
提到 .NET Core 和 AWS 的话题,.NET AWS 团队有一个很好的工具来改进 lambda 的测试:https://github.com/aws/aws-lambda-dotnet/tree/master/Tools/LambdaTestTool
部署项目
让我们来看看如何将项目导入AWS。为此,我们将使用 serverless 框架。该框架的定义是:
serverless 框架是一个 CLI 工具,允许用户构建和部署自动缩放、按执行付费、事件驱动的函数。
为了把 serverless 添加我们的项目,我们应该执行以下命令:
npm install serverless --save-dev定义基础架构
默认情况下,基础架构的定义将放在 serverless.yml 文件中。该文件看起来像这样:
service: ${file(env.configs.yml):feature}
frameworkVersion: ">=1.6.0 <2.1.0"
provider:
name: aws
stackName: ${file(env.configs.yml):feature}-${file(env.configs.yml):environment}
runtime: dotnetcore2.1
region: ${file(env.configs.yml):region}
accountId: ${file(env.configs.yml):accountId}
environment:
DynamoDbConfiguration__TableName: ${file(env.configs.yml):dynamoTable}
iamRoleStatements:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- dynamodb:*
Resource: "arn:aws:dynamodb:${self:provider.region}:*:table/${self:provider.environment.DynamoDbConfiguration__TableName}"
package:
artifact: bin/release/netcoreapp2.1/deploy-package.zip
functions:
create:
handler: DotNetServerless.Lambda::DotNetServerless.Lambda.Functions.CreateItemFunction::Run
events:
- http:
path: items
method: post
cors: true
get:
handler: DotNetServerless.Lambda::DotNetServerless.Lambda.Functions.GetItemFunction::Run
events:
- http:
path: items/{id}
method: get
cors: true
update:
handler: DotNetServerless.Lambda::DotNetServerless.Lambda.Functions.UpdateItemFunction::Run
events:
- http:
path: items
method: put
cors: true
resources:
Resources:
ItemsDynamoDbTable:
Type: 'AWS::DynamoDB::Table'
DeletionPolicy: Retain
Properties:
AttributeDefinitions:
- AttributeName: Id
AttributeType: S
- AttributeName: Code
AttributeType: S
KeySchema:
- AttributeName: Id
KeyType: HASH
- AttributeName: Code
KeyType: RANGE
ProvisionedThroughput:
ReadCapacityUnits: 1
WriteCapacityUnits: 1
TableName: ${self:provider.environment.DynamoDbConfiguration__TableName}以上代码使用 AWS 的 cloud formation 对基础架构进行一些操作。provider 节点定义了有关 lambda 的某些信息,例如堆栈名称、运行时以及有关AWS账户的一些信息。
此外,它还描述了 lambda 的角色和授权,例如,应该允许 lambda 对 DynamoDb 表执行操作。
functions 节点定义了不同的 lambda 函数,并将其与特定的 HTTP 路径进行映射。
最后,resources 节点用于设置 DynamoDB 表模式。
配置文件
serverless.yml 定义通常与另一个 YAML 文件结合使用,该文件仅定义与环境相关的配置。例如,DynamoDbConfiguration__TableName 节点就是这种情况,该节点使用以下语法从另一个 YAML 文件获取信息:${file(env.configs.yml):dynamoTable}。以下代码段显示了 env.config.yml 文件的一个示例:
feature: version: 1.0.0.0region: environment: accountId: dynamoTable: 最后的想法
这篇文章涵盖了一些关于 serverless 计算的理论主题,以及 .Net Core 实现 lambda 函数的例子。
着重讲解了如何使用 serverless 计算来快速推进我们的架构。
此外,勇于尝试是一个不断发展的产品很关键的一方面,它对于快速适应业务的变化是很重要的。
最后,您可以在以下存储库中找到一些 serverless 的 lambda 示例。
https://github.com/serverless/examples/tree/master/aws-dotnet-rest-api-with-dynamodb
原文:https://samueleresca.net/2018/12/fast-growing-architectures-with-serverless-and-net-core/
推荐阅读
(点击标题可跳转阅读)
开始你的API:NetApiStarter
.NET Core WebAPI 缓存神器Redis
.NET Core迁移前的准备工作
看完本文有收获?请转发分享给更多人
关注「DotNet」加星标,提升.Net技能

好文章,我在看❤️

















)

