| 大标题 | 小节 |
|---|---|
| 一、DOM选择器 | 1. id 选择器:getElementById("id名");2. class 选择器: getElementByClassName("class名");3. 标签选择器: getElementsByTagName("标签名");4. name 选择器: getElementById("name的属性值");5. ES5新增的两种选择器: querySelector()、querySelectorAll();6. 父级选子级 children、子级选父级parentNode |
| 二、DOM属性的操作 | 1. 内置属性; 2. 自定义属性:通过attribute系列; 总结 |
| 三、节点的操作 | 1. 节点树; 2. 节点的操作; 3. 过滤空白节点 |
| 四、高级选择器 | previousSibling、previousElementSibling、nextSibling、nexElementSibling、firstChild、firstElementChild、lastChild、lastElementChild、ownerDocument |
| 五、元素的操作 | 1. 增:createElement()配和appendChild();2. 删除: remove()、removeChild(具体子元素);3. 修改(不建议改标签): outerHTML、innerHTML |
| 六、获取元素宽高 | 1.页面滚动的距离; 2. 页面可视区域的大小、整个页面的大小; 3. 获取图片宽高 |
| 七、获取样式 | 元素.style.css样式常用作设置,不用来获取; |
| 八、添加、删除、修改class |
文档对象模型 DOM
1. 概念:DOM(document object model),文档对象模型(document),当网页被加载时,浏览器会创建页面的DOM。
2. 作用:通过可编程的对象模型,JavaScript 获得了足够的能力来创建动态的 HTML,修改 HTML = 改变元素、属性、样式和事件。。
修改 HTML DOM意味着:
(1)改变 HTML 内容;(2)改变 CSS 样式;(3)改变 HTML 属性;(4)创建新的 HTML 元素;(5)删除已有的 HTML 元素;(6)改变事件(处理程序)。
当浏览器载入 HTML 文档, 它就会成为 Document 对象。Document 对象是 HTML 文档的根节点,它使我们可以从脚本中对 HTML 页面中的所有元素进行访问。
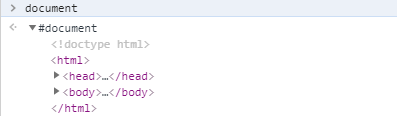
console.dir(document);,查看DOM的详细信息。
一、DOM 选择器
我们通过 js 可以改变元素的内容(innerHTML)、属性(value)、样式(width、height)之前,要先选择出这个元素。
1. id 选择器:getElementById("id名")
(1) 通过 id 选择指定 id 的元素,括号中的“id名”前面不需要“#”。
(2)当有多个相同 id 名时,id 选择器选择第一个,体现了 id 的唯一性。
<body><input type="text" name="" id="ipt"><input type="text" name="" id="ipt"><input type="text" name="" id="ipt">
</body>
</html>
<script>var ipts = document.getElementById("ipt");console.log(ipts)
</script>

2. class选择器:getElementsByClassName("class名")
(1) 通过 class 选择指定 class 的元素,括号中的“class名”前面不需要“.”。低版本ie(ie8+)不兼容;
(2)不管相同 class 名的元素有多少个,它返回的都是数组,这个数组是伪数组。注意要选择具体元素时加 [0/1/2/...]。
<body><input type="text" name="" class="cont"><input type="text" name="" class="cont"><input type="text" name="" class="cont"><input type="text" name="" class="te">
</body>
</html>
<script>var teClass = document.getElementsByClassName("te");var conts = document.getElementsByClassName("cont");console.log("class名相同的只有自身",teClass)console.log("class名相同的有多个",conts)
</script>

3. 标签选择器:getElementsByTagName("标签名")
- 返回的是数组,这个数组是伪数组。选择具体元素时后面记得加
[0/1/2/...]。<body><input type="text" name="" id="ipt" class="cont"><input type="text" name="" id="ipt" class="cont"><input type="text" name="" id="ipt" class="cont"><input type="text" name="" id="ipt" class="te"><span>1</span> </body> </html> <script>var ipts = document.getElementsByTagName("input");var spans = document.getElementsByTagName("spans");console.log(ipts)console.log(spans) </script>
4. name 选择器:getElementsByName("name属性的值")
(1) 选择的是具有 “name” 属性的元素,常见的有表单元素;低版本ie(ie8+)不兼容;
(2)返回的是数组,这个数组是伪数组。
<body><input type="text" name="user"><input type="text" name="like"><input type="text" name="like"><input type="text" name="like"><span name="span">1</span> <!-- 自己添加的 name 属性也可以被选择 -->
</body>
<script>var user = document.getElementsByName("user");var likes = document.getElementsByName("like");console.log(user);console.log(likes);
</script>

5. ES5 新增的两种选择器:querySelector()、querySelectorAll()
(1)querySelector("标签名"/ "#id名" / ".class名");;
-
返回的是单个对象,不管选择 多个 id 还是多个 class,返回的都是第一个元素。低版本ie(ie8+)不兼容;
<body><input type="text" id="ipt" class="cont"><input type="text" id="ipt" class="cont"><input type="text" id="ipt" class="cont"><input type="text" id="ipt1" class="te"> </body> </html> <script>var ipt1 = document.querySelector("#ipt1");var cont = document.querySelector(".cont");console.log(ipt1);console.log(cont); </script>
-
该选择器还能支持简单的 css3 选择器。
docuemnt.querySelector("input[name = user]"); document.querySelector("div span");
(2)querySelectorAll("标签名"/ "#id名" / ".class名");;
- 返回的是数组,不管选择的是什么都返回数组,这是个伪数组。低版本ie(ie8+)不兼容;
6. 父级选子级children、子级选父级parentNode
ie8 及 ie8 以下不兼容。
(1)children:父选子,返回数组,这是个伪数组;
<div class="msg"><h1>1</h1><h1>2</h1><h1>3</h1>
</div>
var omsg= document.querySelector(".msg");
var achild = omsg.children;
console.log(achild); //HTMLCollection(3) [h1, h1, h1]
(2)parentNode:子选父,返回单个元素;
<div class="msg"><h1>1</h1><h1>2</h1><h1>3</h1>
</div>
var omsg= document.querySelector(".msg");
var achild = omsg.children;
console.log(achild[1].parentNode); //<div class="msg">...</div>

二、 DOM属性的操作
简单来说,html 中标签的属性就是 DOM 属性。更多的属性和方法查看菜鸟教程。
为了方便记忆,这里把js中的DOM属性的操作分为了两种:内置属性和自定义属性。
(1)内置属性有:
- ① HTML标签上默认(自带)的属性。
- ② js 上操作标签内容的属性;
(2)自定义属性有:
- ① 在HTML标签上自定义的属性名和属性值;
- ② 利用 js 给标签添加的自定义的属性名和属性值。
| 操作DOM属性需要学习的方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
setAtrribute("属性名", "属性值"); | 属性名不存在就是新增,存在就是修改属性值。 |
getAtrribute("属性名"); | 获取属性值; |
removeAtrribute("属性名"); | 删除已有的属性名和它的属性值,若没有就会报错。 |
hasAttribute("属性名"); | 判断属性是否存在,如果存在返回 true,否则返回 false。 |
1. 内置属性:
(1)HTML标签上默认(自带)的属性。
例如a标签中的href、target、title;img中的src、title、alt属性等就是内置属性。
-
① 获取:两种方法:一、获取 class 时要用
obox.className,用.获取除 class 类名外的属性;二、使用getAttribute(),注意获取类名时直接getAttibute("class");<div class="box" id="box"><a href="/aaa" target="_blank" title="title111">这是a标签1</a> </div> <script>var obox = document.querySelector("div");var oa1 = document.querySelector("a");//console.log(obox.class); //undefinedconsole.log(obox.className); //box,获取类名console.log(oa1.href); // /aaaconsole.log(oa1.getAttribute("title")); //title111 </script> -
② 新增/修改:两种方法:一、通过“
.”,注意新增/修改类名时是“.className”,其他正常新增/修改;二、使用setAttribute(),注意设置类名时直接setAttibute("class", "定义class名");<a href="/aaa" target="_blank" title="title111" id="one">这是a标签1</a> <a href="/www.xxx" id="two">这是省略title属性的a标签</a> <script>var oa1 = document.getElementById("one");var oa2 = document.getElementById("two");oa1.class = "a1"; //无效oa2.className = "a2";oa2.target = "_blank";oa2.setAttribute("title","title222");console.log(oa1);console.log(oa2) </script>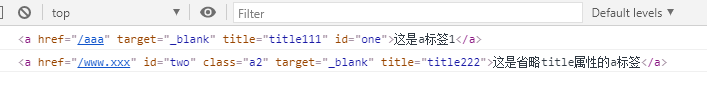
-
③ 删除:只能通过
removeAttribute()来删除。<a href="/aaa" target="_blank" title="title111" id="one">这是a标签1</a> <script>var oa1 = document.getElementById("one");delete oa1.title; //无效oa1.removeAttribute("href");console.log(oa1); </script>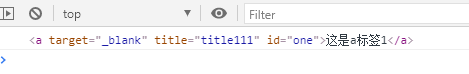
(2)内置的 js 操作标签内容的几个属性:innerHTML、innerText、tagName;
① innerHTML,设置或者返回元素的内容,包括标签。innerHTML 属性对于获取或替换 HTML 元素的内容很有用,它可以用于获取或改变任意 HTML 元素,包括 <html> 和 <body>;所有主流浏览器都支持。
② innerText,返回被选择的元素中的所有文字内容;不支持Firefox浏览器;
③ tagName,以字符串形式返回某个元素的标记名(大写),只能获取,修改标签名不生效。
outHTML,返回的是标签本身,可用来改标签,比如把 p标签改成 span标签;
<body><div class="box"><span>文字</span><p>这是一个段落</p></div>
</body>
<script>var obox = document.getElementsByClassName("box")[0];console.log(obox.innerHTML);console.log(obox.innerText);console.log(obox.tagName); //DIV 返回大写的标签名
</script>
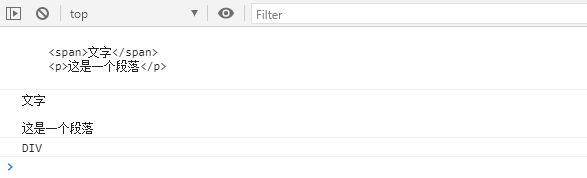
innerHTML和innerText都可以设置元素内容,但是innerHTML设置标签可以被浏览器解析,而innerText会把标签当成文本。
2. 自定义属性: 通过 attibute系列
(1)获取: getAttribute("自定义属性名");,不能通过“.”获取。
<body><!-- p标签上的index就是自定义的属性 --><p class="p" index="haha">段落1</p>
</body>
</html>
<script>var op = document.querySelector(".p");console.log(op.index); //undefined 无效console.log(op.getAttribute("index")); //haha
</script>
(2)设置/修改: setAttribute("自定义属性名","值");
- 通过“
.”设置无效,但是用“.”设置的属性的属性值,可以被“.”获取到,也只能被“.”获取到。
<body><p class="p">段落1</p>
</body>
</html>
<script>var op = document.querySelector(".p");var op = document.querySelector(".p");op.index = "haha"; //无效console.log(op.index); //hahaconsole.log(op.getAttribute("index")); //nullop.setAttribute("key","lala"); //通过js的方法给p标签添加自定义属性key。console.log(op)
</script>
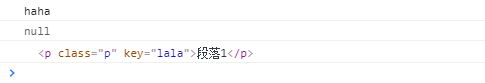
(3)删除: removeAttribute("自定义属性名");
<body><p class="p" index="haha">段落1</p>
</body>
</html>
<script>var op = document.querySelector(".p");op.removeAttribute("index")console.log(op); //成功
</script>

总结
(1)不管 HTML标签的属性是内置的,还是自定义的,js 都可以使用 attribute 系列的方法去操作HTML标签的属性。此外,js 还可以使用 “.” 来操作(除删除操作外)HTML标签的内置属性。
(2)js 可以通过 innerHTML、innerText、来获取和设置标签的文本内容,通过tagName获取选择的标签名。
三、 节点的操作
| 节点名称 | 描述 | nodeName 属性规定节点的名称[只读] | nodeValue 属性规定节点的值 | nodeType 返回节点的类型[只读] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根节点 | 整个文档(html)是一个文档节点; | #document | null | 数字 9 |
| 元素节点 | 每个 HTML 元素(标签、标记)是元素节点; | 大写的标签名 | undefined 或 null | 数字 1 |
| 属性节点 | 每个 HTML 属性(标签的属性)是属性节点,它也属于元素节点; | 属性名 | 属性值 | 数字 2 |
| 文本节点 | HTML 元素内的文本是文本节点(包括注释里面的文本、换行); | #text | 文本内容 | 数字 3 |
| 注释节点 | 注释是注释节点; | #comment | 注释内容 | 数字 8 |
1. 节点树
HTML DOM 将 HTML 文档视作树结构,这种结构被称为节点树。节点树中的节点彼此拥有层级关系,这些关系用 “父节点”、“子节点”、“同胞节点(常称为兄弟节点)” 等术语来表示。
用一段代码来示例:

(1)父节点:
<html> 节点没有父节点;它是根节点;
<head> 和 <body> 的父节点是 <html> 节点
<meta>、<title>的父节点是 <head> 节点;
<h1>、<a> 的父节点是 <body> 节点;
(2)子节点:
<html> 节点拥有两个子节点:<head> 和 <body>;
<head> 节点拥有四个子节点:3个<mate>节点、<title> 节点;
<title> 节点也拥有一个子节点:文本节点 “什么是节点”;
<body> 节点拥有两个子节点:<h1> 和 <a>;
(3)兄弟节点:
<head> 和 <body> 节点是同胞节点;
<meta> 和 <title> 节点是同胞节点;
<h1> 和 <a> 节点是同胞节点;
2. 节点操作
| 节点操作方法 | 描述 | 使用 |
|---|---|---|
| nodeName | 只读的,规定节点的名称; | 节点.nodeName |
| nodeValue | 规定节点的值; | 节点.nodeValue |
| nodeType | 只读的,返回节点的类型; | 节点.nodeType |
(1) 根节点的操作
console.log(document.nodeName); //#document 获取根节点的名称
console.log(document.nodeValue); //null 获取根节点的值
console.log(document.nodeType); //9 根节点的类型
(2) 属性节点的操作:元素.attributes;
属性在元素身上,要操作一个属性节点,首先选中元素节点。 返回一个 伪数组。
- 伪数组可以用数组的索引、length、遍历(for),但不能用数组的方法(push()、pop()、forEach,map,filter)。
<input type="text" id="txt" name="user" placeholder="请输入"/>
<script>var atxt = document.getElementById("txt");console.log("atxt.attributes----",atxt.attributes); //伪数组console.log("atxt.attributes[0]----",atxt.attributes[0]); //type="text"console.log("atxt.attributes[0].value----",atxt.attributes[0].value); //textconsole.log("atxt.attributes.type----",atxt.attributes.type); //type="text" 不建议使用console.log("atxt.type----",atxt.type); //text
</script>

- 获取属性节点的
nodeName、nodeValue、nodeType;console.log(atxt.attributes[0].nodeName); //type console.log(atxt.attributes[0].nodeValue); //text console.log(atxt.attributes[0].nodeType); //2
(3) 文本节点的操作: childNodes、parentNode;
通过父选子 、子选父;
| 名称 | 区别 |
|---|---|
children | 获取到的是一个伪数组,是所有子元素/标签(不包括空白节点)的集合。 |
childNodes | 获取到的是一个伪数组,是所有节点(元素节点、文本节点(空白节点也是文本节点)、注释节点等)的集合。ie8不包含空文本节点。 |
parentNode | 获取父元素节点。 |
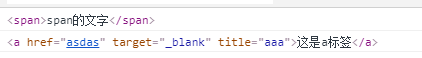
<div class="box" title="这是div" haha="index">文字<!-- 注释 --><span>span的文字</span><a href="asdas" target="_blank" title="aaa">这是a标签</a>
</div>
<script>
var obox = document.querySelector(".box");
console.log(obox.children); //HTMLCollection(2) [span, a]
console.log(obox.childNodes); //NodeList(7) [text, comment, text, span, text, a, text]
//text 文本节点,comment 注释节点,span/a (标签)元素节点
</script>

节点.childNodes[i],获取到的是节点本身,是个对象,而不是字符串;console.log(obox.childNodes[0]); //返回节点本身 console.log(obox.childNodes[0].nodeName); //#text console.log(obox.childNodes[0].nodeValue); //文字 节点的值 console.log(obox.childNodes[0].nodeType); //3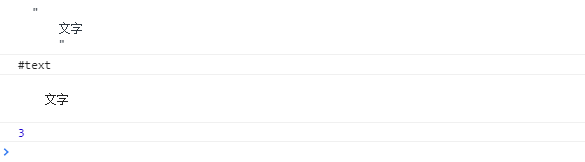
3. 过滤空白节点
var list = obox.childNodes;
for(var i=0; i<list.length; i++){ //遍历所有节点if(list[i].nodeType == 1){ //元素节点的nodeType=1console.log(list[i]);}
}
四、高级选择器
previousSibling、previousElementSibling、nextSibling、nexElementSibling、firstChild、firstElementChild、lastChild、lastElementChild、ownerDocument
关系(兄弟、父子)选择器(ie8不支持)
1. 兄弟之间:
(1)相邻的前一个节点: previousSibling;
(2)相邻的前一个元素节点: previousElementSibling;
(3)相邻的下一个节点: nextSibling;
(4)相邻的下一个元素节点: nexElementSibling;
2. 父子之间:
(1)第一个子节点: firstChild;
(2)第一个子元素节点: firstElementChild,ie7/8 不支持;
(3)最后一个子节点: lastChild;
(4)最后一个子元素节点: lastElementChild;
3. 获取根节点: ownerDocument 相当于 document;
<body><span>第一个文本</span><ul id="list"><li>1</li><li>2</li><li>3</li><li>4</li></ul><p>我是p</p>
</body>
<script>
var olist = document.getElementById("list");console.log(olist.previousSibling); //#textconsole.log(olist.previousElementSibling); //<span>第一个文本</span>console.log(olist.nextSibling); //#textconsole.log(olist.nextElementSibling); //<p>我是p</p>console.log(olist.firstChild); //#textconsole.log(olist.firstElementChild); //<li>1</li>console.log(olist.lastChild); //#textconsole.log(olist.lastElementChild); //<li>4</li>console.log(olist.ownerDocument); //#document
</script>
五、 元素的操作
1. 增:createElement()配和appendChild()
先创建元素(元素节点),然后把它追加到已有的元素上。
(1)先创建: document.createElement("标签名");
创建文本节点用createTextNode("文本节点名称"),使用方式同 createElement();
(2)插入(通常先给标签设置一些样式、内容,最后再插入):
- ① 作为父元素的最后一个子元素插入:
document.appendChild("创建的标签");<body><div id="box"></div> </body> </html> <script>var obox = document.getElementById("box");var addSpan = document.createElement("span"); //创建一个span元素span.innerHTML = "你好"; //给 span 元素设置内容,最后一步再插入obox.appendChild(addSpan); //把创建好的 span 元素插入到 obox 中 </script>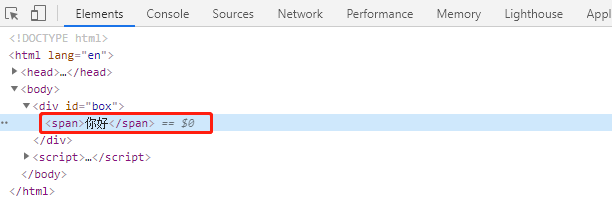
- 插入到之前:
insertBefore(newNode,existNode);
2. 删除:remove()、removeChild(具体子元素)
删除元素有两种方式:直接删除remove(),根据父删除子 removeChild(具体子元素)。
(1)直接删除(建议使用): remove();
(2)根据父删除子: removeChild(具体子元素);
<div id="box"><h2 class="title">标题</h2><div id="msg">想要修改div标签<p>这是一个段落</p></div></div>
<script>var obox = document.getElementById("box");//删----直接删var otitle = document.querySelector(".title");otitle.remove();//删----根据父删除子var omsg = document.getElementById("msg");var op = omsg.children[0]; //children获取的是所有子元素omsg.removeChild(op); //removeChild()必须传参,删除 omsg 的子节点 op
</script>

3. 修改(不建议改标签): outerHTML、innerHTML
<body><div id="box"><p class="msg"><b>标题</b> <span>文字</span></p></div>
</body>
<script>var obox = document.getElementById("box");console.log(obox.outerHTML);console.log(obox.innerHTML)obox.outerHTML = "<main>"+obox.innerHTML+"</main>"; //outerHTML 是用来改边标签的var op = document.querySelector(".msg");op.innerHTML = "<em>hello</em>"; //innerHTML 修改的是元素的内容
</script>

六、获取元素宽高 - 各种尺寸
| 获取元素尺寸的主要属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
offsetParent | 返回元素的偏移容器,即离自身最近的上一级写了定位的元素,没有就返回 <body>。 |
offsetWidth、offsetHeight | 返回元素的 宽度/高度,包括边框(border)和填充(padding),但不是边距(margin)。content的width + border + padding |
offsetTop、offsetLeft | 返回当前元素的相对 垂直/水平 偏移位置(垂直方向是 top+margin值,水平方向是 left+margin值)的偏移容器 |
clientWidth、clientHeight | 在页面上返回内容的 可视宽度/高度(不包括边框,边距或滚动条)content的width + padding |
clientTop、clientLeft | 当前元素的 上/左边框 的大小。 |
scrollWidth、scrollHeight | 返回元素的整个 宽度/高度(包括带滚动条的隐蔽的地方)。 |
scrollTop、scrollLeft | 返回当前视图中的实际元素的 顶部边缘和顶部边缘/左边缘和左边缘 之间的距离。 |
<style>*{margin:0;padding:0;}.boxLarge{border: 5px solid #000;height: 300px;position: relative;}.box{width: 200px;height: 100px;background:#99f;padding:10px; border: 5px solid #000;position: absolute;top: 10px;left: 20px;margin:30px;}
</style>
<body><div class="boxLarge"><p class="box"></p></div>
</body>
</html>
<script>var largeBox = document.querySelector(".boxLarge");var op = document.querySelector("p");console.log("offsetParent",op.offsetParent);console.log("offsetWidth",op.offsetWidth,op.offsetHeight);console.log("offsetTop",op.offsetTop,op.offsetLeft);console.log("clientWidth",op.clientWidth,op.clientHeight);console.log("clientTop",op.clientTop,op.clientLeft);
</script>

1. 页面滚动的距离
onscroll = function(){var yTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop; //纵向滚动 滚动条距离页面顶部的距离var xLeft = document.documentElement.scrollLeft; //横向滚动 滚动条距离页面左边的距离console.log(yTop);console.log(xLeft);
}
兼容写法(兼容低版本浏览器):
onscroll = function(){var yTop = document.body.scrollTop;var xLeft = document.body.scrollLeft;console.log(yTop);console.log(xLeft);
}
2. 页面可视区域的大小、整个页面的大小
onresize = function(){//页面可视区域的大小var dWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth;var dHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight;console.log(dWidth); console.log(dHeight);//页面整体的大小,即body/html(除了margin值)的大小var bWidth = document.body.clientWidth;var bHeight = document.body.clientHeight;console.log(bWidth); //3000console.log(bHeight); //2000}

3. 获取图片宽高
因为图片要获取资源路径,所以用到 onload。 onload用于页面(window)和图片 (图片的元素)。
var oimg = document.queryselect("img");oimg.onload = function(){console.log(oimg.offsetWidth);
}
4. 注意: 鼠标类尺寸样式都是X,Y,浏览器及元素的各项尺寸时Height,Width;(这里后面再详细介绍)</font
七、获取样式
1. 设置样式:元素.style.css样式;
这种方法常用来设置,而不是获取。
var obox = document.getElementById("box");console.log(obox.style.width)//obox.style.width = 600+ "px";console.log(obox.style.width)//600px
2. 获取样式:getComputedStyle(元素,false).小驼峰样式名;
用 getComputedStyle(元素,false).小驼峰样式名,ie7+用 元素.currentStyle.样式名;
function getStyle(ele, attr){if(ele.currentStyle){//return ele.currentStyle.width;//当对象身上的属性是变量时,要用 [] 来访问,而不用 .return ele.currentStyle[attr];} else {return getComputedStyle(ele,false)[attr];
}
console.log( getStyle(obox,"height") )
八、添加、删除、修改class
(1)在已经有 class 的 DOM 上添加新的 class:元素.classList.add("class名称");
(2)在已经有 class 的 DOM 上删除新的 class:元素.classList.remove("class名称");
(3)将当前的 class 名改成另外一个名称:元素.className("class名称");







ES6)



 G2. Playlist for Polycarp (hard version))




:HttpModule和HttpApplication)
)


