
在工作中,往往有这样的需求,对于同一个sql条件查询,首先需要统计记录条数,用以计算pageCount,然后再对结果进行分页查询显示,看下面一个例子。
<sql id="studentProperties"><!--sql片段-->select stud_id as studId, name, email, dob, phonefrom students</sql><select id="countAll" resultType="int">select count(1) from (<include refid="studentProperties"></include><!--复用-->) tmp</select><select id="findAll" resultType="Student" parameterType="map">select * from (<include refid="studentProperties"></include><!--复用-->) tmp limit #{offset}, #{pagesize}</select>这就是sqlFragment,它可以为select|insert|update|delete标签服务,可以定义很多sqlFragment,然后使用include标签引入多个sqlFragment。在工作中,也是比较常用的一个功能,它的优点很明显,复用sql片段,它的缺点也很明显,不能完整的展现sql逻辑,如果一个标签,include了四至五个sqlFragment,其可读性就非常差了。
sqlFragment里的内容是可以随意写的,它不需要是一个完整的sql,它可以是“,phone”这么简单的文本。
1.sqlFragment的解析过程
sqlFragment存储于Configuration内部。
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<XNode>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");解析sqlFragment的过程非常简单。
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder.configurationElement(XNode)方法部分源码。
// 解析sqlFragment
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 为select|insert|update|delete提供服务
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));sqlFragment存储于Map<String, XNode>结构当中。其实最关键的,是它如何为select|insert|update|delete提供服务的。
2.select|insert|update|delete标签中,解析include标签的过程
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode()方法源码。
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
// 重点关注的方法
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);注释“pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed”,含义为解析完,并移除。为什么要移除呢?秘密都隐藏在applyIncludes()方法内部了。
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLIncludeTransformer.applyIncludes(Node, Properties)方法源码。
/*** Recursively apply includes through all SQL fragments.* @param source Include node in DOM tree* @param variablesContext Current context for static variables with values*/private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext) {if (source.getNodeName().equals("include")) {// new full context for included SQL - contains inherited context and new variables from current include nodeProperties fullContext;String refid = getStringAttribute(source, "refid");// replace variables in include refid valuerefid = PropertyParser.parse(refid, variablesContext);Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(refid);Properties newVariablesContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext);if (!newVariablesContext.isEmpty()) {// merge contextsfullContext = new Properties();fullContext.putAll(variablesContext);fullContext.putAll(newVariablesContext);} else {// no new context - use inherited fullyfullContext = variablesContext;}// 递归调用applyIncludes(toInclude, fullContext);if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) {toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true);}// 将include节点,替换为sqlFragment节点source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source);while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) {// 将sqlFragment的子节点(也就是文本节点),插入到sqlFragment的前面toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude);}// 移除sqlFragment节点toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude);} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {NodeList children = source.getChildNodes();for (int i=0; i<children.getLength(); i++) {// 递归调用applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext);}} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {// replace variables in all attribute valuessource.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {// replace variables ins all text nodessource.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));}}上面是对源码的解读,为了便于理解,我们接下来采用图示的办法,演示其过程。
3.图示过程演示
①解析节点
<select id="countAll" resultType="int">select count(1) from (<include refid="studentProperties"></include>) tmp</select>②include节点替换为sqlFragment节点
<select id="countAll" resultType="int">select count(1) from (<sql id="studentProperties">select stud_id as studId, name, email, dob, phonefrom students</sql>
) tmp</select>③将sqlFragment的子节点(文本节点)insert到sqlFragment节点的前面。注意,对于dom来说,文本也是一个节点,叫TextNode。
<select id="countAll" resultType="int">select count(1) from (select stud_id as studId, name, email, dob, phonefrom students<sql id="studentProperties">select stud_id as studId, name, email, dob, phonefrom students</sql>
) tmp</select>④移除sqlFragment节点
<select id="countAll" resultType="int">select count(1) from (select stud_id as studId, name, email, dob, phonefrom students
) tmp</select>⑤最终结果如图所示
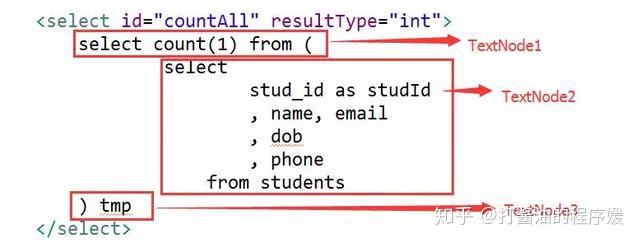
如此一来,TextNode1 + TextNode2 + TextNode3,就组成了一个完整的sql。遍历select的三个子节点,分别取出TextNode的value,append到一起,就是最终完整的sql。
这也是为什么要移除<selectKey> and <include>节点的原因。
这就是Mybatis的sqlFragment,以上示例,均为静态sql,即static sql。
最后
感谢大家看到最后,如文章有不足,欢迎大家在评论区支持,给予意见。如果觉得我的文章对你有帮助,那就给我一个赞同吧。
每天都会分享java相关技术文章或行业资讯。欢迎大家关注和转发文章。
-dfs)









与any())

--学习笔记...)

》发布)


)

