shared_ptr使用的注意事项:
1.不能使用一个原始地址初始化多个共享智能指针
2.函数不能返回管理了this的共享智能指针对象
3.共享智能指针不能循环引用
- 不能使用一个原始地址初始化多个共享智能指针
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;//shared_ptr使用的注意事项:
//1.不能使用一个原始地址初始化多个共享智能指针
//2.函数不能返回管理了this的共享智能指针对象
//3.共享智能指针不能循环引用struct Test
{shared_ptr<Test> getSharedPtr(){return shared_ptr<Test>(this);}~Test(){cout << "class Test is disstruct ..." << endl;}
};int main()
{Test *t = new Test;shared_ptr<Test> ptr1(t);shared_ptr<Test> ptr2(t);return 0;
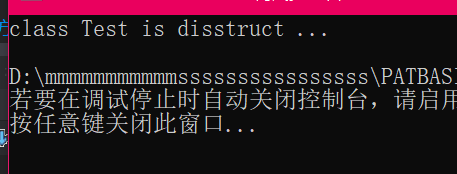
}测试结果:

这块堆内存被析构了两次,所以出现了错误。
正确写法:
int main()
{Test *t = new Test;shared_ptr<Test> ptr1(t);shared_ptr<Test> ptr2 = ptr1;return 0;
}测试结果:
- 函数不能返回管理了this的共享智能指针对象
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;//shared_ptr使用的注意事项:
//1.不能使用一个原始地址初始化多个共享智能指针
//2.函数不能返回管理了this的共享智能指针对象
//3.共享智能指针不能循环引用struct Test
{shared_ptr<Test> getSharedPtr(){return shared_ptr<Test>(this);}~Test(){cout << "class Test is disstruct ..." << endl;}
};int main()
{shared_ptr<Test> sp1(new Test);cout << "use_count = " << sp1.use_count() << endl;shared_ptr<Test> sp2 = sp1->getSharedPtr();cout << "use_count = " << sp1.use_count() << endl;return 0;
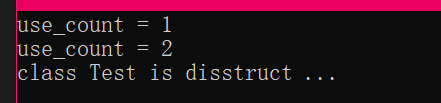
}测试结果:

通过输出的结果可以看到一个对象被析构了两次,其原因是这样的:在这个例子中使用同一个指针 this 构造了两个智能指针对象 sp1 和 sp2,这二者之间是没有任何关系的,因为 sp2 并不是通过 sp1 初始化得到的实例对象。在离开作用域之后 this 将被构造的两个智能指针各自析构,导致重复析构的错误。
这个问题可以通过 weak_ptr 来解决,通过 wek_ptr 返回管理 this 资源的共享智能指针对象 shared_ptr。C++11 中为我们提供了一个模板类叫做 std::enable_shared_from_this,这个类中有一个方法叫做 shared_from_this(),通过这个方法可以返回一个共享智能指针,在函数的内部就是使用 weak_ptr 来监测 this 对象,并通过调用 weak_ptr 的 lock() 方法返回一个 shared_ptr 对象。
使用weak_ptr解决shared_ptr管理的内存被重复析构的问题
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;//shared_ptr使用的注意事项:
//1.不能使用一个原始地址初始化多个共享智能指针
//2.函数不能返回管理了this的共享智能指针对象
//3.共享智能指针不能循环引用struct Test:public enable_shared_from_this<Test>
{shared_ptr<Test> getSharedPtr(){return shared_from_this();}~Test(){cout << "class Test is disstruct ..." << endl;}
};int main()
{shared_ptr<Test> sp1(new Test);cout << "use_count = " << sp1.use_count() << endl;shared_ptr<Test> sp2 = sp1->getSharedPtr();cout << "use_count = " << sp1.use_count() << endl;return 0;
}测试结果:
- 共享智能指针不能循环引用
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;struct TA;
struct TB;struct TA
{shared_ptr<TB> bptr;~TA(){cout << "class TA is disstruct..." << endl;}
};struct TB
{shared_ptr<TA> aptr;~TB(){cout << "class TB is disstruct" << endl;}
};void test()
{shared_ptr<TA> ap(new TA);shared_ptr<TB> bp(new TB);cout << "TA use_count = " << ap.use_count() << endl;cout << "TB use_count = " << bp.use_count() << endl;ap->bptr = bp;bp->aptr = ap;cout << "TA use_count = " << ap.use_count() << endl;cout << "TB use_count = " << bp.use_count() << endl;}int main()
{test();return 0;
}

测试结果:
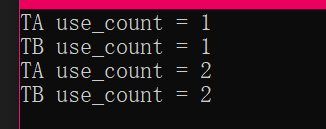
在测试程序中,共享智能指针 ap、bp 对 TA、TB 实例对象的引用计数变为 2,在共享智能指针离开作用域之后引用计数只能减为1,这种情况下不会去删除智能指针管理的内存,导致类 TA、TB 的实例对象不能被析构,最终造成内存泄露。通过使用 weak_ptr 可以解决这个问题,只要将类 TA 或者 TB 的任意一个成员改为 weak_ptr,修改之后的代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;struct TA;
struct TB;struct TA
{weak_ptr<TB> bptr;~TA(){cout << "class TA is disstruct..." << endl;}
};struct TB
{shared_ptr<TA> aptr;~TB(){cout << "class TB is disstruct" << endl;}
};void test()
{shared_ptr<TA> ap(new TA);shared_ptr<TB> bp(new TB);cout << "TA use_count = " << ap.use_count() << endl;cout << "TB use_count = " << bp.use_count() << endl;ap->bptr = bp;bp->aptr = ap;cout << "TA use_count = " << ap.use_count() << endl;cout << "TB use_count = " << bp.use_count() << endl;}int main()
{test();return 0;
}
测试结果:
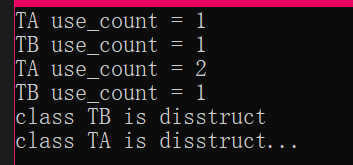
通过输出的结果可以看到类 TA 或者 TB 的对象被成功析构了。
上面程序中,在对类 TA 成员赋值时 ap->bptr = bp; 由于 bptr 是 weak_ptr 类型,这个赋值操作并不会增加引用计数,所以 bp 的引用计数仍然为 1,在离开作用域之后 bp 的引用计数减为 0,类 TB 的实例对象被析构。
在类 TB 的实例对象被析构的时候,内部的 aptr 也被析构,其对 TA 对象的管理解除,内存的引用计数减为 1,当共享智能指针 ap 离开作用域之后,对 TA 对象的管理也解除了,内存的引用计数减为 0,类 TA 的实例对象被析构。

)
![[C++11]shared_ptr共享智能指针的初始化与使用](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C++11]shared_ptr共享智能指针的初始化与使用)



![[C++11]弱引用智能指针weak_ptr初始化和相关的操作函数](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C++11]弱引用智能指针weak_ptr初始化和相关的操作函数)


)

![[C++11]独占的智能指针unique_ptr的删除器](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C++11]独占的智能指针unique_ptr的删除器)


)
![[C++11]共享智能指针shared_ptr指定删除器](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C++11]共享智能指针shared_ptr指定删除器)

![[C++11]独占的智能指针unique_ptr的初始化和使用](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C++11]独占的智能指针unique_ptr的初始化和使用)
)
