写DFS函数的时候首先确定当前位置是否已经加入路径
DFS函数大概率会传递“位置信息”,根据位置信息获取下一步的选择,(大部分是在循环中)选择、执行、回退
在哪做选择,就在哪退出选择,参考题9
def DFS():# 出口if 满足出口条件:将满足条件的路径加入结果方法返回for 选择 in 选择列表:# 做选择将该选择从选择列表移除路径.add(选择)DFS(路径, 选择列表)# 撤销选择路径.remove(选择)将该选择再加入选择列表
DFS和BFS本质上是决策树的遍历。
动态规划要求重叠子问题的条件,而DFS/BFS则是没有任何条件的纯暴力搜索。而且,BFS找到的路径一定是最短的,但代价通常比DFS要大得多。
DFS通常的问题形式是,找各种意义的路径:棋盘摆放、集合划分等等。
BFS通常的问题形式是,寻找(决策树上的)最短路径。
画出递归树,想想每个节点该怎么做
文章目录
- ==写DFS函数的时候首先确定当前位置是否已经加入路径==
- 1.DFS - N皇后问题
- 2.DFS - 子集(幂集)
- 3.DFS - 组合
- 4.DFS - 括号生成
- 5.BFS - 二叉树的最小深度
- 6.BFS - 转盘锁
- 7.DFS - 组合总数
- 8.字符串的全排列
- 9.是否存在word路径
- 10.最长递增路径
- 11.循环依赖
1.DFS - N皇后问题
- 每个格子都面临选择:放或者不放皇后
- 注意一个优化点:如果某行放了皇后,则下次递归直接跳到下行
class Solution(object):res = []def solveNQueens(self, n):""":type n: int:rtype: List[List[str]]"""self.res = []path = [["." for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]self.dfs(path, 0, 0, n)return self.resdef dfs(self, path, x, y, queens_left):n = len(path)# 出口if queens_left == 0:path_strs = []for i in range(n):path_strs.append("".join(path[i]))self.res.append(path_strs)returnelif x > n - 1 or y > n - 1:return# 一般情况# 选择1:放皇后is_queen_available = Truefor k in range(n): # 检查行和列is_queen_available = False if path[x][k] == "Q" else is_queen_availableis_queen_available = False if path[k][y] == "Q" else is_queen_availabletemp_x, temp_y = x - 1, y - 1 # 检查左上方和右上方while (temp_x >= 0 and temp_y >= 0):if path[temp_x][temp_y] == "Q":is_queen_available = Falsetemp_x -= 1temp_y -= 1temp_x, temp_y = x - 1, y + 1while (temp_x >= 0 and temp_y <= n - 1):if path[temp_x][temp_y] == "Q":is_queen_available = Falsetemp_x -= 1temp_y += 1if is_queen_available:path[x][y] = "Q" # 做选择queens_left -= 1self.dfs(path, x + 1, 0, queens_left)path[x][y] = "." # 撤销选择queens_left += 1# 选择2:不放皇后if y == n - 1:x_new = x + 1y_new = 0else:x_new = xy_new = y + 1self.dfs(path, x_new, y_new, queens_left)2.DFS - 子集(幂集)
- 每次递归都面临问题:是否将下标 idx 的数字加入结果集
- 撤销选择使用 path.pop() 而不能使用 path = path[: -1]
class Solution(object):res = []def subsets(self, nums):""":type nums: List[int]:rtype: List[List[int]]"""self.res = [[]]def dfs(path, nums, idx):# 出口if idx > len(nums) - 1:return# 做选择:idx放入结果path.append(nums[idx])self.res.append(path[:])dfs(path, nums, idx + 1)path.pop() # 撤销选择,不能使用 path = path[: -1]# 做选择:idx不放入结果dfs(path, nums, idx + 1)dfs([], nums, 0)return self.res
3.DFS - 组合
- 给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合
- 没有思路时画出树结构帮助分析
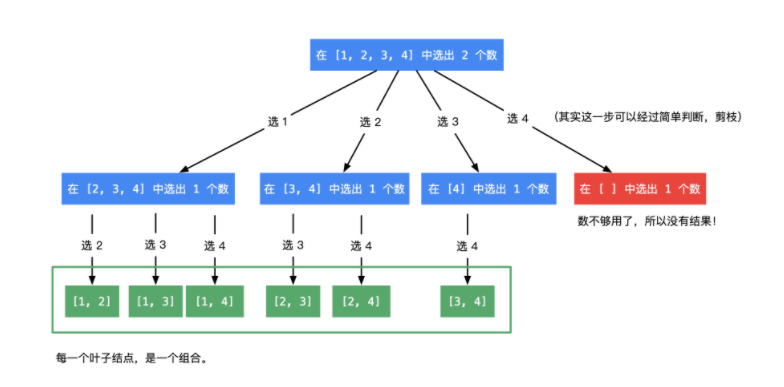
class Solution(object):res = []path = []def combine(self, n, k):""":type n: int:type k: int:rtype: List[List[int]]"""self.res = []self.path = []def dfs(n, k, idx):if len(self.path) == k:self.res.append(self.path[:])return# 站在当前的位置:path已有一些值,则要遍历idx及之后的所有选项for i in range(idx, n + 1):self.path.append(i)dfs(n, k, i + 1)self.path.pop()dfs(n, k, 1)return self.res
4.DFS - 括号生成
- 数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
- 有效括号组合需满足:左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
class Solution(object):res = []path = []def generateParenthesis(self, n):""":type n: int:rtype: List[str]"""self.res = []self.path = []def dfs(n, l, r):# 出口if r == n:self.res.append("".join(self.path))return# 做选择# 1.左右括号相等,只能添加左括号if l == r:self.path.append("(")dfs(n, l + 1, r)self.path.pop()# 2.左括号大于右括号,且l<n,能添加左也能添加右else:if l < n: # 可以加左括号self.path.append("(")dfs(n, l + 1, r)self.path.pop()self.path.append(")")dfs(n, l, r + 1)self.path.pop()dfs(n, 0, 0)return self.res###########################################################################################
"""用字符串记录path,没有回溯"""
class Solution(object):res = []def generateParenthesis(self, n):""":type n: int:rtype: List[str]"""self.res = []self.find(n, "", 0, 0)return self.resdef find(self, n, s, left, right):# 出口if left == n and right == n:self.res.append(s)# 做出所有的选择# 如果左括号不大于右括号,只能添加左括号elif left <= right:self.find(n, s + "(", left + 1, right)# 可以添加右括号,也能添加左括号(如果还能添加)else:if left != n:self.find(n, s + "(", left + 1, right)self.find(n, s + ")", left, right + 1)
5.BFS - 二叉树的最小深度
找好搜索的结束条件,当一个节点没有左右子节点时,到达叶节点。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):def minDepth(self, root):""":type root: TreeNode:rtype: int"""if root is None:return 0queue = [root]depth = 1while (len(queue) > 0):length = len(queue)for i in range(length):temp_node = queue[i]# 结束条件if temp_node.left is None and temp_node.right is None:return depthif temp_node.left is not None:queue.append(temp_node.left)if temp_node.right is not None:queue.append(temp_node.right)queue = queue[length:]depth += 1
6.BFS - 转盘锁
class Solution(object):def openLock(self, deadends, target):""":type deadends: List[str]:type target: str:rtype: int"""# 工具方法def plus(num, bit):origin = int(num[bit])if origin < 9:origin += 1else:origin = 0if bit == 0:return str(origin) + num[1: ]elif bit == 3:return num[0: 3] + str(origin)else:return num[0: bit] + str(origin) + num[bit + 1: ]def minus(num, bit):origin = int(num[bit])if origin > 0:origin -= 1else:origin = 9if bit == 0:return str(origin) + num[1: ]elif bit == 3:return num[0: 3] + str(origin)else:return num[0: bit] + str(origin) + num[bit + 1: ]# 特判if "0000" in deadends:return -1# BFSadded = ["0000"] # 不走回头路,重要!queue = ["0000"]times = 0while (len(queue) > 0):length = len(queue)for i in range(length):code = queue[i]# 出口if code == target:return times# 处理每一位for j in range(4):temp_code = plus(code, j) # +1if temp_code not in deadends and temp_code not in added:queue.append(temp_code)added.append(temp_code)temp_code = minus(code, j) # -1if temp_code not in deadends and temp_code not in added:queue.append(temp_code)added.append(temp_code)times += 1queue = queue[length:]return -1
以上为经典的BFS解法。对于已知终点的BFS问题,可以采用双向BFS加速运行,从起点和终点向中间扩展,直到出现交集。
int openLock(String[] deadends, String target) {Set<String> deads = new HashSet<>();for (String s : deadends) deads.add(s);// 用集合不用队列,可以快速判断元素是否存在Set<String> q1 = new HashSet<>();Set<String> q2 = new HashSet<>();Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();int step = 0;q1.add("0000");q2.add(target);while (!q1.isEmpty() && !q2.isEmpty()) {// 哈希集合在遍历的过程中不能修改,用 temp 存储扩散结果Set<String> temp = new HashSet<>();/* 将 q1 中的所有节点向周围扩散 */for (String cur : q1) {/* 判断是否到达终点 */if (deads.contains(cur))continue;if (q2.contains(cur))return step;visited.add(cur);/* 将一个节点的未遍历相邻节点加入集合 */for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {String up = plusOne(cur, j);if (!visited.contains(up))temp.add(up);String down = minusOne(cur, j);if (!visited.contains(down))temp.add(down);}}/* 在这里增加步数 */step++;// temp 相当于 q1// 这里交换 q1 q2,下一轮 while 就是扩散 q2q1 = q2;q2 = temp;}return -1;
}
7.DFS - 组合总数
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
- 如何保证同一元素可被无限选取?
class Solution(object):res = []path = []def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):""":type candidates: List[int]:type target: int:rtype: List[List[int]]"""self.res = []self.path = []def dfs(candidates, target, now_sum, idx):# 出口if now_sum == target and self.path not in self.res:self.res.append(self.path[:])returnelif now_sum > target:return# 做选择for i in range(idx, len(candidates)):self.path.append(candidates[i])now_sum += candidates[i]dfs(candidates, target, now_sum, i) # 此步是保证同一数字无限选择的关键,《i从idx开始》now_sum -= candidates[i]self.path.pop()dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0)return self.res8.字符串的全排列
- 标准的模板,参考文章开头
class Solution(object):def permutation(self, s):""":type s: str:rtype: List[str]"""# 一个全排列问题# 用DFS"""在DFS做选择/撤销时,加入path!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"""length = len(s)path = []visited = [0 for _ in range(length)]res = []def dfs(s, length):# 递归出口if sum(visited) == length:resstr = "".join(path)if resstr not in res:res.append(resstr)return # 做选择+撤销选择for i in range(length):if visited[i] == 0:visited[i] = 1path.append(s[i])dfs(s, length)path.pop()visited[i] = 0dfs(s, length)return res
9.是否存在word路径
- 不能在注释处“撤销选择”,因为“做选择”是在dfs开始是进行的,不能从子选项中回退
class Solution:def hasPath(self , matrix , word ):def dfs(x, y, m, n, pos):visited[x][y] = True # 在这个层面上做的选择,不能从子选项中回退path.append(matrix[x][y])if pos == len(word) - 1:return True# 做选择+撤销选择res = Falselx, ly = x, y - 1if ly >= 0 and not visited[lx][ly] and matrix[lx][ly] == word[pos + 1]:res = res or dfs(lx, ly, m, n, pos + 1)
# visited[lx][ly] = False
# path.pop()rx, ry = x, y + 1if ry < n and not visited[rx][ry] and matrix[rx][ry] == word[pos + 1]:res = res or dfs(rx, ry, m, n, pos + 1)
# visited[rx][ry] = False
# path.pop()ux, uy = x - 1, yif ux >= 0 and not visited[ux][uy] and matrix[ux][uy] == word[pos + 1]:res = res or dfs(ux, uy, m, n, pos + 1)
# visited[ux][uy] = False
# path.pop()dx, dy = x + 1, yif dx < m and not visited[dx][dy] and matrix[dx][dy] == word[pos + 1]:res = res or dfs(dx, dy, m, n, pos + 1)
# visited[dx][dy] = False
# path.pop()visited[x][y] = False # 应该在这里撤销选择path.pop()return resm = len(matrix)if m == 0:return Falsen = len(matrix[0])if n == 0:return Falsevisited = [[False for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]path = []for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if matrix[i][j] == word[0]:res = dfs(i, j, m, n, 0)if res:return Truereturn False
- 如果想在各个选项中“选择”并“撤销”,可以采用下面的写法,但初始条件要修改
class Solution:def hasPath(self , matrix , word ):def dfs(x, y, m, n, pos):if pos == len(word) - 1:return True # 做选择+撤销选择res = False lx, ly = x, y - 1if ly >= 0 and not visited[lx][ly] and matrix[lx][ly] == word[pos + 1]:visited[lx][ly] = True path.append(word[pos + 1])res = res or dfs(lx, ly, m, n, pos + 1)visited[lx][ly] = False path.pop()rx, ry = x, y + 1if ry < n and not visited[rx][ry] and matrix[rx][ry] == word[pos + 1]:visited[rx][ry] = True path.append(word[pos + 1])res = res or dfs(rx, ry, m, n, pos + 1)visited[rx][ry] = False path.pop()ux, uy = x - 1, y if ux >= 0 and not visited[ux][uy] and matrix[ux][uy] == word[pos + 1]:visited[ux][uy] = True path.append(word[pos + 1])res = res or dfs(ux, uy, m, n, pos + 1)visited[ux][uy] = False path.pop()dx, dy = x + 1, y if dx < m and not visited[dx][dy] and matrix[dx][dy] == word[pos + 1]:visited[dx][dy] = True path.append(word[pos + 1])res = res or dfs(dx, dy, m, n, pos + 1)visited[dx][dy] = False path.pop() return res m = len(matrix)if m == 0:return False n = len(matrix[0])if n == 0:return False visited = [[False for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if matrix[i][j] == word[0]:path = [word[0]]visited[i][j] = Trueres = dfs(i, j, m, n, 0) if res:return True visited[i][j] = False return False
10.最长递增路径
给定一个 n 行 m 列矩阵 matrix ,矩阵内所有数均为非负整数。 你需要在矩阵中找到一条最长路径,使这条路径上的元素是递增的。并输出这条最长路径的长度
- 如果用纯DFS会超时
- 发现重叠子问题:记录以每个位置开始的最长路径长度,如果邻接的格子比当前更大,则一定没走过
class Solution:def solve(self , matrix ):# write code herem, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])# visited = [[False for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]# 改良版dp = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]def dfs(x, y, m, n):if dp[x][y] > 0:return dp[x][y]u, d, l, r = 0, 0, 0, 0ux, uy = x - 1, ydx, dy = x + 1, ylx, ly = x, y - 1rx, ry = x, y + 1# 如果邻接的格子比当前更大,则一定没走过if ux >= 0 and matrix[ux][uy] > matrix[x][y]:u = dfs(ux, uy, m, n)if dx < m and matrix[dx][dy] > matrix[x][y]:d = dfs(dx, dy, m, n)if ly >= 0 and matrix[lx][ly] > matrix[x][y]:l = dfs(lx, ly, m, n)if ry < n and matrix[rx][ry] > matrix[x][y]:r = dfs(rx, ry, m, n)dp[x][y] = 1 + max(l, d, u, r)return dp[x][y]res = 1for i in range(m):for j in range(n):res = max(dfs(i, j, m, n), res)return res
11.循环依赖
class P3:def __init__(self):self.res = []self.path = []def find(self, serivces):num = len(serivces)visited = [False for _ in range(num)]def dfs(idx, num):# idx已经加入!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!(n0, n1) = serivces[idx]# 检查是否有循环依赖for t in self.path[: -1]: # 因为最后一个元素是新加入的所以不能用来检测成环!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!if t[0] == n1 or t[1] == n1:self.res.append(self.path[:])return None# 继续进行for i in range(num):if not visited[i] and serivces[i][0] == n1:self.path.append(serivces[i])visited[i] = Truedfs(i, num)self.path.pop()visited[i] = Falsefor i in range(num):self.path.append(serivces[i])visited[i] = Truedfs(i, num)self.path.pop()visited[i] = Falsereturn self.resprint(P3().find([('A', 'B'), ('B', 'C'), ('C', 'A'), ('A', 'D')]))




![[C#.NET 拾遗补漏]10:理解 volatile 关键字](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C#.NET 拾遗补漏]10:理解 volatile 关键字)









——访问修饰符正确姿势)




