以TC58NVG2S3ETA00 为例:
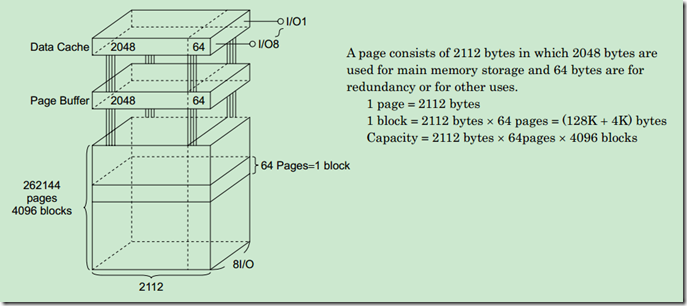
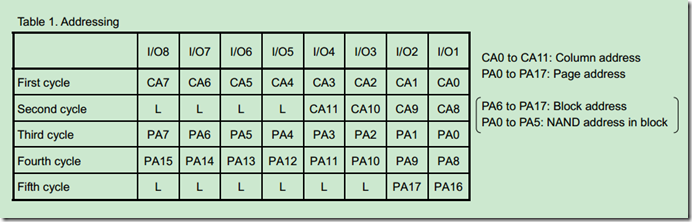
下面是它的一些物理参数:
图一

图二
图三
图四
图五

图6-0
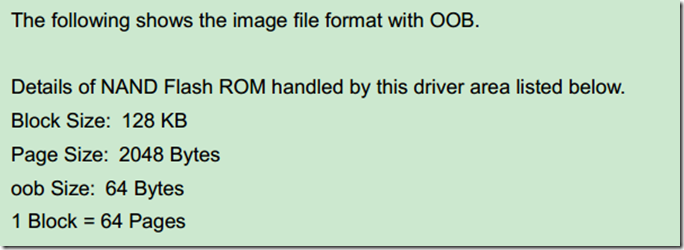
图6-1
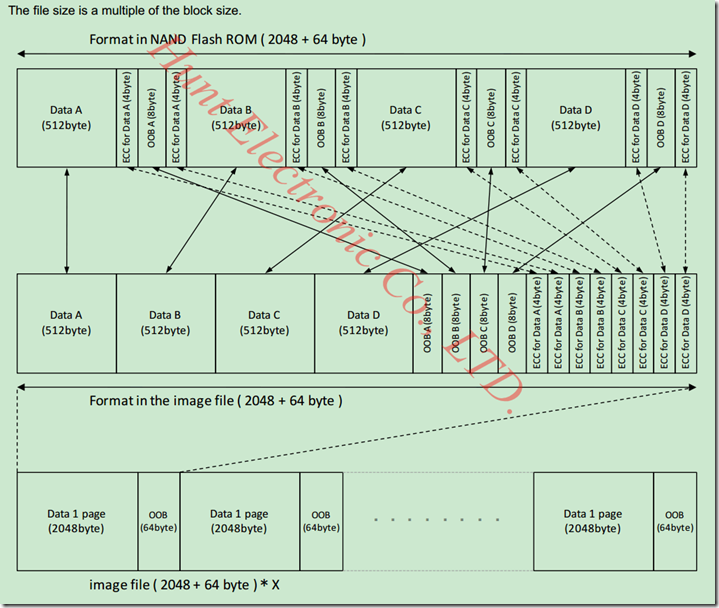
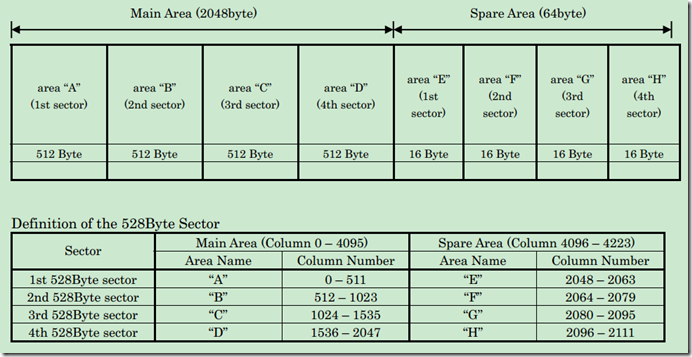
说明一下,在图6-1中中间的那个布局表可以看做是实际的NandFlash一页数据的布局,其中Data区域用于存放有效的数据,也就是我们可以通过类似read、write、pread、pwrite可以访问的区域,那每页中的64字节的OOB区域是无法通过前面的几个函数访问的,他们会自动跳过OOB区域,访问OOB区域需要借助特殊的命令。
简单说明一下:Data A(512B)对应的ECC校验码存放在ECC for Data A(4 byte)中,OOB A (8byte) 对应的ECC校验码存放在紧接着的下一个ECC for Data A(4 byte)中,虽然用4字节存放ECC,但是对于本例,ECC只占3个字节。在实际使用中如果解决方案中用不到OOB A/B/C/D,可以不用管他们对应的ECC,只需要关心Data区域对应的ECC。如果使能了硬件ECC,硬件会自动把计算生成的ECC写到OOB中。可以参考http://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/3467960.html 。
读NandFlash需要按页读,即一次读一页;写NandFlash需要按页写,即每次写一页;擦除NandFlash需要按块擦,即每次要擦除一块。
对与NandFlash等块设备的访问操作,mtd-utils工具集中提供了非常好的支持(可以到http://www.linux-mtd.infradead.org/进行了解),要使用mtd-utils工具集首先需要搞到mtd-utils的源码,并且使用目标设备上的交叉工具编译链进行编译,具体方法可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/3415550.html,其中介绍了如何生成可以再目标板上运行的mtd-utils工具。关于mtd-utils工具的使用可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/3415663.html 其中介绍了mtd-utils中常用的工具。
我们可以参考mtd-utils中工具的实现,从而完成在自己的应用程序中实现对NandFlash的操作。常用的命令如下:
#define MEMGETINFO _IOR('M', 1, struct mtd_info_user)
#define MEMERASE _IOW('M', 2, struct erase_info_user)
#define MEMWRITEOOB _IOWR('M', 3, struct mtd_oob_buf)
#define MEMREADOOB _IOWR('M', 4, struct mtd_oob_buf)
#define MEMLOCK _IOW('M', 5, struct erase_info_user)
#define MEMUNLOCK _IOW('M', 6, struct erase_info_user)
#define MEMGETREGIONCOUNT _IOR('M', 7, int)
#define MEMGETREGIONINFO _IOWR('M', 8, struct region_info_user)
#define MEMSETOOBSEL _IOW('M', 9, struct nand_oobinfo)
#define MEMGETOOBSEL _IOR('M', 10, struct nand_oobinfo)
#define MEMGETBADBLOCK _IOW('M', 11, __kernel_loff_t)
#define MEMSETBADBLOCK _IOW('M', 12, __kernel_loff_t)
#define OTPSELECT _IOR('M', 13, int)
#define OTPGETREGIONCOUNT _IOW('M', 14, int)
#define OTPGETREGIONINFO _IOW('M', 15, struct otp_info)
#define OTPLOCK _IOR('M', 16, struct otp_info)
#define ECCGETLAYOUT _IOR('M', 17, struct nand_ecclayout_user)
#define ECCGETSTATS _IOR('M', 18, struct mtd_ecc_stats)
#define MTDFILEMODE _IO('M', 19)
#define MEMERASE64 _IOW('M', 20, struct erase_info_user64)
#define MEMWRITEOOB64 _IOWR('M', 21, struct mtd_oob_buf64)
#define MEMREADOOB64 _IOWR('M', 22, struct mtd_oob_buf64)
#define MEMISLOCKED _IOR('M', 23, struct erase_info_user)
打开设备
这里需要注意的是,打开的设备结点是/dev/mtd?,而不是/dec/mtdblock?,原因可以参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/3316523.html,其中介绍了mtd与mtdblock的区别。
获取设备信息
__u32 erasesize;__u32 writesize;__u32 oobsize;// Amount of OOB data per block (e.g. 16)/* The below two fields are obsolete and broken, do not use them * (TODO: remove at some point) */ __u32 ecctype;__u32 eccsize; };struct mtd_info_user mtd;
擦除NandFlash
#include <mtd/mtd-abi.h>
#include <linux/types.h>struct erase_info_user {__u32 start;__u32 length;
};typedef struct erase_info_user erase_info_t;erase_info_t erase;int isNAND, bbtest = 1;erase.length = DevInfo->erasesize;
// erase.length 表示的是擦除大小,也就是一块的大小,如128KB
// DevInfo->size 为某个/dev/mtdx的大小
// erasse.start应该是按块对齐递增
isNAND = (DevInfo->typenum== MTD_NANDFLASH) ? 1 : 0;for (erase.start = 0; erase.start < DevInfo->size; erase.start += DevInfo->erasesize)
{if (bbtest) {loff_t offset = erase.start;int ret = ioctl(DevInfo->fd, MEMGETBADBLOCK, &offset); //判断是不是坏块if (ret > 0) {if (!quiet)DEBUG ("\nSkipping bad block at 0x%08x\n", erase.start);continue;//发现是坏块,应该跳过
} else if (ret < 0) {if (errno == EOPNOTSUPP) {bbtest = 0;if (isNAND) {fprintf(stderr, "%s: Bad block check not available\n", DevInfo->dir);return 1;}} else {fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: MTD get bad block failed: %s\n", DevInfo->dir, strerror(errno));return 1;}}}if (!quiet){fprintf(stderr, "\rErasing %d Kibyte @ %x -- %2llu %% complete.", \(DevInfo->erasesize) / 1024, erase.start,(unsigned long long) erase.start * 100 / (DevInfo->size));}if (ioctl(DevInfo->fd, MEMERASE, &erase) != 0) //执行擦除操作
{fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: MTD Erase failure: %s\n", DevInfo->dir,strerror(errno));continue;}
} 写NandFlash
这里分为写数据区和写OOB区
写数据区,对于本例一次要写一页,也就是2KB,写OOB区,对于本例可以操作的只有32字节,剩下的32字节用于存放ECC。
struct mtd_oob_buf {__u32 start;__u32 length;unsigned char *ptr;
};int nandwrite(DeviceInfo* meminfo)
{int imglen = 0, pagelen;bool baderaseblock = false;int blockstart = -1;loff_t offs;int ret, readlen;unsigned char tmp_oob[32];//OOB A/B/C/D,一共32字节struct mtd_oob_buf OOB_INFO ;sourceaddr = meminfo->head->file_offset; //要读的部分在镜像文件中的偏移量sourcelen = meminfo->head->size; //要读的部分的大小int num_to_read = 0;OOB_INFO.start = 0;OOB_INFO.length = meminfo->head->oob_usr_length; //32字节,用户可以访问的OOB的大小,也就是OOB A/B/C/DOOB_INFO.ptr = tmp_oob;pagelen = meminfo->writesize; // 2KBimglen = sourcelen; // 镜像文件的长度
mtdoffset = meminfo->head->flash_offset; //要写的部分在/dev/mtdx中的偏移量,以字节为单位/* Determine if we are reading from standard input or from a file. */if (0 == sourceaddr) {DEBUG("Have no sourceaddr return ****************************\n");return 1;}// Check, if length fits into deviceif ( ((imglen / pagelen) * meminfo->writesize) > (meminfo->size - mtdoffset)) {fprintf (stderr, "Image %d bytes, NAND page %d bytes, OOB area %u bytes, device size %u bytes\n",imglen, pagelen, meminfo->writesize, meminfo->size);perror ("Input file does not fit into device");goto closeall;}while ((imglen>0) && (mtdoffset < meminfo->size)){//blockstart 将来存放的是正在写的那块的起始地址,并且是块对齐的//mtdoffset 表示的是在某个mtd设备中的整体偏移量,可以按块递增,也可以按页递增//设置blockstart的目的是:// 假如检测到一个好的块,开始进行写操作,但是在写的过程中发生了写错误,可以认为这块已经//是坏块了,需要重新再找一个好的块,然后重新写入之前的数据,因此需要知道刚才那个坏块的起始地址// mtdoffset & (~meminfo->erasesize + 1) 这种获取块起始地址的算法值得借鉴while (blockstart != (mtdoffset & (~meminfo->erasesize + 1))){blockstart = mtdoffset & (~meminfo->erasesize + 1);offs = blockstart;baderaseblock = false;if (!quiet){fprintf (stderr, "\rWriting data to block %d at offset 0x%x", \blockstart / meminfo->erasesize, blockstart);}/* Check all the blocks in an erase block for bad blocks */// meminfo->fd 是某个/dev/mtdx的文件描述符do {if ((ret = ioctl(meminfo->fd, MEMGETBADBLOCK, &offs)) < 0){perror("ioctl(MEMGETBADBLOCK)");goto closeall;}if (ret == 1){baderaseblock = true;if (!quiet){fprintf (stderr, "Bad block at %x block(s) ""from %x will be skipped\n",(int) offs, blockstart);}}if (baderaseblock){mtdoffset = blockstart + meminfo->erasesize;}offs += meminfo->erasesize;} while ( offs < blockstart + meminfo->erasesize );}readlen = meminfo->writesize; // 2KBif (0 != sourceaddr){if((meminfo->head->imageType == YAFFS) || (meminfo->head->imageType == OOB_RAW)){writeoob = true;}else{writeoob = false;}memset(writebuf, 0xff, sizeof(writebuf));if(imglen < readlen){num_to_read = imglen;}else{num_to_read = readlen;}// 从镜像文件中偏移量为sourceaddr处读取num_to_read个字节到writebuf中// ALLIMAGEFD 为镜像文件的文件描述符if(pread(ALLIMAGEFD, writebuf, num_to_read, sourceaddr) < 0) {perror("fail to pread\n");return -1;}sourceaddr += num_to_read;if(writeoob){memset(tmp_oob, 0xff , OOB_FREE_MAX);// 从镜像文件中偏移量为sourceaddr+meminfo->head->oob_usr_offset处读取meminfo->head->oob_usr_length个字节到tmp_oob中,其中meminfo->head->oob_usr_offset是OOB A相对与OOB区域的偏移量,meminfo->head->oob_usr_length 在本例中为32字节if(pread(ALLIMAGEFD, tmp_oob, meminfo->head->oob_usr_length, sourceaddr+meminfo->head->oob_usr_offset) < 0){perror("fail to pread\n");return -1;}sourceaddr += meminfo->oobsize;}}if(-1 == pwrite(meminfo->fd, writebuf, meminfo->writesize, mtdoffset)) //写NandFlash
{/*下面这段程序所完成的就是刚才所说的在写之前检测到是好块,但是在写的过程出现了写错误,这个时候需要完成?如下流程:1、计算已经在当前块上写入多少内容,比如下面的rewind_blocks是为了计算在当前块上已经写了多少页,这里需要注意的是;rewind_bytes又加了一个readlen,也就是一页的大小,目的是保证sourceaddr的可以回退到刚开始写当前块是sourceaddr的值,可以看到在上面的程序中每次将要写的内容读到writebuf后,sourceaddr已经进行了自增操作,并没有保证刚读到writebuf中的内容可以成功写入。但是mtdoffset进行自增的前提是偏移量为mtdoffset的页写成功。其实程序可以这么改进:将sourceaddr的自增操作跟mtdoffset的自增操作放在一起,此时rewind_bytes就不需要再加readlen了。对于oob,一般只有yaffs镜像中有oob,而向cramfs、jffs2、ubifs这没有,如果有oob也需要对rewind_byte进行处理2、对当前块进行擦除3、如果需要进行坏块标记,则将当前块标记为坏块4、将mtdoffset指向当前块的下一块起始地址5、恢复imglen为刚开始处理当前块时的值,由于imglen也是保证当前页成功写入后才自减,所以只需要加上rewind_blocks即可*/int rewind_blocks;off_t rewind_bytes;erase_info_t erase;perror("ioctl(MEMEWRITEPAGE)");/* Must rewind to blockstart if we can */rewind_blocks = (mtdoffset - blockstart) / meminfo->writesize; /* Not including the one we just attempted */rewind_bytes = (rewind_blocks * meminfo->writesize) + readlen;if (writeoob){rewind_bytes += (rewind_blocks + 1) * meminfo->oobsize;}sourceaddr -= rewind_bytes;erase.start = blockstart;erase.length = meminfo->erasesize;fprintf(stderr, "Erasing failed write from %08lx-%08lx\n",(long)erase.start, (long)erase.start+erase.length-1);if (ioctl(meminfo->fd, MEMERASE, &erase) != 0){perror("MEMERASE");goto closeall;}if (markbad){loff_t bad_addr = mtdoffset & (~meminfo->erasesize + 1);fprintf(stderr, "Marking block at %08lx bad\n", (long)bad_addr);if (ioctl(meminfo->fd, MEMSETBADBLOCK, &bad_addr)) {perror("MEMSETBADBLOCK");/* But continue anyway */}}mtdoffset = blockstart + meminfo->erasesize;imglen += rewind_blocks * meminfo->writesize;if(writeoob){imglen += rewind_blocks * meminfo->oobsize;}continue;}imglen -= readlen;if(writeoob){imglen -= meminfo->oobsize;OOB_INFO.start = mtdoffset;if (ioctl(meminfo->fd, MEMWRITEOOB, &OOB_INFO)){perror("fail to ioctl");}}mtdoffset += meminfo->writesize;}closeall:if ((imglen > 0)){perror ("Data was only partially written due to error\n");exit (EXIT_FAILURE);}return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
对于写NandFlash,有的设备支持一次性把data和oob一块写进去。代码如下:
struct mtd_info_user {uint8_t type;uint32_t flags;uint32_t size; // Total size of the MTD
uint32_t erasesize;uint32_t writesize;uint32_t oobsize; // Amount of OOB data per block (e.g. 16)/* The below two fields are obsolete and broken, do not use them* (TODO: remove at some point) */uint32_t ecctype;uint32_t eccsize;
};struct mtd_epage_buf
{unsigned long long start;unsigned long data_len;unsigned long oob_len;unsigned char * data_ptr;unsigned char * oob_ptr;
};
#define MEMEWRITEPAGE _IOWR('M', 23, struct mtd_epage_buf)
#define MAX_PAGE_SIZE 8192
#define MAX_OOB_SIZE 512
/*
* Buffer array used for writing data
*/
unsigned char writebuf[MAX_PAGE_SIZE];
char oobbuf[MAX_OOB_SIZE];
int nandwrite(int argc, char * const argv[])
{/*int cnt = 0;*/int fd = -1;/*int ifd = -1;*/int imglen = 0, pagelen;bool baderaseblock = false;int blockstart = -1;struct mtd_info_user meminfo;struct mtd_epage_buf eccbuf;loff_t offs;int ret, readlen;/*process_options(argc, argv);*/mtdoffset = 0; /* reinit */erase_buffer(oobbuf, sizeof(oobbuf));if (pad && writeoob) {fprintf(stderr, "Can't pad when oob data is present.\n");exit (EXIT_FAILURE);}/* Open the device */if ((fd = open(mtd_device, O_RDWR)) == -1) {perror(mtd_device);exit (EXIT_FAILURE);}/* Fill in MTD device capability structure */if (ioctl(fd, MEMGETINFO, &meminfo) != 0) {perror("MEMGETINFO");close(fd);exit (EXIT_FAILURE);}/* Determine if we are reading from standard input or from a file. */if (NULL == sourceaddr) {DEBUG("Have no sourceaddr return ****************************\n");return 0;}pagelen = meminfo.writesize + ((writeoob) ? meminfo.oobsize : 0);/** For the standard input case, the input size is merely an* invariant placeholder and is set to the write page* size. Otherwise, just use the input file size.** TODO: Add support for the -l,--length=length option (see* previous discussion by Tommi Airikka <tommi.airikka@ericsson.com> at* <http://lists.infradead.org/pipermail/linux-mtd/2008-September/* 022913.html>*/imglen = sourcelen;// Check, if file is page-alignedif ((!pad) && ((imglen % pagelen) != 0)) {fprintf (stderr, "Input file is not page-aligned. Use the padding ""option.\n");goto closeall;}// Check, if length fits into deviceif ( ((imglen / pagelen) * meminfo.writesize) > (meminfo.size - mtdoffset)) {fprintf (stderr, "Image %d bytes, NAND page %d bytes, OOB area %u bytes, device size %u bytes\n",imglen, pagelen, meminfo.writesize, meminfo.size);perror ("Input file does not fit into device");goto closeall;}const int allSizeConst = imglen;/*DEBUG("file:%s, line:%d, imglen:%d, mtdoffset:%d, meminfo.size:%d\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, imglen, mtdoffset, meminfo.size);*//** Get data from input and write to the device while there is* still input to read and we are still within the device* bounds. Note that in the case of standard input, the input* length is simply a quasi-boolean flag whose values are page* length or zero.*/while (imglen && (mtdoffset < meminfo.size)) {// new eraseblock , check for bad block(s)// Stay in the loop to be sure if the mtdoffset changes because// of a bad block, that the next block that will be written to// is also checked. Thus avoiding errors if the block(s) after the// skipped block(s) is also bad (number of blocks depending on// the blockalignwhile (blockstart != (mtdoffset & (~meminfo.erasesize + 1))) {blockstart = mtdoffset & (~meminfo.erasesize + 1);offs = blockstart;baderaseblock = false;if (!quiet)fprintf (stdout, "Writing data to block %d at offset 0x%x\n",blockstart / meminfo.erasesize, blockstart);/* Check all the blocks in an erase block for bad blocks */do {if ((ret = ioctl(fd, MEMGETBADBLOCK, &offs)) < 0) {perror("ioctl(MEMGETBADBLOCK)");goto closeall;}if (ret == 1) {baderaseblock = true;if (!quiet)fprintf (stderr, "Bad block at %x block(s) ""from %x will be skipped\n",(int) offs, blockstart);}if (baderaseblock) {mtdoffset = blockstart + meminfo.erasesize;}offs += meminfo.erasesize;} while ( offs < blockstart + meminfo.erasesize );}readlen = meminfo.writesize;if (NULL != sourceaddr) {if (pad && (imglen < readlen)){readlen = imglen;erase_buffer(writebuf + readlen, meminfo.writesize - readlen);}memcpy(writebuf, sourceaddr, readlen);sourceaddr += readlen;} if (writeoob) {memcpy(oobbuf, sourceaddr, meminfo.oobsize);sourceaddr += meminfo.oobsize;}eccbuf.data_ptr = writebuf;eccbuf.data_len = meminfo.writesize;eccbuf.oob_ptr = oobbuf;eccbuf.oob_len = meminfo.oobsize;eccbuf.start = mtdoffset;if (ioctl(fd, MEMEWRITEPAGE, &eccbuf) != 0){int rewind_blocks;off_t rewind_bytes;erase_info_t erase;perror("ioctl(MEMEWRITEPAGE)");/* Must rewind to blockstart if we can */rewind_blocks = (mtdoffset - blockstart) / meminfo.writesize; /* Not including the one we just attempted */rewind_bytes = (rewind_blocks * meminfo.writesize) + readlen;if (writeoob)rewind_bytes += (rewind_blocks + 1) * meminfo.oobsize;sourceaddr -= rewind_bytes;erase.start = blockstart;erase.length = meminfo.erasesize;fprintf(stderr, "Erasing failed write from %08lx-%08lx\n",(long)erase.start, (long)erase.start+erase.length-1);if (ioctl(fd, MEMERASE, &erase) != 0) {perror("MEMERASE");goto closeall;}if (markbad) {loff_t bad_addr = mtdoffset & (~meminfo.erasesize + 1);fprintf(stderr, "Marking block at %08lx bad\n", (long)bad_addr);if (ioctl(fd, MEMSETBADBLOCK, &bad_addr)) {perror("MEMSETBADBLOCK");/* But continue anyway */}}mtdoffset = blockstart + meminfo.erasesize;imglen += rewind_blocks * meminfo.writesize;continue;}imglen -= (readlen + meminfo.oobsize);mtdoffset += meminfo.writesize;
}closeall:close(fd);if ((imglen > 0)) {perror ("Data was only partially written due to error\n");exit (EXIT_FAILURE);}/* Return happy */return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
读OOB
读OOB跟写OOB类似,只不过使用的命令是MEMREADOOB。
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mtd/mtd-user.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#define N 32
#define OFS (0)
#define block_size (128*1024)
#define page_size (2*1024)int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int fd;int i, j;unsigned char oob_data[32] ={0x53, 0x50, 0x4c, 0x20, 0, 0xff, 0, 0xff, 0x53, 0x50, 0x4c, 0x20, 0, 0xff, 0, 0xff, 0x53, 0x50, 0x4c, 0x20, 0, 0xff, 0, 0xff, 0x53, 0x50, 0x4c, 0x20, 0, 0xff, 0, 0xff};unsigned char oobbuf[N];struct mtd_oob_buf oob = {0, N, oobbuf};struct mtd_oob_buf my_oob = {0, N, oob_data};fd = open("/dev/mtd0", O_RDWR);if(fd < 0){perror("fail to open\n");exit(-1);}if(ioctl(fd, MEMWRITEOOB, &my_oob)){perror("fail to ioctl");exit(-1);}memset(oobbuf, 0, sizeof(oobbuf));oob.start = OFS;if (ioctl(fd, MEMREADOOB, &oob)){perror("fail to ioctl");exit(-1);}for(i=0; i<N; i++){if(i%8 == 0){printf("\n");}printf("%#x ", oobbuf[i]);}printf("\n\n");close (fd);return 0;}
以上只是本人在工作中遇到的,仅供参考。


)




![(转载)9个主流的开源许可协议[整理]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/(转载)9个主流的开源许可协议[整理])
![java属于面相_[Java教程]面相对象](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/java属于面相_[Java教程]面相对象)
)



)



)

