Spring源码系列文章
Spring源码解析(一):环境搭建
Spring源码解析(二):bean容器的创建、默认后置处理器、扫描包路径bean
Spring源码解析(三):bean容器的刷新
Spring源码解析(四):单例bean的创建流程
Spring源码解析(五):循环依赖
Spring源码解析(六):bean工厂后置处理器ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
Spring源码解析(七):bean后置处理器AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
Spring源码解析(八):bean后置处理器CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
目录
- 一、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor简介
- 二、postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(查询注解信息)
- 1、查询@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解
- 2、查询@Resource注解
- 3、checkConfigMembers()方法的作用
- 三、postProcessProperties(属性填充)
- 1、inject 执行注入
- 2、getResourceToInject() 获取注入的值
- 四、postProcessBeforeInitialization(执行初始化方法)
- 五、postProcessBeforeDestruction(执行销毁方法)
一、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor简介
主要类图如下:
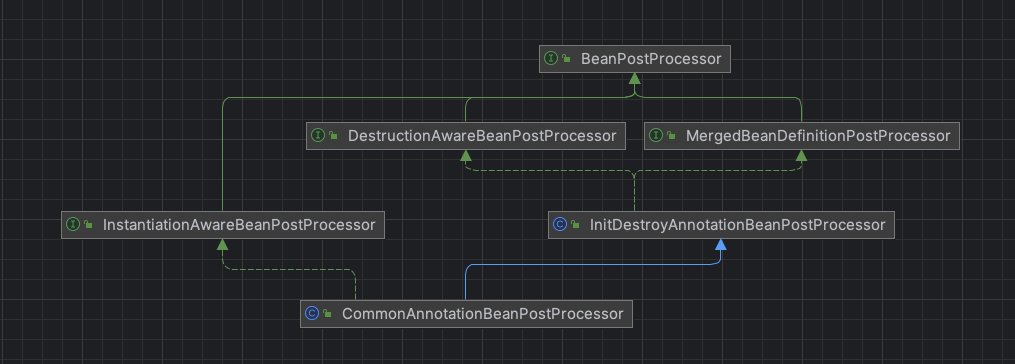
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition- 查找bean的@Resource属性和@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy方法并缓存起来
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties- @Resource注解属性填充
BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization- 初始化前执行解析@PostConstruct注解的初始化方法
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeDestruction- 销毁前执行解析@PreDestroy主键的销毁方法
二、postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(查询注解信息)
- 执行时机:实例化之后会调用所有MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName){//查询@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy`注解并缓存super.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(beanDefinition, beanType, beanName);//查询@Resource注解并缓存 InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
1、查询@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解
- 先从缓存
lifecycleMetadataCache中获取 - 找不到则通过
buildLifecycleMetadata构建生命周期元数据,并放入缓存 生命周期元数据,即初始化销毁方法的元数据
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {// 先查缓存中有没有初始化销毁方法元数据// lifecycleMetadataCache是一个map集合,它的key就是当前类的clazz// value是当前类初始化销毁方法元数据if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) {// 如果缓存中没有,则去查询注解构建对应元数据return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);}// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);if (metadata == null) {synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) {metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);if (metadata == null) {// 如果缓存中没有,则去查询注解构建对应元数据metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);//放入缓存,key就是当前类的clazzthis.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);}return metadata;}}return metadata;
}
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的构造方法
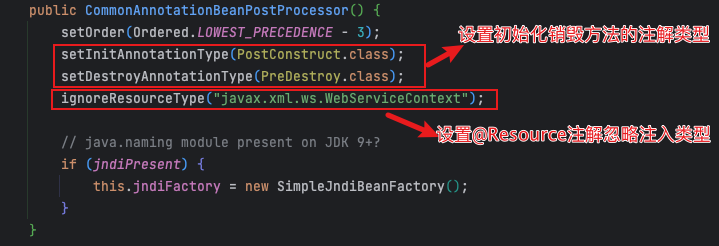
构建生命周期元数据
- AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass()是判断clazz中是否存在
@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解 - 遍历
clazz及父类的所有方法,获取@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解信息- 都将method封装成
LifecycleElement - 分别放入initMethods和destroyMethods集合中
- 都将method封装成
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {/*** this.initAnnotationType为PostConstruct.class* this.destroyAnnotationType为PreDestroy.class* 在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor默认的构造方法中赋值* AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass()是判断clazz中是否存在PostConstruct和PreDestroy注解*/if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, Arrays.asList(this.initAnnotationType, this.destroyAnnotationType))) {//不存在PostConstruct和PreDestroy注解,直接返回一个空的生命周期元数据return this.emptyLifecycleMetadata;}List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>();List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();Class<?> targetClass = clazz;do {final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();/*** ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods()方法很简单* 遍历targetClass所有的方法,将它作为参数回调接口方法*/ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {/****************************处理@PostConstruct注解******************************/ //method.isAnnotationPresent()判断方法上有没有指定的注解(反射的知识)if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {//(1)构建LifecycleElementLifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);//加入到初始化方法集合中currInitMethods.add(element);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);}}/****************************处理@PreDestroy注解******************************/ if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);}}});initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);//获取父类,因为父类中也有可能指定了生命周期方法targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();}while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);//返回声明周期元数据return (initMethods.isEmpty() && destroyMethods.isEmpty() ? this.emptyLifecycleMetadata ://(2)构建LifecycleMetadatanew LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods));
}
2、查询@Resource注解
- 与查询生命周期元数据一样,先从缓存中获取,找不到构建
private InjectionMetadata findResourceMetadata(String beanName, final Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);//判断是否需要重新解析clazzif (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {if (metadata != null) {metadata.clear(pvs);}//解析clazz,构建注入@Resource注解元数据metadata = buildResourceMetadata(clazz);this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);}}}return metadata;
}
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的静态方法
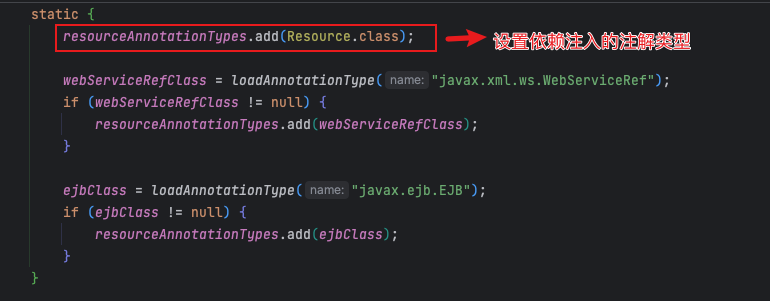
构建@Resource元数据
- 先判断clazz是否存在@Resource注解,没有则返回空对象
- 静态方法属性上添加@Resource注解会抛异常,添加@Autowired注解则是不处理不报错
- 忽略注入的方法属性类型:ignoredResourceTypes=“
javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext” - @Resource注解只能加载
单个参数的方法上
private InjectionMetadata buildResourceMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {//判断clazz是否包含resourceAnnotationTypes中的注解if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, resourceAnnotationTypes)) {return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;}List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();Class<?> targetClass = clazz;do {final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();/********************************处理属性*********************************/ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {//webServiceRef相关,不用管if (webServiceRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static fields");}currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(field, field, null));}//ejb相关,不用管else if (ejbClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static fields");}currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(field, field, null));}//这里开始处理有@Resource注解的属性了else if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {//@Resource不能加载静态属性上if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static fields");}//忽略注入的属性类型:ignoredResourceTypes="javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext"if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(field.getType().getName())) {//构建ResourceElement对象加入到currElements集合中//我们看一下ResourceElement的构造方法currElements.add(new ResourceElement(field, field, null));}}});/********************************处理方法*********************************/ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {//获取桥接方法,你就把它当成一个普通的方法对象Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {return;}//webServiceRef相关,不用管if (method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {if (webServiceRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static methods");}if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);}PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));}//ejb相关,不用管else if (ejbClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static methods");}if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);}PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));}//这里开始处理有@Resource注解的方法了else if (bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {//@Resource不能加载静态方法上if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static methods");}//获取方法所有参数的类型Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();//@Resource注解只能加载单参数的方法上if (paramTypes.length != 1) {throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);}//忽略参数名字为javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext的方法if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(paramTypes[0].getName())) {/*** 该方法在@Autowired注解原理的时候已经说过了* 就是判断当前方法是不是clazz类某个属性的get或set方法,如果是,就* 返回这个属性的属性描述*/PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);//构建ResourceElement对象加入到currElements集合中currElements.add(new ResourceElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));}}}});elements.addAll(0, currElements);//接着去找父类的@Resource注解targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();}while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);//构建InjectionMetadatareturn InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
ResourceElement的构造方法
- 获取@Resource注解的name和type属性值
- name默认值:
字段名称/方法去掉set,然后将首字母转小写 - type如果填写类型,会与注入字段类型做校验
public ResourceElement(Member member, AnnotatedElement ae, @Nullable PropertyDescriptor pd) {super(member, pd);//获取@Resource注解信息Resource resource = ae.getAnnotation(Resource.class);//获取注解name属性值String resourceName = resource.name();//获取注解type属性值Class<?> resourceType = resource.type();/*** this.isDefaultName表示是否使用默认名* 注解name属性值为空的时候,就表示使用默认名* 属性的名字或者方法名截取后的值*/this.isDefaultName = !StringUtils.hasLength(resourceName);//使用默认名if (this.isDefaultName) {//获取属性名或方法名resourceName = this.member.getName();//以set开头的方法if (this.member instanceof Method && resourceName.startsWith("set") && resourceName.length() > 3) {//实际上就是截取方法名,去掉set,然后将首字母转小写resourceName = Introspector.decapitalize(resourceName.substring(3));}}/*** 正常情况name写的什么名字,这里就返回什么*/else if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {resourceName = embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(resourceName);}// resourceType的默认值为Object.class// 此时在@Resource上指定注入类型if (Object.class != resourceType) {// 检查指定的类型resourceType是否匹配属性或方法参数checkResourceType(resourceType);}else {// 没有指定类型,则根据Member获取类型resourceType = getResourceType();}this.name = (resourceName != null ? resourceName : "");this.lookupType = resourceType;//这个忽略,没用过String lookupValue = resource.lookup();this.mappedName = (StringUtils.hasLength(lookupValue) ? lookupValue : resource.mappedName());//@Lazy注解处理Lazy lazy = ae.getAnnotation(Lazy.class);this.lazyLookup = (lazy != null && lazy.value());
}
3、checkConfigMembers()方法的作用
- 这个方法,查询@Autowired @PostConstruct @PreDestroy @Resource注解元数据后都会调用此方法
checkConfigMembers()方法的作用之一是考虑可能存在多个注解同时标注在同一个属性上的情况,避免重复处理- 通过将已处理的成员标记为外部管理的配置成员,它确保Spring容器在处理依赖注入时不会重复处理同一个属性
- 简单理解就是
去重,然后将需要处理的数据放入Set<InjectedElement> checkedElements集合中,后续统一处理
三、postProcessProperties(属性填充)
- 在postProcessProperties 方法中完成了Bean 中
@Resource注解的属性填充 - 上一步postProcessMergedBeanDefinition已经筛选出需要注入的属性放入injectionMetadataCache中
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {//获取@Resource注解的注入元数据,前面已经讲过了InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);try {//执行注入metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of resource dependencies failed", ex);}return pvs;
}
1、inject 执行注入
- 从checkedElements中拿到所有的属性和方法元数据遍历注入
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {//遍历获取每个需要被注入的元素(属性或方法)for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {//无论是属性或方法都封装为ResourceElementelement.inject(target, beanName, pvs);}}
}
- 设置字段和方法的访问性,强行赋值
field.setAccessible(true);method.setAccessible(true);
getResourceToInject():获取注入的值
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)throws Throwable {/*********************************属性******************************/ if (this.isField) {Field field = (Field) this.member;//不需要set方法,直接强行赋值ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);//getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName)重点是这个方法field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));}/*********************************方法******************************/ else {if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {return;}try {Method method = (Method) this.member;//不管方法的修饰符,强行执行方法ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));}catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {throw ex.getTargetException();}}
}
2、getResourceToInject() 获取注入的值
懒加载注入,创建一个代理对象返回- 一般注入,从spring容器中获取beanName对应的bean对象
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {/*** (1)懒加载自动注入,创建一个代理对象返回* (2)否则直接去spring容器中获取requestingBeanName对应的bean对象*/return (this.lazyLookup ? buildLazyResourceProxy(this, requestingBeanName) :getResource(this, requestingBeanName));
}
懒加载注入对象
protected Object buildLazyResourceProxy(final LookupElement element, final @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {//创建一个目标资源TargetSource ts = new TargetSource() {@Overridepublic Class<?> getTargetClass() {return element.lookupType;}@Overridepublic boolean isStatic() {return false;}@Overridepublic Object getTarget() {//代理类的目标对象也是getResource方法获取的return getResource(element, requestingBeanName);}@Overridepublic void releaseTarget(Object target) {}};//代理工厂ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();pf.setTargetSource(ts);//设置接口if (element.lookupType.isInterface()) {pf.addInterface(element.lookupType);}//类加载器ClassLoader classLoader = (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory ?((ConfigurableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory).getBeanClassLoader() : null);//获取代理对象return pf.getProxy(classLoader);
}
普通方式注入对象
protected Object getResource(LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {if (StringUtils.hasLength(element.mappedName)) {return this.jndiFactory.getBean(element.mappedName, element.lookupType);}if (this.alwaysUseJndiLookup) {return this.jndiFactory.getBean(element.name, element.lookupType);}//上面两个不用管,jndi相关,没用过if (this.resourceFactory == null) {throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.lookupType,"No resource factory configured - specify the 'resourceFactory' property");}//获取匹配的依赖对象return autowireResource(this.resourceFactory, element, requestingBeanName);
}
没有指定@Resource注解中的name属性- 从容器中根据默认名获取对应bean
- 根据默认名找不到,通过类型查找注入,还找不到报错
指定@Resource注解中的name属性- 从容器中根据指定名称获取bean,找不到报错
protected Object autowireResource(BeanFactory factory, LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {Object resource;Set<String> autowiredBeanNames;String name = element.name;if (factory instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory) {AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = (AutowireCapableBeanFactory) factory;/*** 获取依赖描述* 实际上就是* new LookupDependencyDescriptor((Field) this.member, this.lookupType);* new LookupDependencyDescriptor((Method) this.member, this.lookupType);*/DependencyDescriptor descriptor = element.getDependencyDescriptor();/*** 默认名字,没有指定name* !factory.containsBean(name)成立,容器中没有默认名对应的bean*/if (this.fallbackToDefaultTypeMatch && element.isDefaultName && !factory.containsBean(name)) {autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();//使用beanFactory解析依赖描述,获取依赖bean对象//该方法上篇文章已经讲过,此处不再赘述,这个方法是核心重点方法,一定要看懂resource = beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);if (resource == null) {throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.getLookupType(), "No resolvable resource object");}}//按指定名name获取依赖对象else {//本质上就是factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);resource = beanFactory.resolveBeanByName(name, descriptor);autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);}}else {resource = factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);}//注册依赖关系if (factory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) factory;for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {if (requestingBeanName != null && beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {beanFactory.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, requestingBeanName);}}}return resource;
}
四、postProcessBeforeInitialization(执行初始化方法)
- 执行时机:
初始化前且其他init初始化方法前执行
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {//获取所有生命周期元数据LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());try {//执行生命周期初始化方法metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);}catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException());}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex);}return bean;
}
执行初始化方法
public void invokeInitMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable {Collection<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods = this.checkedInitMethods;Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethodsToIterate =(checkedInitMethods != null ? checkedInitMethods : this.initMethods);if (!initMethodsToIterate.isEmpty()) {for (LifecycleElement element : initMethodsToIterate) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Invoking init method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod());}//执行LifecycleElement的invoke方法element.invoke(target);}}
}
public void invoke(Object target) throws Throwable {//反射执行生命周期初始化方法ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.method);this.method.invoke(target, (Object[]) null);
}
五、postProcessBeforeDestruction(执行销毁方法)
- 执行流程与初始化方法一样,就不说了
- 执行时机:bean容器关闭 context.close();调用
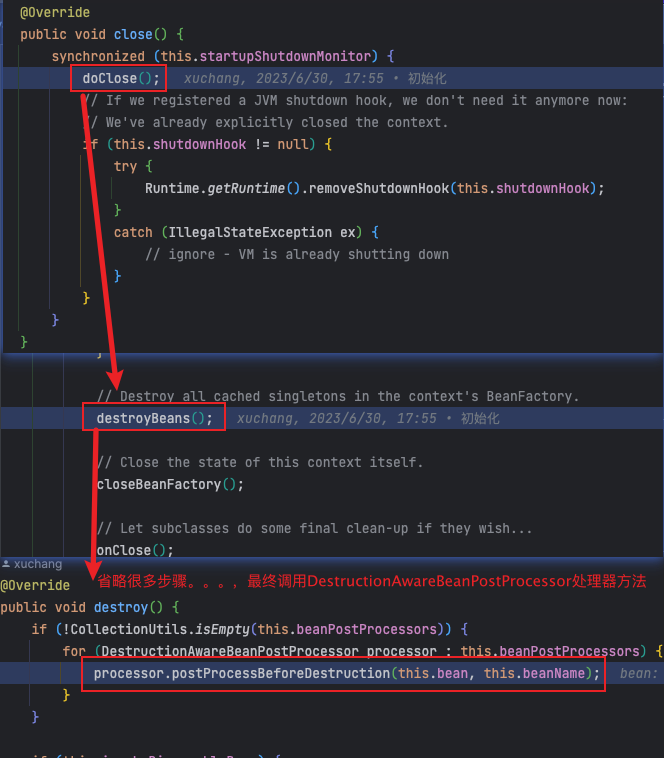
)


![[Microsoft][ODBC 驱动程序管理器] 未发现数据源名称并且未指定默认驱动程序](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Microsoft][ODBC 驱动程序管理器] 未发现数据源名称并且未指定默认驱动程序)


)










)
)
