本章主要讲图像复原与重建,首先是了解一下各种噪声的特点与模型,还有形成的方法。一些重点的噪声,如高斯噪声,均匀噪声,伽马噪声,指数噪声,还有椒盐噪声等。
本章主要的噪声研究方法主要是加性噪声。
标题
- 图像退化/复原处理的一个模型
- 噪声模型
- 噪声的空间和频率特性
- 一些重要的噪声概率密度函数(PDF)
- 高斯噪声
import sys
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import PIL
from PIL import Imageprint(f"Python version: {sys.version}")
print(f"Numpy version: {np.__version__}")
print(f"Opencv version: {cv2.__version__}")
print(f"Matplotlib version: {matplotlib.__version__}")
print(f"Pillow version: {PIL.__version__}")
Python version: 3.7.6 (default, Jan 8 2020, 20:23:39) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]
Numpy version: 1.18.1
Opencv version: 4.2.0
Matplotlib version: 3.1.3
Pillow version: 7.0.0
def normalize(mask):return (mask - mask.min()) / (mask.max() - mask.min())
图像退化/复原处理的一个模型
-
退化
把图像退化建模为一个算子H\mathcal{H}H,算子与一个加性噪声项共同对输入图像f(x,y)f(x, y)f(x,y)进行运算,生成一幅退化的图像g(x,y)g(x, y)g(x,y)。 -
复原
已知退化图像g(x,y)g(x, y)g(x,y)、关于H\mathcal{H}H和加性噪声项η(x,y)\eta(x, y)η(x,y),要复原的目的是得到原图的一个估计f^(x,y)\hat{f}(x, y)f^(x,y),并使得与f(x,y)f(x, y)f(x,y)尽可能接近。 -
退化模型
f(x,y)⇒退化函数H⇒⊕噪声η(x,y)⇒g(x,y)f(x, y) \Rightarrow 退化函数\mathcal{H} \Rightarrow \oplus \ \ 噪声\eta(x, y) \Rightarrow g(x, y)f(x,y)⇒退化函数H⇒⊕ 噪声η(x,y)⇒g(x,y) -
复原模型
g(x,y)⇒复原滤波器⇒f^(x,y)g(x, y) \Rightarrow 复原滤波器 \Rightarrow \hat{f}(x, y)g(x,y)⇒复原滤波器⇒f^(x,y)
若H\mathcal{H}H是一个线性位置不变片子,则空间域中的退化图像为
g(x,y)=(h⋆f)(x,y)+η(x,y)(5.1)g(x, y) = (h\star f)(x, y) + \eta(x, y) \tag{5.1}g(x,y)=(h⋆f)(x,y)+η(x,y)(5.1)
频率域的等效公式为
G(u,v)=H(u,v)F(u,v)+N(u,v)(5.2)G(u, v) = H(u, v)F(u, v) + N(u, v) \tag{5.2}G(u,v)=H(u,v)F(u,v)+N(u,v)(5.2)
噪声模型
噪声的空间和频率特性
当噪声的傅里叶谱是常量时,噪声通常称为白噪声
一些重要的噪声概率密度函数(PDF)
高斯噪声
高斯随机变量的PDF如下
P(z)=12πσe−(z−zˉ)2/2σ2,−∞<z<∞(5.3)P(z) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma}}e^{-(z-\bar z)^2 /2\sigma^2} , -\infty<z<\infty \tag{5.3}P(z)=2πσ1e−(z−zˉ)2/2σ2,−∞<z<∞(5.3)
式中,zzz表示灰度,zˉ\bar{z}zˉ是zzz的均(平均)值,σ\sigmaσ是zzz的标准差。zzz值在区间zˉ±σ\bar{z} \pm \sigmazˉ±σ内的概率约为0.68,zzz值在区间zˉ±2σ\bar{z} \pm 2\sigmazˉ±2σ内的概率约为0.95。
def gauss_pdf(z):mean = np.mean(z)sigma = np.std(z)gauss = (1 /(np.sqrt(2*np.pi*sigma))) * np.exp(-((z - mean)**2)/(2*sigma))return gauss
更正下面代码,如果之前已经复制的,也请更正
def add_gaussian_noise(img, mu=0, sigma=0.1):"""add gaussian noise for imageparam: img: input image, dtype=uint8param: mean: noise meanparam: sigma: noise sigmareturn: image_out: image with gaussian noise"""# image = np.array(img/255, dtype=float) # 这是有错误的,将得不到正确的结果,修改如下image = np.array(img, dtype=float)noise = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, image.shape)# 这是另外一种采样法,但不是很正确
# x = np.linspace(-(mu + 10 * sigma), (mu + 10 * sigma), 500)
# gauss = 1/(np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma) * np.exp(-(x - mu)**2 / (2 * sigma**2))
# gauss = gauss / gauss.max()
# noise = np.random.choice(gauss, size=image.shape)image_out = image + noiseimage_out = np.uint8(normalize(image_out)*255)return image_out
# 高斯PDF
mean = 0
sigma = 20
image = np.zeros([512, 512])
noise = np.random.normal(mean, sigma, image.shape)
z_ = np.mean(noise)
sigma = np.std(noise)
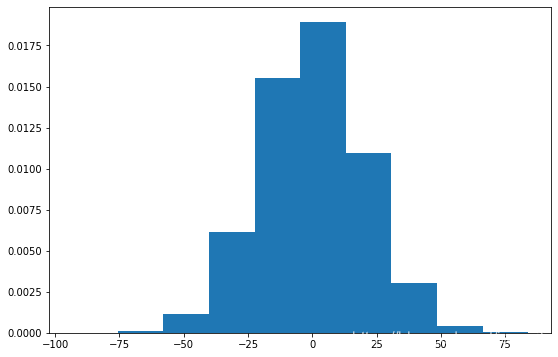
print(f"z_ -> {z_}, sigma^2 -> {sigma}")# noise_max = max(abs(noise.min()), noise.max())
# # noise = noise_max - noise
# noise = noise / noise_maxz_ = np.mean(noise)
sigma = np.std(noise)
print(f"z_ -> {z_}, sigma^2 -> {sigma}")
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
hist = plt.hist(noise.flatten(), density=True)
plt.show()
z_ -> -0.017029652654878595, sigma^2 -> 20.04642811124816
z_ -> -0.017029652654878595, sigma^2 -> 20.04642811124816
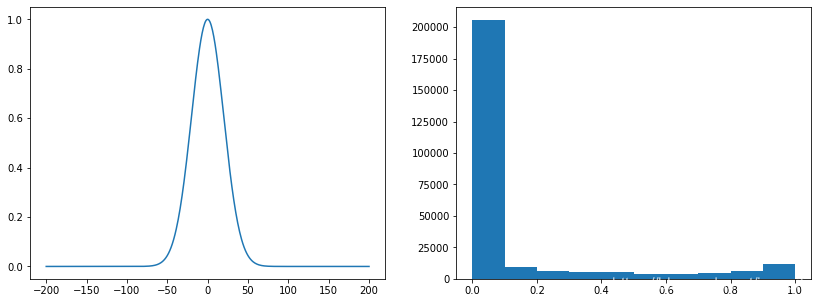
# 采样
mu = 0
sigma = 20
x = np.linspace(-(mu + 10 * sigma), (mu + 10 * sigma), 500)
gauss = 1/(np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma) * np.exp(-(x - mu)**2 / (2 * sigma**2))
gauss = gauss / gauss.max()
choice = np.random.choice(gauss, size=image.shape)plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
plt.subplot(1,2,1), plt.plot(x, gauss)
plt.subplot(1,2,2), plt.hist(choice.flatten())
plt.show()
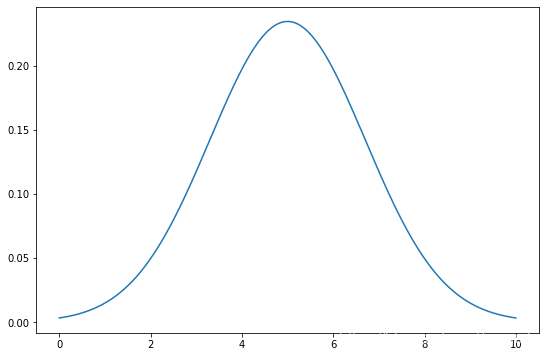
# 高斯PDF
z = np.linspace(0, 10, 500)z_ = np.mean(z)
sigma = np.std(z)print(f"z_ -> {z_}, sigma^2 -> {sigma}")
gauss = gauss_pdf(z)plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.plot(z, gauss)
plt.show()
z_ -> 5.0, sigma^2 -> 2.8925306337070777
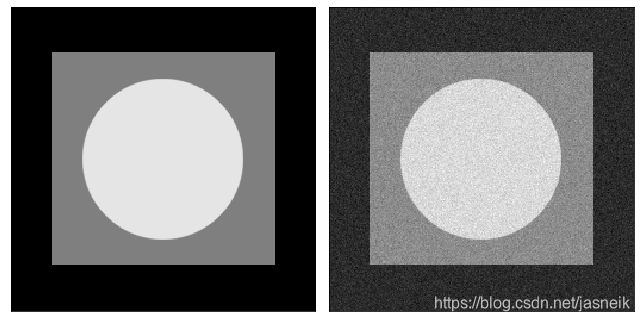
# 高斯加性噪声
img_ori = cv2.imread("DIP_Figures/DIP3E_Original_Images_CH05/Fig0503 (original_pattern).tif", 0)
# img_ori = np.ones([256, 256]) * 128
img_gauss = add_gaussian_noise(img_ori, mu=0, sigma=10) # Fix 2021-12-16, image show below donot fixed, so the result might be not the sameplt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img_ori, 'gray', vmin=0, vmax=255), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(img_gauss, 'gray'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
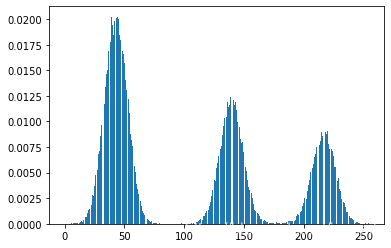
hist, bins = np.histogram(img_gauss.flatten(), bins=255, range=[0, 255], density=True)
bar = plt.bar(bins[:-1], hist[:])


和call()的区别)

 - 图像复原与重建2 - 瑞利噪声)

AF参数“自动调焦”...)


)

 - 图像复原与重建3 - 爱尔兰(伽马)噪声)



 - 图像复原与重建4 - 指数噪声)
客户端验证)
函数用法)
)
 - 图像复原与重建5 - 均匀噪声)